Anti-Human Modulator of Apoptosis 1 (Intermediate Domain) (MAP1)
Data
- -
- -
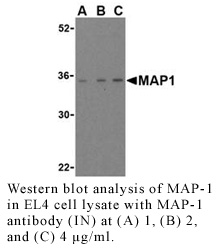
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Rabbit Immunogen PN:M1214 Product Concentration 0.5 mg/ml Formulation This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative. Storage and Handling This polyclonal antibody is stable for at least one week when stored at 2-8°C. For long term storage, aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at –20°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day Ambient RRIDAB_2831239 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Rabbit Anti-Human Modulator of Apoptosis 1 (MAP1) recognizes an epitope in the intermediate domain of Human and Mouse MAP1. This polyclonal antibody was purified using affinity chromatography. Background Apoptosis plays a major role in normal organism development, tissue homeostasis, and removal of damaged cells. Disruption of this process has been implicated in a variety of diseases such as cancer (reviewed in 1). Members of the Bcl-2 family are known to be critical regulators of this process. These proteins are characterized by the presence of several conserved motifs termed Bcl-2 homology (BH) domains (reviewed in 2 and 3). A related protein termed MAP-1 has recently been identified. This protein contains a BH3-like domain and induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in mammalian cells when overexpressed. It forms homodimers and associates with Bcl-2 family members such as Bax, Bcl-2, and Bcl-XL in vitro and in vivo.4 It has been suggested that MAP-1 associates with the tumor suppressor RASSF1A following death receptor activation, allowing a conformational change in Bax that leads to cellular apoptosis. PubMed References & Citations1. Lockshin, RA. et al. (2000) Cell Death Differ. 7:2 2. Cory, S. et al. (2003) Oncogene 22:8590 3. Heiser, D. et al. (2004) Exp. Geron. 39:1125 4. Tan, KO. et al. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276:2802 Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
- -
- -