Anti-Mouse CD223 (LAG-3) [Clone C9B7W] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse CD223 (LAG-3) [Clone C9B7W] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade
Product No.: C2852
Clone C9B7W Target CD223 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names CD223, LAG3 Isotype Rat IgG1 Applications B , FA , FC , in vivo , IP , WB |
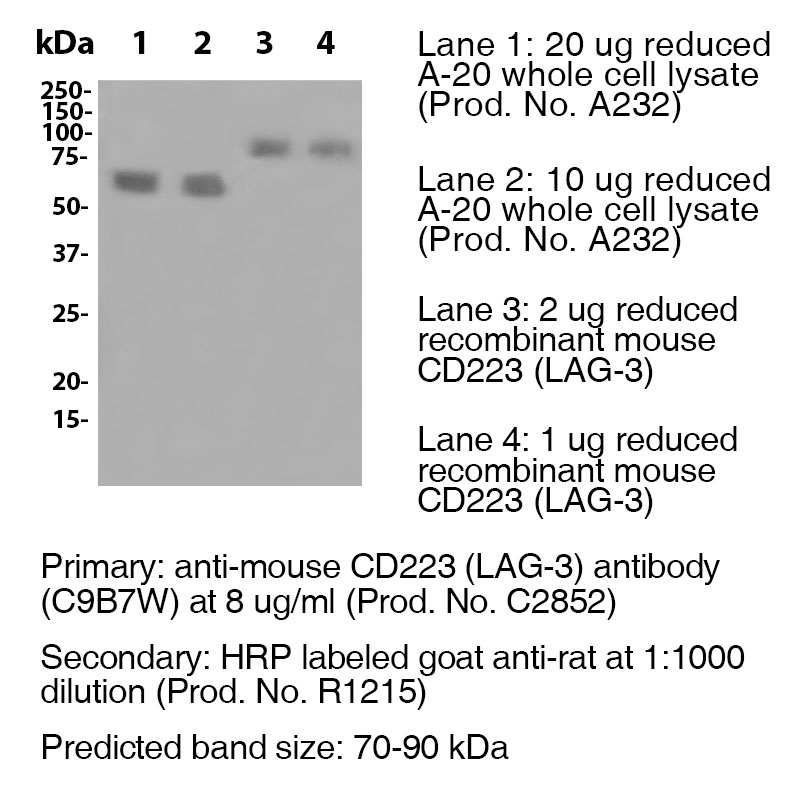
Data
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Rat Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Dilution Buffer Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level <0.5 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥98% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Pathogen Testing To protect mouse colonies from infection by pathogens and to assure that experimental preclinical data is not affected by such pathogens, all of Leinco’s Purified Functional PLATINUM™ antibodies are tested and guaranteed to be negative for all pathogens in the IDEXX IMPACT I Mouse Profile. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2829608 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Clone C9B7W recognizes and specifically binds to an epitope in the D2 domain of CD223. Background LAG-3 is a 70-kD, type-I transmembrane glycoprotein within the Ig superfamily with four extracellular Ig-like domains (D1 to D4) and is structurally homologous to CD4. LAG-3 is a cell surface molecule with various biologic effects on T cell function. It has been reported to be involved in Treg suppressive function. It negatively regulates cellular proliferation, activation, and homeostasis of T cells, in a similar manner to CTLA-4 and PD-1. Human LAG-3 is approximately 70% homologous with murine LAG3, and it binds MHC class II molecules with higher affinity than CD4. As an immune checkpoint receptor, LAG-3 is the target of various drug development programs seeking to expand treatments for cancer and autoimmune disorders. In its soluble form, LAG-3 is being developed as a cancer drug. As an antagonist, LAG-3 antibody can activate T effector cells via the downregulation of the LAG-3 inhibiting signal into pre-activated LAG-3+ cells. In addition, it can inhibit antigen-specific Treg suppressive activity. As an agonist antibody, it can be used to diminish an autoimmune response and is currently being investigated for the treatment of plaque psoriasis. Antigen Distribution CD223 is expressed on T regulatory cells, activated T cells and NK cells. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Immunology . Inhibitory Molecules Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Clone C9B7W is extensively used in in vivo mouse studies to block the function of LAG-3 (CD223), a key immune checkpoint molecule that negatively regulates T cell activation and proliferation. Its most common in vivo applications include:
Mechanism: Key Notes:
Summary Table: Key In Vivo Uses of C9B7W in Mice
C9B7W is a standard tool in mouse immunology for dissecting the role of LAG-3 in diverse disease settings. Based on the available literature, the C9B7W antibody (anti-mouse LAG-3/CD223) is commonly used in combination with or alongside several other antibodies and proteins in research studies: Immune Checkpoint AntibodiesThe C9B7W antibody is frequently combined with anti-PD-1 antibodies in studies investigating dual checkpoint blockade strategies. This combination approach examines how blocking both LAG-3 and PD-1 pathways can enhance anti-tumor immunity and therapeutic efficacy. T Cell Activation AntibodiesIn functional assays, C9B7W is often used with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 antibodies to stimulate T cell activation. These antibodies are essential tools for studying LAG-3 expression and function on activated T cells, as LAG-3 is an activation-induced surface molecule. Detection and Characterization ToolsFor experimental detection and validation purposes, polyclonal anti-mouse CD223 antibodies are used alongside C9B7W, particularly in ELISA assays where C9B7W serves as the capture antibody and polyclonal antibodies function as detection antibodies. MHC Class II MoleculesC9B7W is extensively studied in the context of its interaction with MHC class II molecules, including MHC-II tetramers (such as OVA-MHC-II-IA^b^ tetramers). These tetramers are used to assess whether C9B7W blocks the binding of LAG-3 to MHC class II, which is LAG-3's natural ligand. Surface Markers for T Cell SubsetsResearchers commonly examine C9B7W-stained cells alongside other markers like CD4, CD8, CD25, and CD49b to identify specific T cell populations, including regulatory T cells and Type 1 regulatory T cells. Clone C9B7W is a widely used rat monoclonal antibody targeting mouse LAG-3 (CD223). The key findings from scientific literature citations of this clone are:
Summary Table: Main Properties and Findings of C9B7W
In sum, C9B7W is a D2-specific monoclonal antibody that disrupts LAG-3 dimerization and function, resulting in inhibition of immune checkpoint activity, but does not directly block MHC class II binding. These properties underpin its widespread use in mouse immunology for mechanistic studies and therapeutic testing. Dosing regimens for the C9B7W clone, which targets mouse CD223 (LAG-3), can vary significantly across different mouse models. The specific dosing details, including the amount, frequency, and route of administration, are often tailored to the experimental context and the particular mouse model being used. Key Considerations:
Examples of Variability:
Overall, the dosing regimens for clone C9B7W are highly adaptable and depend on the specific research goals and the characteristics of the mouse model being studied. References & CitationsTechnical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Formats Available
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
C2252 | |
C2253 | |
C2254 | |
C2255 | |
C2256 | |
C2249 | |
C2251 | |
C2250 | |
L306 | |
C2155 | |
L502 | |
C2852 | |
L313 | |
L310 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.