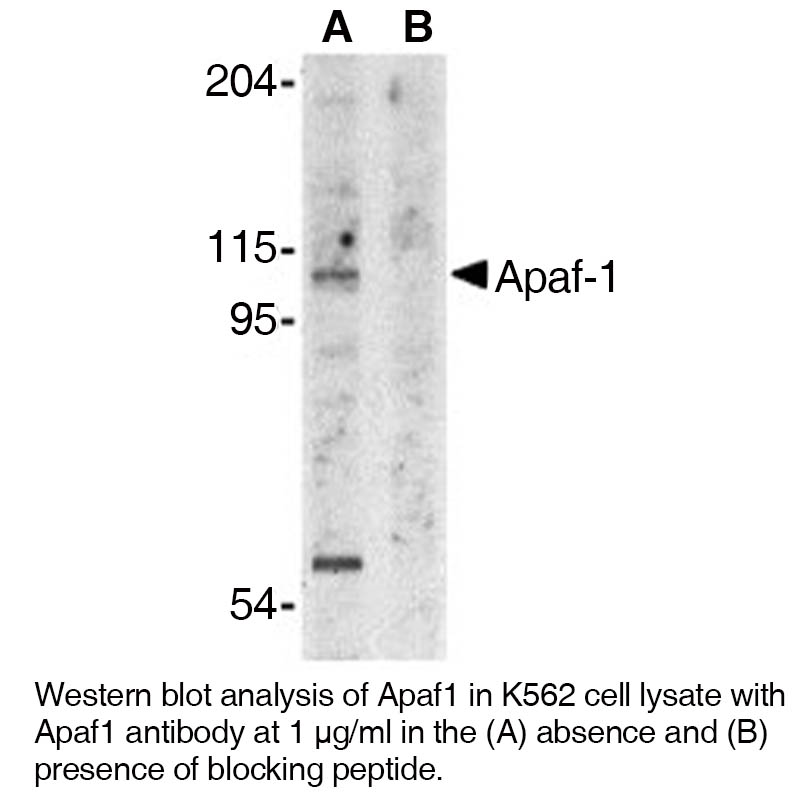
Anti-Human Apoptosis Protease Activating Factor-1 (NT) (Apaf-1)
Data
- -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Rabbit Immunogen PN:A174 Product Concentration 0.5 mg/ml Formulation This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative. Storage and Handling This polyclonal antibody is stable for at least one week when stored at 2-8°C. For long term storage, aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at –20°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day Ambient RRIDAB_2828053 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Rabbit Anti-Human Apoptosis Protease Activating Factor-1 (Apaf-1) recognizes an epitope near the N-terminus of human, mouse and rat Apaf-1. This polyclonal antibody was purified using affinity chromatography. Background Apoptosis is related to many diseases and induced by a family of cell death receptors and their ligands. Cell death signals are transduced by death domain containing adapter molecules and members of the caspase family of proteases. The mammalian homologues of the key cell death gene CED-4 in C. elegans has been identified recently from human and mouse and designated Apaf-1 (for apoptosis protease-activating factor 1).1,2 Apaf-1 binds to cytochrome c (Apaf-2) and caspase-9 (Apaf-3), which leads to caspase-9 activation. Activated caspase-9 in turn cleaves and activates caspase-3 that is one of the key proteases, being responsible for the proteolytic cleavage of many key proteins in apoptosis.3 Apaf-1 can also associate with caspase-4 and caspase-8.4 Apaf-1 is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues. References & Citations1. Zou, H. et al. (1997) Cell 90:405-13 2. Cecconi, F. et al. (1998) Cell 94:727-37 3. Li, P. et al. (1997) Cell 91:479-89 4. Hu, Y. et al. (1998) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:4386-91 Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.