Recombinant Human G-CSF
Data
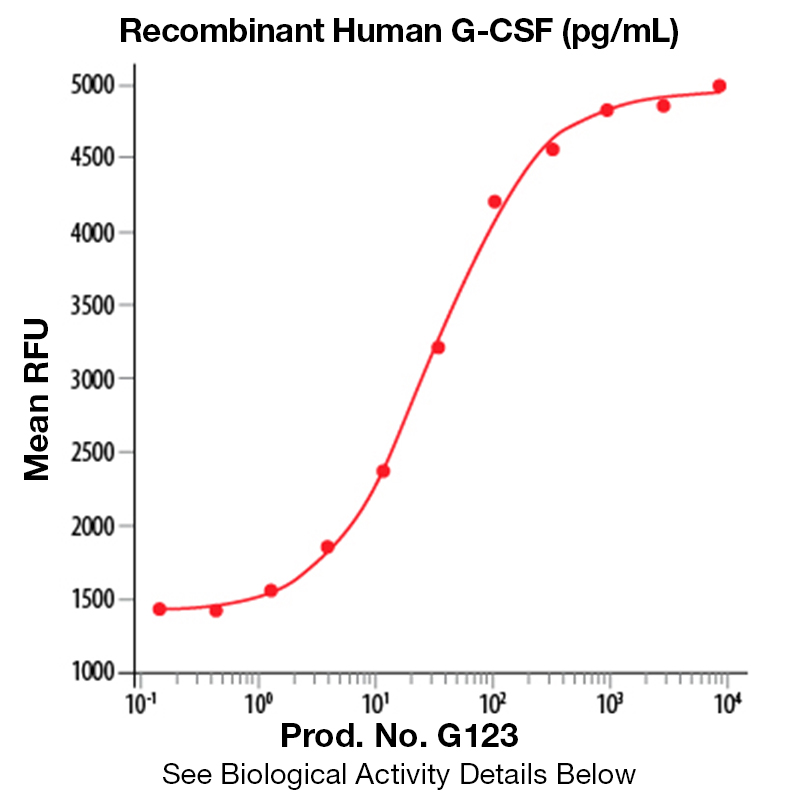
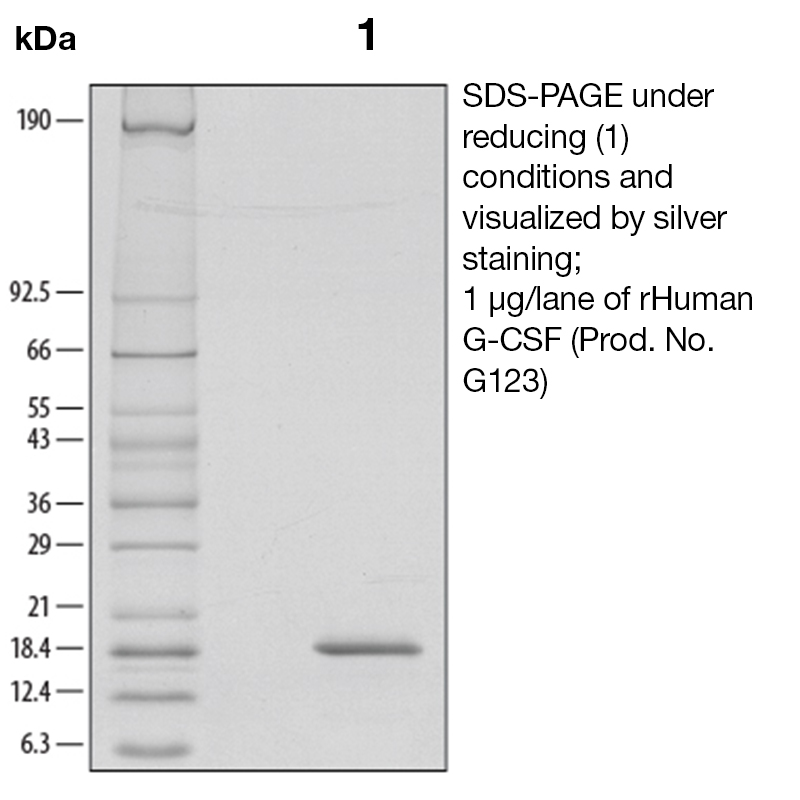
BackgroundGranulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), also known as CSF-3, is an essential cytokine belonging to the CSF family of hormone-like glycoproteins that regulate haematopoietic cell proliferation and differentiation (1). It is produced primarily by monocytes and macrophages upon activation by endotoxin, TNF-α and IFN-γ but can be secreted by other cell types after LPS or IL-1 activation. In addition, various carcinoma cell lines and myeloblastic leukemia cells can express G-CSF constitutively (2). The cell surface receptor for G-CSF is G-CSF-R, also known as CD114. G-CSF synergizes with some other cytokines, including GM-CSF and IL-4. Bone marrow is stimulated by G-CSF to produce granulocytes and stem cells. G-CSF is also a potent inducer of hematopoietic stem cell mobilization from the bone marrow into the bloodstream and therefore used clinically to facilitate hematopoietic recovery after bone marrow transplantation. G-CSF also acts as a neurotrophic factor as its receptor is expressed by neurons in the brain and spinal cord. The action of G-CSF in the central nervous system is to induce neurogenesis, to increase the neuroplasticity and to counteract apoptosis (3). These proprieties are currently under investigations for the development of treatments of neurological diseases such as cerebral ischemia. Human and murine G-CSF are cross-species reactive. Protein DetailsPurity >97% by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by silver stain. Endotoxin Level <0.1 EU/µg as determined by the LAL method Biological Activity The biological activity of Human G-CSF was determined in a cell proliferation assay using a murine myeloblastic cell line, NFS-60 (Shirafuji, N. et al., 1989, Exp. Hematol. 17:116). The expected ED<sub>50</sub> for this effect is typically 10 - 60 pg/ml. Protein Accession No. Amino Acid Sequence tplgpasslp qsfllkcleq vrkiqgdgaa lqeklcatyk lchpeelvll ghslgipwap lsscpsqalq lagclsqlhs glflyqgllq alegispelg ptldtlqldv adfattiwqq meelgmapal qptqgampaf asafqrragg vlvashlqsf levsyrvlrh laqp N-terminal Sequence Analysis Met State of Matter Solution Predicted Molecular Mass The predicted molecular weight of Recombinant Human G-CSF is Mr 18.8 kDa. However, the actual molecular weight as observed by migration on SDS-PAGE is 18.5 kDa (reducing conditions) Predicted Molecular Mass 18.8 Formulation This recombinant protein solution was 0.2 µm filtered and formulated in Acetic Acid. Storage and Stability This protein is stable for three months when stored at 2°C to 8°C. DO NOT FREEZE. Loss of activity of >60% will be observed if this protein frozen. See Product Insert for exact lot specific storage instructions. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C NCBI Gene Bank Leinco Protein AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Recombinant Human Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor (G-CSF) is a valuable tool for a wide range of research applications due to its well-characterized biological effects and versatility. Here are several key reasons why you should consider using recombinant human G-CSF in your research: 1. Promotes Neutrophil Lineage DevelopmentRecombinant human G-CSF specifically stimulates the proliferation, differentiation, and survival of neutrophil progenitor cells. This makes it ideal for studies focused on hematopoiesis, myeloid cell biology, and immune cell development. 2. Accelerates Neutrophil RecoveryG-CSF accelerates the replenishment of neutrophils following myelosuppressive treatments (e.g., chemotherapy or radiation). This property is useful for modeling recovery from neutropenia and studying host defense mechanisms in experimental systems. 3. Supports Functional AssaysG-CSF enhances the functional activity of mature neutrophils, including chemotaxis, phagocytosis, and microbial killing. It can be used in functional assays to investigate neutrophil responses to infection, inflammation, or immune modulation. 4. Enables Cell Culture and Differentiation StudiesRecombinant human G-CSF is optimized for use in cell culture systems, supporting the expansion and differentiation of hematopoietic progenitor cells. It is widely used in protocols for generating neutrophils and other myeloid cells from primary or stem cell sources. 5. Facilitates Preclinical and Translational ResearchG-CSF has been extensively studied in both animal models and clinical settings, providing a strong foundation for translational research. Its use in preclinical studies can help bridge findings from bench to bedside, particularly in areas such as immunotherapy, infection, and regenerative medicine. 6. Low Toxicity and Well-Characterized Safety ProfileRecombinant human G-CSF has a favorable safety profile, making it suitable for repeated administration in experimental models. Its low toxicity allows for long-term studies and chronic dosing regimens. 7. Versatile ApplicationsBeyond hematopoiesis, G-CSF has been explored in diverse research areas, including:
8. Availability of Long-Acting and Modified FormsAdvanced recombinant G-CSF variants (e.g., fusion proteins, PEGylated forms) offer extended half-life and improved pharmacokinetics, enabling less frequent dosing and more sustained effects in experimental models. In summary, recombinant human G-CSF is a powerful and flexible reagent for research involving neutrophil biology, immune function, hematopoiesis, and host defense. Its well-documented effects, ease of use, and broad applicability make it an essential tool for both basic and applied research. Yes, you can use Recombinant Human G-CSF as a standard for quantification or calibration in your ELISA assays, provided that the recombinant protein is suitable for your specific ELISA kit and experimental conditions. Key Points to Consider:
Example from Literature:
Conclusion:If your Recombinant Human G-CSF is of high purity, biologically active, and matches the sequence used in the ELISA kit, it can be used as a standard for quantification or calibration in your ELISA assays. Always validate the standard curve and ensure compatibility with your specific kit and experimental setup. Recombinant human G-CSF has been validated for numerous clinical and research applications across multiple therapeutic domains: Hematological and Oncological ApplicationsThe primary and most extensively validated application is chemotherapy-induced neutropenia (CIN) prevention and management. Recombinant human G-CSF enables optimal chemotherapy delivery by reducing febrile neutropenia risks, allowing patients to maintain appropriate chemotherapy dosing without undue reductions or delays. The factor rapidly increases neutrophil production, reducing both the maturation and release times of bone marrow neutrophils from the normal 4-5 days to 1-2 days. Beyond chemotherapy support, recombinant human G-CSF has been validated for treating severe chronic neutropenia and acquired neutropenia, including conditions such as aplastic anemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. The protein is also widely employed for mobilization of CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells from bone marrow to peripheral blood for use in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Immunomodulatory and Inflammatory ApplicationsResearch has demonstrated that recombinant human G-CSF possesses anti-inflammatory and immune-regulatory properties beyond its hematological effects. The factor induces peripheral regulatory T-cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells, which help regulate immune responses to infection and inflammation. Clinical investigation has extended to infectious disease contexts, including a randomized trial in hospitalized COVID-19 patients with lymphopenia, where treatment increased lymphocyte and leukocyte cell counts and was associated with reduced progression to invasive ventilation and lower 21-day mortality in patients with severe lymphopenia. Neuroprotective ApplicationsRecombinant human G-CSF has been validated as a therapeutic candidate for stroke, demonstrating anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. Animal studies confirm its ability to decrease pro-inflammatory cytokine release (TNF, IFN-γ, IL-6) while enhancing anti-inflammatory cytokine production such as IL-4. Additional Validated ApplicationsThe protein exhibits anti-apoptotic and pro-angiogenic properties, and has been investigated in contexts including granulocyte transfusion therapy and immunocompetent patient populations. Research has also explored its potential role in reproductive medicine and other specialized clinical settings. To reconstitute and prepare Recombinant Human G-CSF for cell culture experiments, dissolve the lyophilized protein in sterile buffer to a concentration suitable for your application, typically between 0.05–1.0 mg/mL, using sterile water or PBS with carrier protein (such as 0.1% BSA) to enhance stability and prevent adsorption. Step-by-step protocol:
Additional notes:
Summary Table: Common Reconstitution Conditions
These guidelines ensure maximal activity and stability of recombinant human G-CSF for cell culture applications. References & Citations1. Khanna-Gupta, A. et al. (2006) J. Leukoc. Biol. 79:1011 2. Nagata, S. et al. (1986) Nature 319:415 3. Demetri, GD. et al. (1991) Blood 78:2791 Certificate of AnalysisIMPORTANT Use lot specific datasheet for all technical information pertaining to this recombinant protein. |
Related Products
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
G664 | |
G669 | |
G134 | |
G123 | |
G129 | |
G114 | |
G140 | |
G115 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.