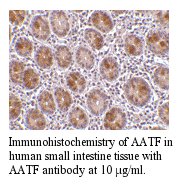
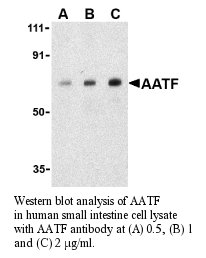
Anti-Human Apoptosis Antagonizing Transcription Factor (AATF)
Data
- -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Rabbit Immunogen PN:A240 Product Concentration 0.5 mg/ml Formulation This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative. Storage and Handling This polyclonal antibody is stable for at least one week when stored at 2-8°C. For long term storage, aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at – 20°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day Ambient RRIDAB_2828070 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Rabbit Anti-Human AATF recognizes human and mouse Apoptosis Antagonizing Transcription Factor (AATF). This polyclonal antibody was purified using affinity chromatography. Background AATF (apoptosis antagonizing transcription factor) was initially discovered as an interaction partner of ZIP kinase (ZIPK) (1), a member of death-associated protein (DAP) kinase family of pro-apoptotic serine/threonine kinases (2). AATF is a phosphoprotein containing an acidic region and a putative leucine zipper domain and nuclear localization signal, features which are typical of transcription factors. AATF inhibits the ZIPK-mediated pro-apoptotic pathway and may activate other anti-apoptotic pathways (3). Recently, it has also been shown to protect neural cells against oxidative damage induced by amyloid b-peptide and to inhibit aberrant production of the b-peptide by interacting with Par-4 (prostate apoptosis response-4), another pro-apoptotic leucine zipper protein that is associated with neuronal degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (4,5), suggesting that AATF may have potential therapeutic applications in both familial and sporadic forms of AD. References & Citations1. Page, G. et al. (1999) FEBS Lett. 462:187-191. 2. Kawai, T. et al. (1998) Mol. Cell Biol. 18:1642-51. 3. Lindfors, K. et al. (2000) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 276:660-6. 4. Xie, J. and Guo, Q. (2004) Neurobiol. of Dis. 16:150-7. Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
- -
- -
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.