Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1) [Clone RMP1-14] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1) [Clone RMP1-14] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade
Product No.: P372
Clone RMP1-14 Target PD-1 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names Programmed Death-1, CD279, PD 1 Isotype Rat IgG2a κ Applications B , FA , FC , IHC , in vivo , WB |
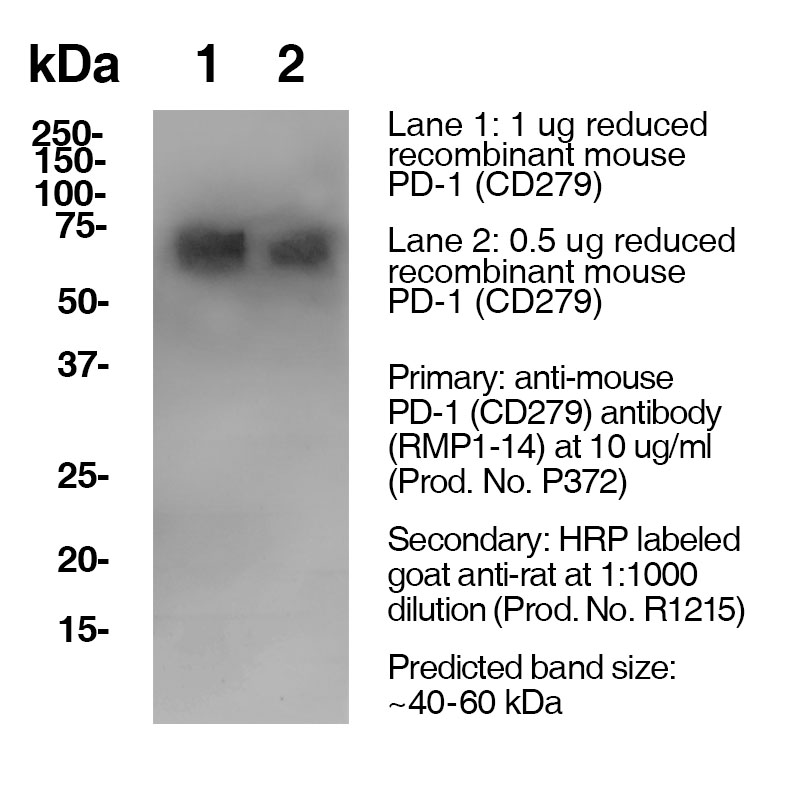
Data
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Rat Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Dilution Buffer Immunogen Mouse PD-1 transfected BHK cells Product Concentration ≥7.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level <0.5 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥95% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Pathogen Testing To protect mouse colonies from infection by pathogens and to assure that experimental preclinical data is not affected by such pathogens, all of Leinco’s Purified Functional PLATINUM™ antibodies are tested and guaranteed to be negative for all pathogens in the IDEXX IMPACT I Mouse Profile. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2749820 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Clone RMP1-14 recognizes an epitope on mouse PD-1. Background PD-1 is a 50-55 kD member of the B7 Ig superfamily. PD-1 is also a member of the extended CD28/CTLA-4 family of T cell regulators and is suspected to play a role in lymphocyte clonal selection and peripheral tolerance. The ligands of PD-1 are PD-L1 and PD-L2, and are also members of the B7 Ig superfamily. PD-1 and its ligands negatively regulate immune responses. PD-L1, or B7-Homolog 1, is a 40 kD type I transmembrane protein that has been reported to costimulate T cell growth and cytokine production. The interaction of PD-1 with its ligand PD-L1 is critical in the inhibition of T cell responses that include T cell proliferation and cytokine production. PD-L1 has increased expression in several cancers. Inhibition of the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1 can serve as an immune checkpoint blockade by improving T-cell responses In vitro and mediating preclinical antitumor activity. Within the field of checkpoint inhibition, combination therapy using anti-PD1 in conjunction with anti-CTLA4 has significant therapeutic potential for tumor treatments. PD-L2 is a 25 kD type I transmembrane ligand of PD-1. Via PD-1, PD-L2 can serve as a co-inhibitor of T cell functions. Regulation of T cell responses, including enhanced T cell proliferation and cytokine production, can result from mAbs that block the PD-L2 and PD-1 interaction. Antigen Distribution PD-1 is expressed on a subset of CD4-CD8- thymocytes, and on activated T and B cells. Ligand/Receptor PD-L1 (B7-H1), PD-L2 Function Lymphocyte clonal selection, peripheral tolerance NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Apoptosis . Cancer . Cell Biology . Cell Death . Immunology . Inhibitory Molecules . Tumor Suppressors Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Clone RMP1-14 is commonly used for in vivo blockade of PD-1 signaling in mice, particularly for research in cancer immunotherapy, immune regulation, and mechanistic studies of immune checkpoint pathways. Key in vivo applications include:
Additional notes:
In summary, RMP1-14 is a cornerstone tool for in vivo PD-1 blockade in murine studies, with principal utility in preclinical cancer immunotherapy and immune regulation research. RMP1-14 is a commonly used monoclonal antibody against mouse PD-1, often utilized in immunotherapy research, particularly in in vivo models. Here are some other antibodies or proteins frequently used alongside RMP1-14:
Using these antibodies in combination with RMP1-14 can provide a comprehensive understanding of PD-1 mediated immune responses and their modulation in various experimental settings. Clone RMP1-14 is a widely used anti-mouse PD-1 monoclonal antibody in immuno-oncology research, mainly known for its effectiveness in preclinical models to block the PD-1 pathway. Key findings from the scientific literature regarding RMP1-14 are as follows:
In summary, RMP1-14 is a validated and potent tool for in vivo mouse studies on PD-1 blockade, valued for its specificity, reproducibility, and well-documented anti-tumor effects, though its properties should be carefully matched to the experimental context. Dosing regimens for the RMP1-14 clone, an anti-mouse PD-1 antibody, can vary across different mouse models primarily based on the specific experimental objectives and the characteristics of the models used. Here are some general guidelines and considerations: Typical Dosing Range
Factors Influencing Dosing Regimens
Troubleshooting and Adjustments
Overall, while there is a standard dosing range for RMP1-14, the regimen can be tailored based on the specific needs and characteristics of individual mouse models. References & Citations1.) Ardolino, M. et al. (2018) J Clin Invest. 128(10):4654-4668. PubMed 2.) Schreiber, RD. et al. (2017) Cancer Immunol Res. 5(2):106-117. 3.) Honjo, T. et al. (1992) EMBO J. 11:3887. 4.) Gubin et al. (2018) Cell. 175:1014–1030 Journal Link 5.) Renner et al. (2019) Cell Reports. 29:135–150 Journal Link 6.) Gubin, M. et al. (2018) Cell 175(4):1014-1030.e19 Journal Link Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Formats Available
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
![Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1) [Clone RMP1-14] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade, Product vial — Leinco Prod. No. P372](https://www.leinco.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/P372-CD279-Clone-RMP1-14-PLAT_Vial-Parent-500x500.jpg)