What is ELISA?
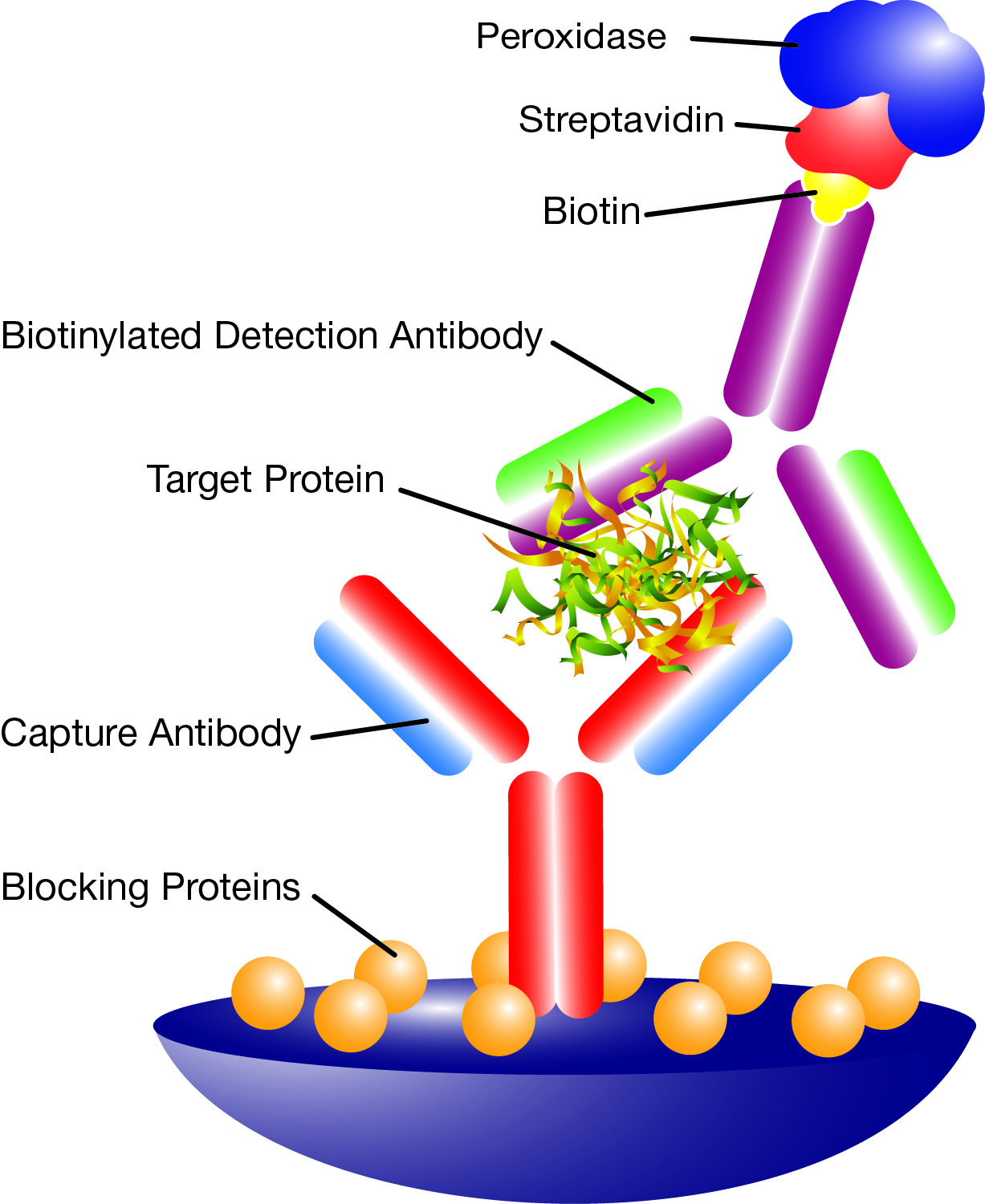
Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay and is a plate-based assay designed for detecting and quantifying peptides, proteins, antibodies and hormones. In an ELISA, an antigen must be immobilized on a solid surface and then complexed with an antibody that is linked to an enzyme. Detection is accomplished by assessing the conjugated enzyme activity. The most crucial element of the detection strategy is a highly specific antibody-antigen interaction. ELISA kits are a quick, convenient, and accurate research tool for the detection and quantitation of targets of interest in cultures and samples.
Performing an ELISA involves at least one antibody with specificity for a particular antigen. The sample with an unknown amount of antigen is immobilized on a solid support, usually a polystyrene microtiter plate either non-specifically or specifically. After the antigen is immobilized, the detection antibody is added, forming a complex with the antigen. The detection antibody can be covalently linked to an enzyme or can itself be detected by a secondary antibody that is linked to an enzyme. Between each step, the plate is typically washed with a mild detergent to remove any proteins or antibodies that are non-specifically bound. After the final wash step, the plate is developed by adding an enzymatic substrate to produce a visible signal, which indicates the quantity of antigen in the sample.
Types of ELISA
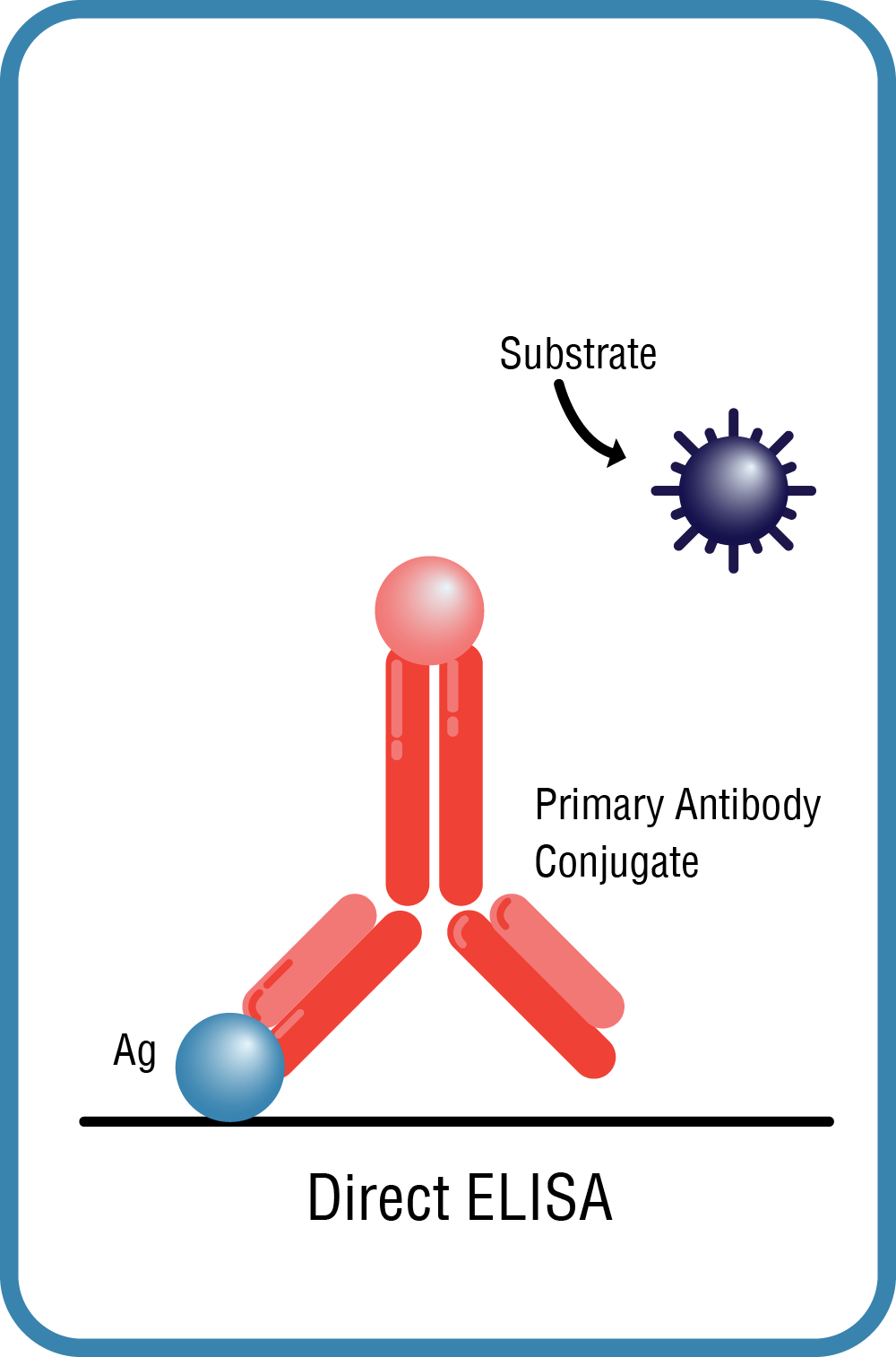
Direct ELISA
- A labeled primary antibody binds to the target
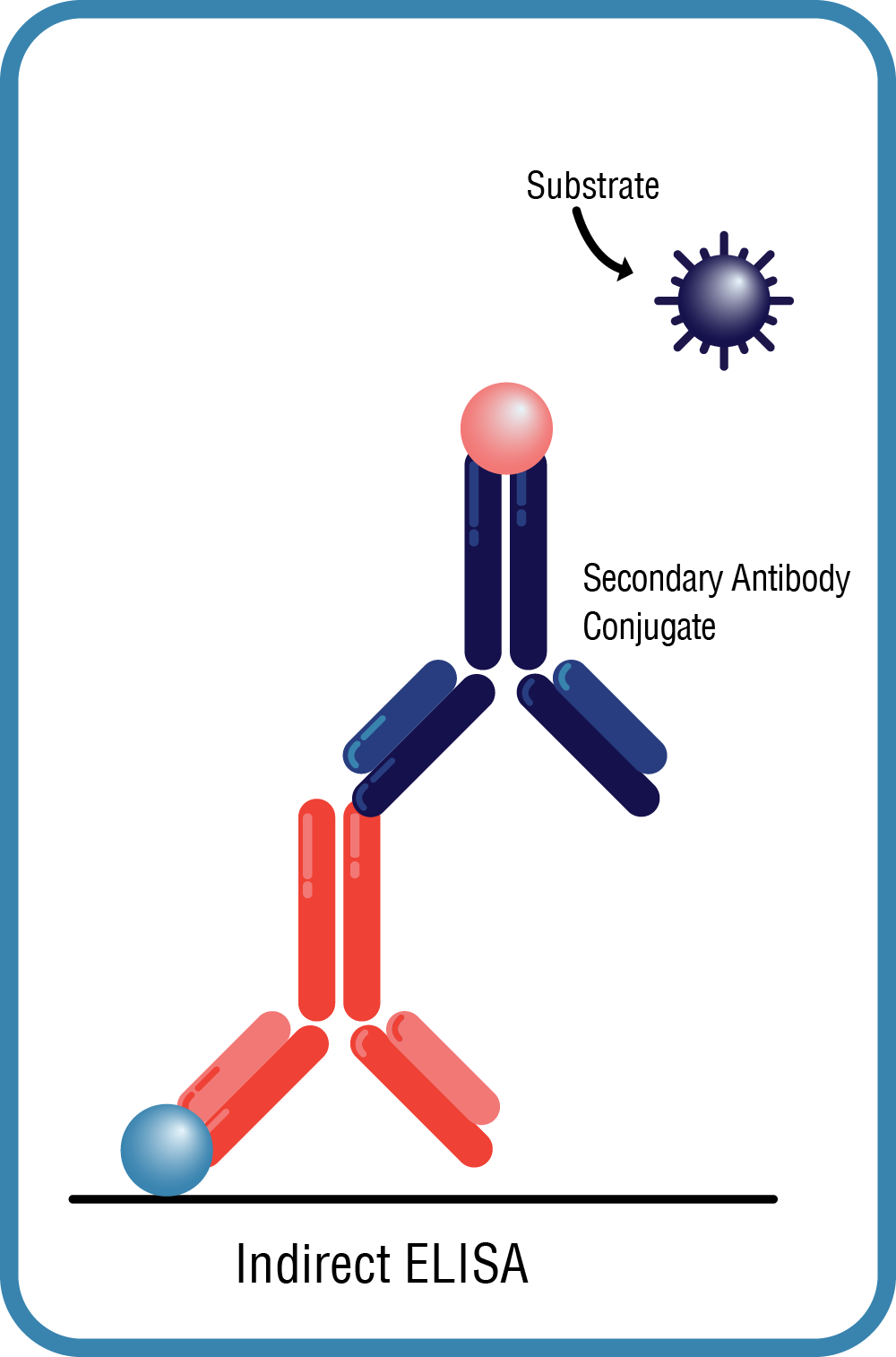
Indirect ELISA
- The most common protocol
- The target is bound by the primary antibody and detected when a labeled secondary antibody binds to the primary antibody
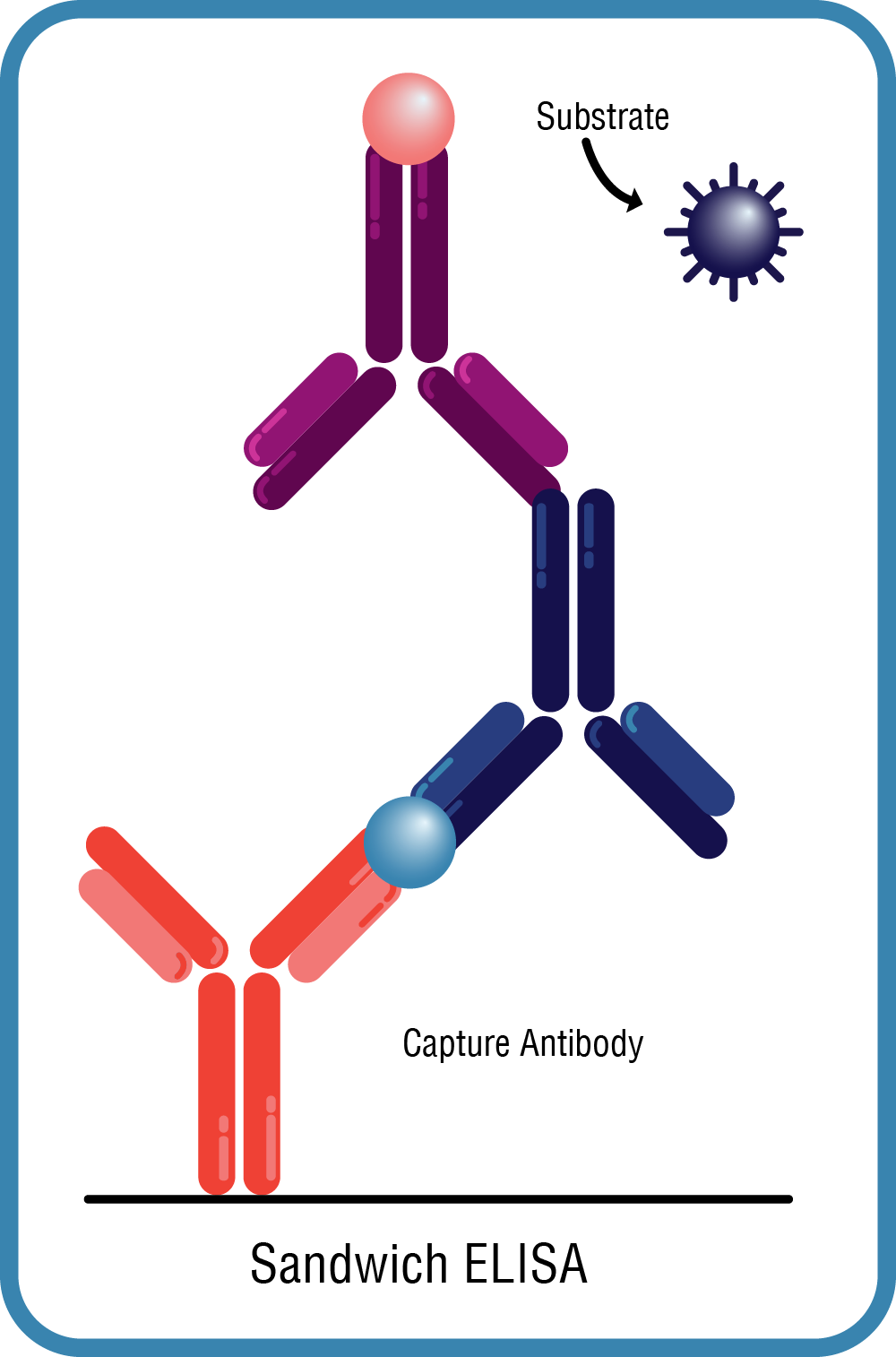
Sandwich ELISA
- Used to detect sample antigen
- The target is adsorbed to the assay plate, then bound by two primary antibodies
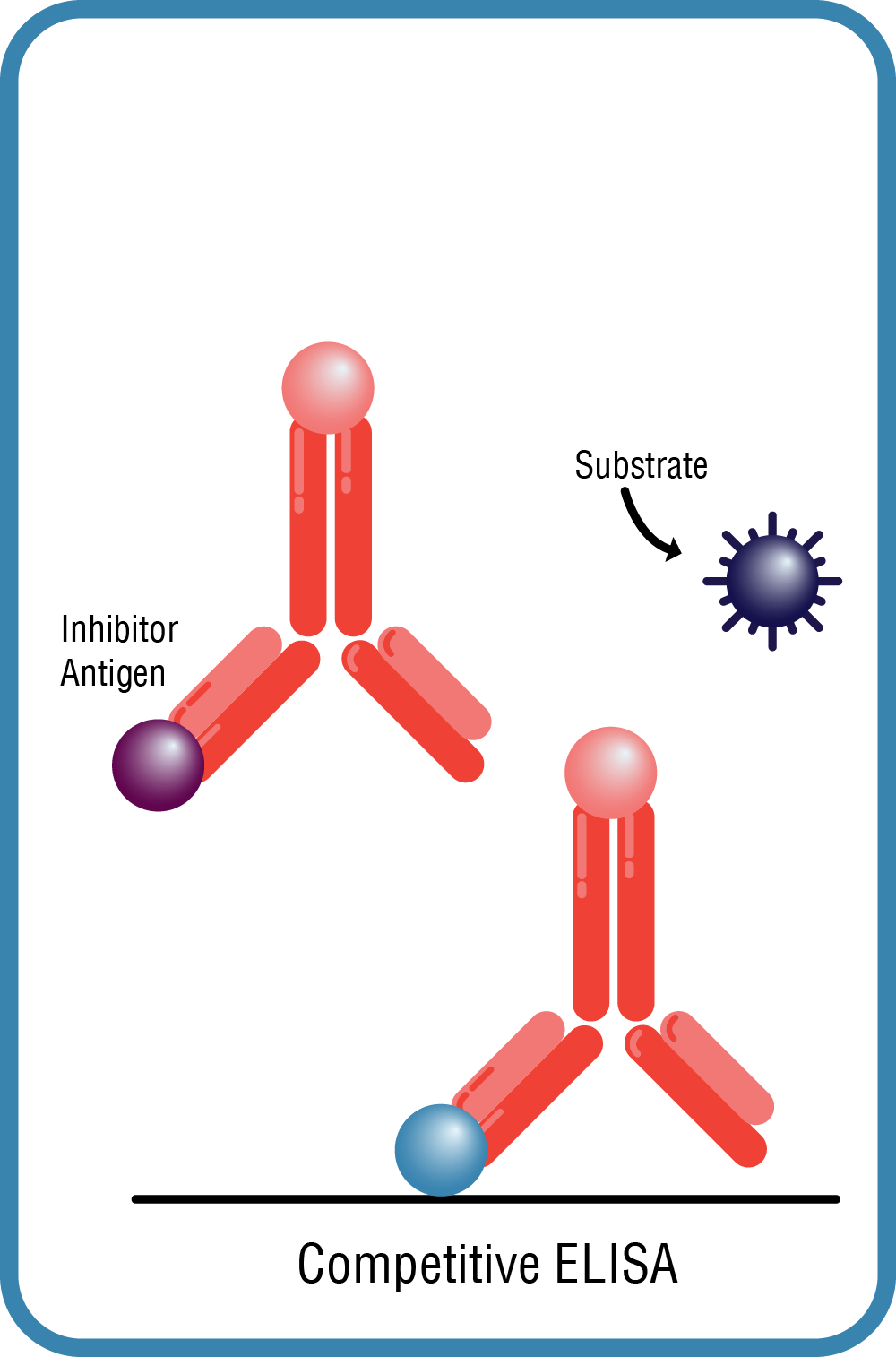
Competitive ELISA
- Often used for smaller targets that may have only one binding site
- Detection through competitive binding
Flexibility →
Use with cell culture supernatant or serum samples. Customize the assay to meet your specific needs.
Consistency →
Calibrated standards provide consistent results.
Economical →
Compared with separately purchasing antibodies and calibrators.