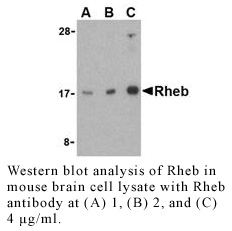
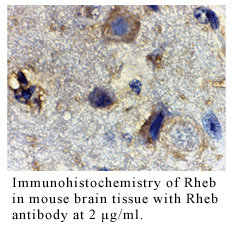
Anti-Human Ras Homolog Enriched in Brain (Intermediate Domain) (
Data
- -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Rabbit Immunogen PN:R1239 Product Concentration 0.5 mg/ml Formulation This polyclonal antibody is formulated in phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 containing 0.02% sodium azide as a preservative. Storage and Handling This polyclonal antibody is stable for at least one week when stored at 2-8°C. For long term storage, aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at –20°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day Ambient RRIDAB_2831683 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Rabbit Anti-Human Ras Homolog Enriched in Brain (Rheb) recognizes an epitope in the intermediate domain of Human, Mouse and Rat Rheb. This polyclonal antibody was purified using affinity chromatography. Background Rheb (Ras homolog enriched in brain) is an evolutionarily conserved member of the Ras family of small GTP-binding proteins originally found to be rapidly induced by synaptic activity in the hippocampus following seizure.1 While it is expressed at relatively high levels in the brain, Rheb is widely expressed in other tissues and may be induced by growth factor stimulation. Similar to other family members, Rheb triggers activation of the Raf-MEK-MAPK pathway.2 Biochemical and genetic studies demon-strate that Rheb has an important role in regulating the insulin/Target of rapamycin (TOR) signaling pathway.3-4 TOR is a serine/threonine protein kinase that acts as a sensor for ATP and amino acids, balancing the availability of nutrients with protein translation and cell growth. A dimeric protein complex termed TSC1/TSC2 indirectly inhibits TOR activity by inhibiting Rheb via the GAP activity of TSC2.3 PubMed References & Citations1. Yamagata, K. et al. (1994) J. Biol. Chem. 269:16333 2. Yee, WM. et al. (1997) Mol. Cell. Biol. 17:921 3. Inoki, K. et al. (2003) Genes Dev. 17:1829 4. Stocker, H. et al. (2003) Nat. Cell Biol. 5:559 Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
- -
- -