Anti-Human Amino-terminal Enhancer of Split (CT) (AES)
Data
- -
- -
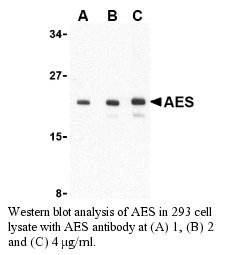
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Rabbit Immunogen PN:A255 Product Concentration 0.5 mg/ml Formulation This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative. Storage and Handling This polyclonal antibody is stable for at least one week when stored at 2-8°C. For long term storage, aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at –20°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day Ambient RRIDAB_2828071 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Rabbit Anti-Amino-terminal Enhancer of Split (CT) (AES) recognizes an epitope near the C-terminus of human, mouse and rat AES. This polyclonal antibody was purified using affinity chromatography. Background Adhesion to extracellular matrix regulates cell survival through both integrin engagement and appropriate cell spreading. Anoikis is the molecular mechanism of apop-tosis induced by integrin detachment.1 Amino-terminal enhancer of split (AES) is a member of the Groucho/ transducin-like enhancer of split (TLE) family of transcriptional regulators, a group of transcriptional co-repressors that play important roles in neurogenesis, segmentation, and sex determination.2,3 AES forms a complex with Bit1 (Bcl-2 inhibitor of transcription 1), a mitochondrial protein that is released into the cytoplasm upon onset of apoptosis.4 It has been suggested that this complex turns off a survival-promoting gene transcription program controlled by the TLE protein family.4 Interestingly, apoptosis of cells transfected with AES and Bit1 could be inhibited if the cells were allowed to attach to fibronectin through the α5β1 integrin suggesting that the Bit1-AES pathway contributing to anoikis is regulated by integrins, and in particular, the α5β1 integrin.4 PubMed References & Citations1. Martin, SS. and Vuori, K. (2004) Biochim Biophys Acta. 1692:145-57. 2. Miyasaka, H. et al. (1993) Eur. J. Biochem. 216:343-52. 3. Chen, G. and Courey, AJ. (2000) Gene 249:1-16. 4. Jan, Y. et al. (2004) Cell 116:751-762. Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
- -
- -
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
A242 | |
A244 |