Anti-ENaC β Antibody (11577)
Anti-ENaC β Antibody (11577)
Product No.: 11577
- -
- -
Clone 16E4 Target ENaC β Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Alternate Names β-NaCH, Epithelial Na(+ channel subunit β, β-ENaC, Nonvoltage-gated sodium channel 1 subunit β, SCNEB Isotype Mouse IgG2a Applications IHC , WB |
Data
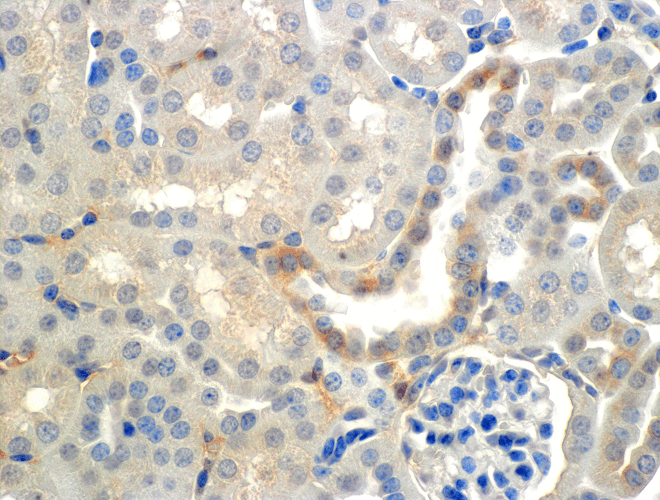 Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-ENaC beta Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 7B8 (11577). Tissue: Kidney (cortex). Species: Mouse. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-ENaC beta Monoclonal Antibody (11577) at 1:150. Localization: Collecting duct principal cells. Magnification: 60X.
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-ENaC beta Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 7B8 (11577). Tissue: Kidney (cortex). Species: Mouse. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-ENaC beta Monoclonal Antibody (11577) at 1:150. Localization: Collecting duct principal cells. Magnification: 60X.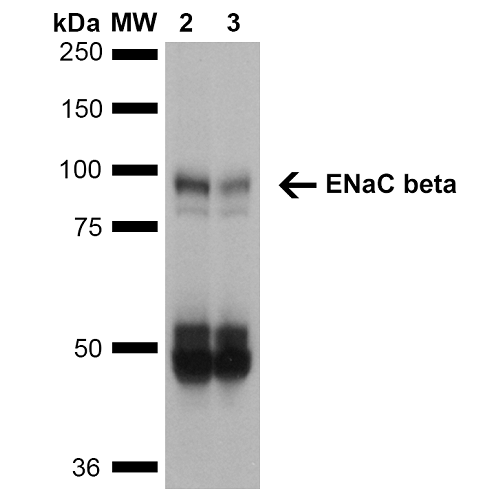 Western Blot analysis of Mouse Whole kidney homogenates showing detection of ~87kDa ENaC beta protein using Mouse Anti-ENaC beta Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 7B8 (11577). Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder (MW). Lane 2: Low-salt diet. Lane 3: Normal-salt diet. Load: 20 µg. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-ENaC beta Monoclonal Antibody (11577) at 1:1000. Predicted/Observed Size: ~87kDa.
Western Blot analysis of Mouse Whole kidney homogenates showing detection of ~87kDa ENaC beta protein using Mouse Anti-ENaC beta Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 7B8 (11577). Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder (MW). Lane 2: Low-salt diet. Lane 3: Normal-salt diet. Load: 20 µg. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-ENaC beta Monoclonal Antibody (11577) at 1:1000. Predicted/Observed Size: ~87kDa. - -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactivity Species Mouse Host Species Mouse Immunogen Synthetic peptide corresponding to C-terminal aa 617-638 of rat ENaC alpha. Product Concentration 1.0 mg/ml Formulation PBS, pH 7.4, 50% glycerol, 0.09% sodium azide. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by Protein G affinity chromatography Storage and Handling This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Regulatory Status For in vitro investigational use only. Not for use in therapeutic or diagnostic procedures. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunoblotting: use at 1ug/mL.
Endusers should determine optimal concentrations for their applications. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionSpecificity Mouse ENaC beta Background The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) is a membrane-bound ion-channel that is selectively permeable to Na+ ions and that is assembled as a heterotrimer composed of three homologous subunits alpha, beta, and g. It is involved primarily in the reabsorption of sodium ions in the collecting ducts of the kidney's nephrons. These channels mediate the first step of active sodium reabsorption essential for the maintenance of body salt and water homeostasis. In vertebrates, the channels control reabsorption of sodium in kidney, colon, lung and sweat glands; they also play a role in taste perception. Antigen DetailsFunction Sodium permeable non-voltage-sensitive ion channel inhibited by the diuretic amiloride (PubMed:9118951). Mediates the electrodiffusion of the luminal sodium (and water, which follows osmotically) through the apical membrane of epithelial cells. Plays an essential role in electrolyte and blood pressure homeostasis, but also in airway surface liquid homeostasis, which is important for proper clearance of mucus. Controls the reabsorption of sodium in kidney, colon, lung and sweat glands. Also plays a role in taste perception. {UniProtKB:P51168, PubMed:9118951}. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Ion Channels References & CitationsTechnical Protocols |


