Anti-Human CD57 Antibody (34054)
Anti-Human CD57 Antibody (34054)
Product No.: 34054
- -
- -
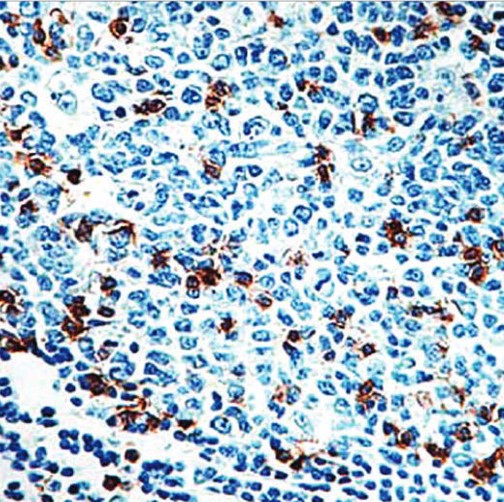
Clone G539.1 Target CD57 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Alternate Names EC 2.4.1.135, β-1,3-glucuronyltransferase 1, Glucuronosyltransferase P, GlcAT-P, UDP-GlcUA:glycoprotein β-1,3-glucuronyltransferase, GlcUAT-P Isotype Mouse IgG1 Applications IHC |
Data
- -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Mouse Immunogen Recombinant human CD57. Formulation Tris buffer, pH 7.3-7.7, 1% BSA, 0.1% sodium azide. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by immunoaffinity chromatography Storage and Handling Store at 2-8°C. Do not freeze. Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunohistochemistry: use at a dilution of 1:100-1:200 on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples after heat-induced epitope retrieval at pH 9 for 10-30 minutes. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Mouse Monoclonal Antibody specific to CD57 Background It was originally believed that CD57 (cluster of differentiation 57) was uniquely expressed on natural killer (NK) cells, but further research showed that CD57 was expressed only on a subset of functionally distinct NK cells. CD57 was subsequently identified on CD8+ T cells as well as on cells of neural crest origin. In neural cells, the CD57 epitope is predominantly restricted to adhesion molecules. CD57 has been utilized as a marker for tumors of neuroendocrine origin including pheochromocytomas, paragangliomas, carcinoid tumors, medulloblastomas, neuromas, neurofibromas, schwannomas, and granular cell tumors. Expression of CD57 can be used to distinguish nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma from T-cell/histiocyte-rich large B-cell lymphoma, nodular sclerosis, Hodgkin's disease, and follicular lymphoma. Function Involved in the biosynthesis of L2/HNK-1 carbohydrate epitope on glycoproteins. Can also play a role in glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis. Substrates include asialo-orosomucoid (ASOR), asialo-fetuin, and asialo-neural cell adhesion molecule. Requires sphingomyelin for activity: stearoyl-sphingomyelin was the most effective, followed by palmitoyl-sphingomyelin and lignoceroyl-sphingomyelin. Activity was demonstrated only for sphingomyelin with a saturated fatty acid and not for that with an unsaturated fatty acid, regardless of the length of the acyl group. {UniProtKB:O35789}. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Cancer Research References & Citations |