Recombinant Human/Mouse/Rat Activin A
Data
- -
- -
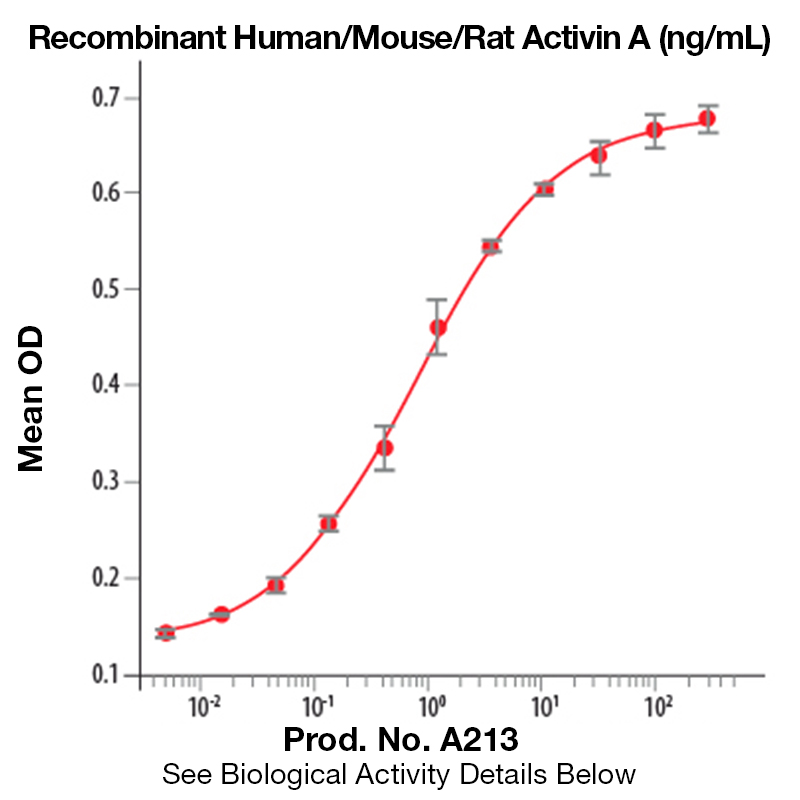
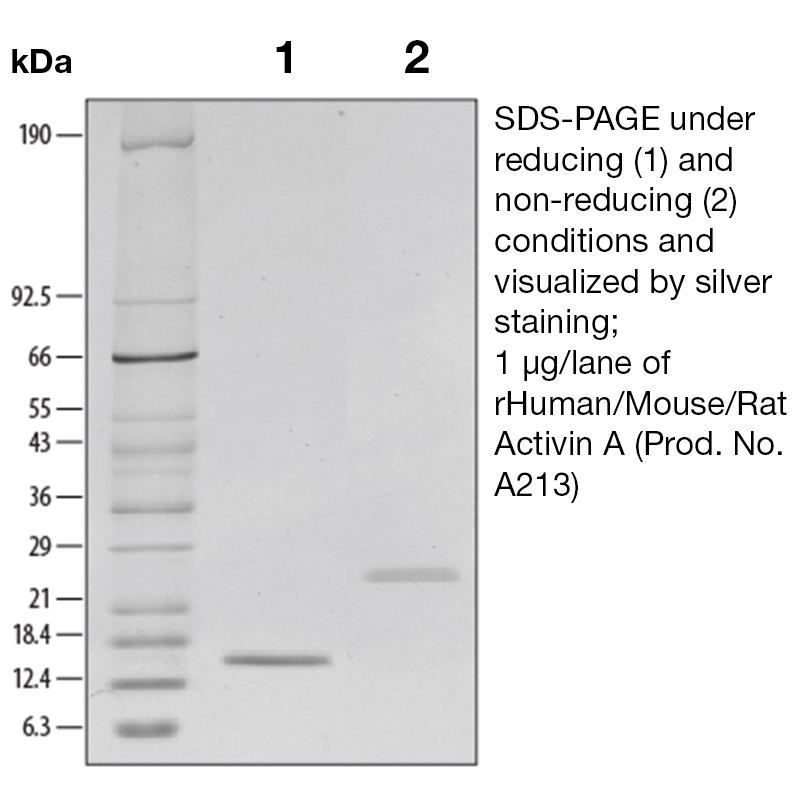
BackgroundActivin A is a member of the TGF beta super family. It was originally identified and isolated because it stimulates the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Activins are structurally related to inhibins, they share common beta subunits, but they exhibit opposite biological activities. Activins are homodimers of beta subunits and inhibins are heterodimers of an alpha subunit and a beta subunit. Since the initial discovery of Activin A, it has been shown to regulate cell differentiation, nerve cell survival, bone growth promotion, cell proliferation, and apoptosis. Activin A expression has been detected in prostate cancer, colon cancer and breast cancer. Because Activin A is able to inhibit cell proliferation by modulating the Rb pathway, it is thought to inhibit cancer development. This may not be the only mechanism by which activin may play a preventative role in cancer development. Activin has also been shown to increase the expression of a protein whose decreased expression is correlated with increased metastatic capacity. In addition, activin has an inhibitory effect on endothelial cell growth and can thereby block angiogenesis, preventing tumor growth and metastasis. The activin/inhibin nomenclature reflects the subunit composition of the proteins: activin A (βA - βA), activin B (βB - βB), activin AB (βA - βB), inhibin A (α - βA) and inhibin B (α - βB). At present, little is known about the contribution of the other β subunits to activin or inhibin formation and biology. At the amino acid sequence level, the mature human βA subunit is 100% identical to mouse βA, while the human and mouse α subunits share approximately 80% identity. Similarly to other TGF-β family members, activins exert their biological activities through binding to the heterodimeric complex composed of two membrane spanning serine-threonine kinases designated type I and type II. Two forms of activin receptor type I (Act RI-A and Act RI-B) and two forms of activin receptor type II (Act RII-A and Act RII-B) have been identified. Activin binds directly to Act RII, the complex then associates with Act RI and initiates signaling. Protein DetailsPurity >95% by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by silver stain. Endotoxin Level <0.01 EU/µg as determined by the LAL method Biological Activity The biological activity of Human Activin A was determined by its ability to induce hemoglobin expression in K562 cells.<sup>1</sup> The expected ED<sub>50</sub>=0.5 - 2.0 ng/ml. Protein Accession No. P08476 Amino Acid Sequence glecdgkvni cckkqffvsf kdigwndwii apsgyhanyc egecpshiag tsgsslsfhs tvinhyrmrg hspfanlksc cvptklrpms mlyyddgqni ikkdiqnmiv eecgcs N-terminal Sequence Analysis Gly311 State of Matter Lyophilized Predicted Molecular Mass The predicted molecular weight of Recombinant Human/Mouse/Rat Activin A is Mr 13 kDa. However, the actual molecular weight as observed by migration on SDS-PAGE is 14 kDa (reducing conditions) and
24 kDa (non-reducing conditions). Predicted Molecular Mass 13 Formulation This recombinant protein was lyophilized from a 0.2 μm filtered solution in 35% acetonitrile (CH3CN) and 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA). Storage and Stability This lyophilized protein is stable for up to twelve months when stored desiccated at -20°C to -70°C. After aseptic reconstitution, this protein may be stored at 2°C to 8°C for one month or for up to three months at -20°C to -70°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. See Product Insert for exact lot specific storage instructions. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day Ambient References & Citations1. Schwall, RH. et al. (1991) Method Enzymol. 198:340. Certificate of AnalysisIMPORTANT Use lot specific datasheet for all technical information pertaining to this recombinant protein. |
Related Products
- -
- -