Anti-Human PD-1 Antibody (34067)
Anti-Human PD-1 Antibody (34067)
Product No.: 34067
- -
- -
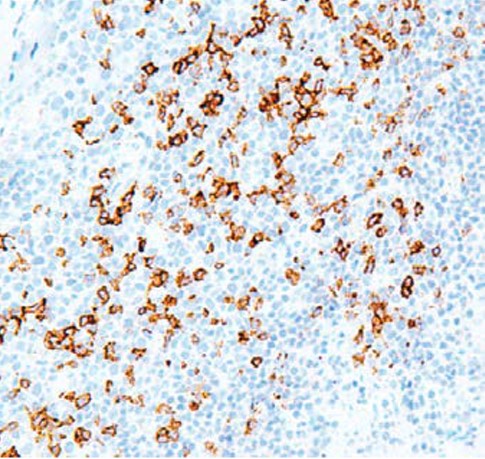
Clone G001.1 Target PD-1 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Alternate Names Protein PD-1, hPD-1, CD antigen CD279 Isotype Mouse IgG2b Applications IHC |
Data
- -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Mouse Immunogen Recombinant human PD-1. Formulation Tris buffer, pH 7.3-7.7, 1% BSA, 0.1% sodium azide. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by immunoaffinity chromatography Storage and Handling Store at 2-8°C. Do not freeze. Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunohistochemistry: use at a dilution of 1:100-1:200 on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples after heat-induced epitope retrieval at pH 9 for 10-30 minutes. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Mouse Monoclonal Antibody specific to PD-1 Background Programmed Death 1 (PD-1) is a member of the CD28/CTLA-4 family of T-cell regulators expressed as a co-receptor on the surface of activated T-cells, B-cells, and macrophages. New studies have suggested that the PD-1/PD-L1 signaling pathway may be linked to anti-tumor immunity as PD-L1 has been shown to induce apoptosis of activated T-cells or inhibit activity of cytotoxic T-cells. In comparison to CD10 and bcl-6, PD-1 is expressed by fewer B- cells and has therefore been considered a more specific and useful diagnostic marker for angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Therapies targeted toward the PD-1 receptor have shown remarkable clinical responses in patients with various types of cancer, including non–small cell lung cancer, melanoma, and renal-cell cancer. Function Inhibitory receptor on antigen activated T-cells that plays a critical role in induction and maintenance of immune tolerance to self (PubMed:21276005). Delivers inhibitory signals upon binding to ligands CD274/PDCD1L1 and CD273/PDCD1LG2 (PubMed:21276005). Following T-cell receptor (TCR) engagement, PDCD1 associates with CD3-TCR in the immunological synapse and directly inhibits T-cell activation (By similarity). Suppresses T-cell activation through the recruitment of PTPN11/SHP-2: following ligand-binding, PDCD1 is phosphorylated within the ITSM motif, leading to the recruitment of the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN11/SHP-2 that mediates dephosphorylation of key TCR proximal signaling molecules, such as ZAP70, PRKCQ/PKCtheta and CD247/CD3zeta (By similarity). {UniProtKB:Q02242, PubMed:21276005}.; The PDCD1-mediated inhibitory pathway is exploited by tumors to attenuate anti-tumor immunity and escape destruction by the immune system, thereby facilitating tumor survival (PubMed:28951311). The interaction with CD274/PDCD1L1 inhibits cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) effector function (PubMed:28951311). The blockage of the PDCD1-mediated pathway results in the reversal of the exhausted T-cell phenotype and the normalization of the anti-tumor response, providing a rationale for cancer immunotherapy (PubMed:22658127, PubMed:25034862, PubMed:25399552). {PubMed:22658127, PubMed:25034862, PubMed:25399552, PubMed:28951311}. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Cancer Research References & Citations |