Anti-CLAC-P Antibody (28115)
Data
- -
- -
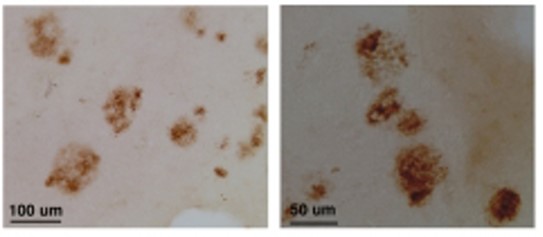
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human ⋅ Mouse Host Species Rabbit Immunogen Synthetic peptide corresponding to aa 430-445 of the NC3 region of human and mouse CLAC-P. Product Concentration Lot Specific Formulation PBS, pH 7.4. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by immunoaffinity chromatography Storage and Handling This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Avoid multiple freeze- thaw cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunoblotting: at 2-5ug/mL, a band of approx. 70 kDa is detected in HEK293 cell lysate
Immunohistochemistry (paraffin): at 5- 10ug/mL, positive staining of senile plaques in AD brains These are recommended concen- trations. User should determine optimal concentrations for their applications. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody specific to CLAC-P Background Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by deposition of beta-amyloid as senile plaques and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. The principal component of AD amyloid is the amyloid beta peptide (Abeta). Although production and deposition of Abeta appear closely related to the pathogenesis of AD, current evidence suggest that Abeta alone is not sufficient to cause neuronal death and symptoms of dementia. A component of senile plaque (SP), CLAC (collagen-like Alzheimer amyloid plaque component ) and its precursor CLAC-P are deposited with extracellular beta-amyloid and have been recently implicated in cell toxicity of beta- amyloid in AD brains. CLAC-P is a unique, membrane-bound collagen-like structure containing three Gly-X-Y repeat motifs and may define a novel class of neuronal collagens. Function Inhibits fibrillization of amyloid-beta peptide during the elongation phase. Has also been shown to assemble amyloid fibrils into protease-resistant aggregates. Binds heparin. {PubMed:15522881, PubMed:15615705, PubMed:15853808, PubMed:16300410}. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Neuroscience References & CitationsTechnical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |