Anti-Human PD-L1 Antibody (34068)
Anti-Human PD-L1 Antibody (34068)
Product No.: 34068
- -
- -
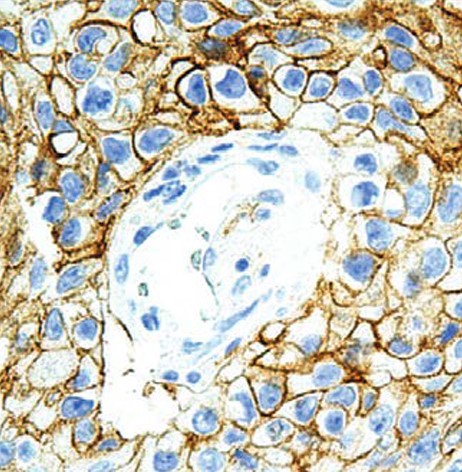
Clone G411.1 Target PD-L1 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Polyclonal Alternate Names PD-L1, PDCD1 ligand 1, Programmed death ligand 1, hPD-L1, B7 homolog 1, B7-H1, CD antigen CD274 Isotype Rabbit IgG Applications IHC |
Data
- -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Rabbit Immunogen Recombinant human PD-L1. Formulation Tris buffer, pH 7.3-7.7, 1% BSA, 0.1% sodium azide. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by immunoaffinity chromatography Storage and Handling Store at 2-8°C. Do not freeze. Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunohistochemistry: use at a dilution of 1:100-1:200 on formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded samples after heat-induced epitope retrieval at pH 9 for 10-30 minutes. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody specific to PD-L1 Background Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1), also known as CD274 or B7 Homolog 1 (B7-H1), is a transmembrane protein involved in suppressing the immune system and rendering tumor cells resistant to CD8+ T cell-mediated lysis through binding of the Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) receptor. Overexpression of PD-L1 may allow cancer cells to evade the actions of the host immune system. In renal cell carcinoma, upregulation of PD-L1 has been linked to increased tumor aggressiveness and risk of death, and, in ovarian cancer, higher expression of this protein has led to significantly poorer prognosis. PD-L1 has also been linked to systemic lupus erythematosus and cutaneous melanoma. When considered in adjunct with CD8+ tumor-infi- ltrating lymphocyte density, expression levels of PD-L1 may be a useful predictor of multiple cancer types, including stage III non-small cell lung cancer, hormone receptor negative breast cancer, and sentinel lymph node melanoma. Function Plays a critical role in induction and maintenance of immune tolerance to self (PubMed:11015443, PubMed:28813417, PubMed:28813410). As a ligand for the inhibitory receptor PDCD1/PD-1, modulates the activation threshold of T-cells and limits T-cell effector response (PubMed:11015443, PubMed:28813417, PubMed:28813410). Through a yet unknown activating receptor, may costimulate T-cell subsets that predominantly produce interleukin-10 (IL10) (PubMed:10581077). {PubMed:10581077, PubMed:11015443, PubMed:28813410, PubMed:28813417}.; The PDCD1-mediated inhibitory pathway is exploited by tumors to attenuate anti-tumor immunity and escape destruction by the immune system, thereby facilitating tumor survival (PubMed:28813417, PubMed:28813410). The interaction with PDCD1/PD-1 inhibits cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) effector function (By similarity). The blockage of the PDCD1-mediated pathway results in the reversal of the exhausted T-cell phenotype and the normalization of the anti-tumor response, providing a rationale for cancer immunotherapy (By similarity). {UniProtKB:Q9EP73, PubMed:28813410, PubMed:28813417}. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Cancer Research References & Citations |