Anti-AMPK alpha 1 Antibody
Anti-AMPK alpha 1 Antibody
Product No.: 13008
- -
- -
Target AMPKα 1 Product Type Polyclonal Alternate Names AMPK subunitα-1, EC 2.7.11.1, Acetyl-CoA carboxylase kinase, ACACA kinase, EC 2.7.11.27, Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase kinase, HMGCR kinase, EC 2.7.11.31, Tau-protein kinase PRKAA1, EC 2.7.11.26 Isotype Whole IgG Applications IHC , IP , WB |
Data
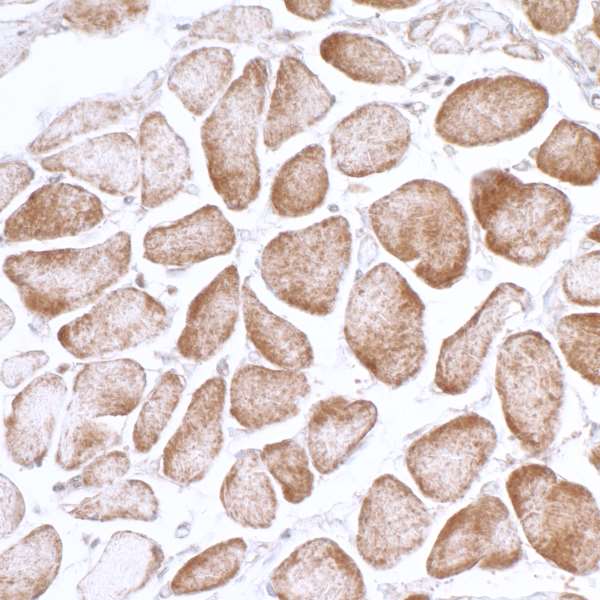 Detection of human AMPK alpha 1 by immunohistochemistry. Sample: FFPE section of human smooth muscle. Antibody: Affinity purified rabbit anti-AMPK alpha 1 (Cat. No. 13008 Lot 3) used at a dilution of 1:1|000 ( 1µg/ml). Detection: DAB
Detection of human AMPK alpha 1 by immunohistochemistry. Sample: FFPE section of human smooth muscle. Antibody: Affinity purified rabbit anti-AMPK alpha 1 (Cat. No. 13008 Lot 3) used at a dilution of 1:1|000 ( 1µg/ml). Detection: DAB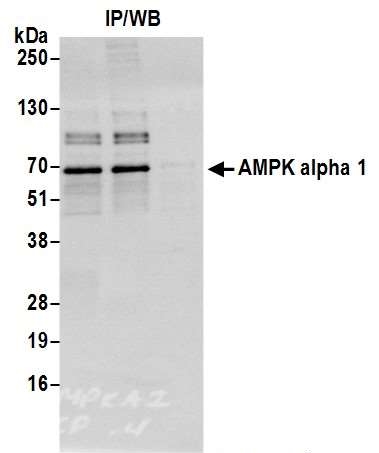 Detection of human AMPK alpha 1 by western blot of immunoprecipitates. Samples: Whole cell lysate (1.0 mg per IP reaction; 20% of IP loaded) from HeLa cells prepared using NETN lysis buffer. Antibodies: Affinity purified rabbit anti-AMPK alpha 1 antibody 13008 (lot 13008-3) used for IP at 3 µg per reaction. AMPK alpha 1 was also immunoprecipitated by a previous lot of this antibody (lot 13008-2). For blotting immunoprecipitated AMPK alpha 1, 13008 was used at 0.4 µg/ml. Detection: Chemiluminescence with an exposure time of 3 seconds.
Detection of human AMPK alpha 1 by western blot of immunoprecipitates. Samples: Whole cell lysate (1.0 mg per IP reaction; 20% of IP loaded) from HeLa cells prepared using NETN lysis buffer. Antibodies: Affinity purified rabbit anti-AMPK alpha 1 antibody 13008 (lot 13008-3) used for IP at 3 µg per reaction. AMPK alpha 1 was also immunoprecipitated by a previous lot of this antibody (lot 13008-2). For blotting immunoprecipitated AMPK alpha 1, 13008 was used at 0.4 µg/ml. Detection: Chemiluminescence with an exposure time of 3 seconds.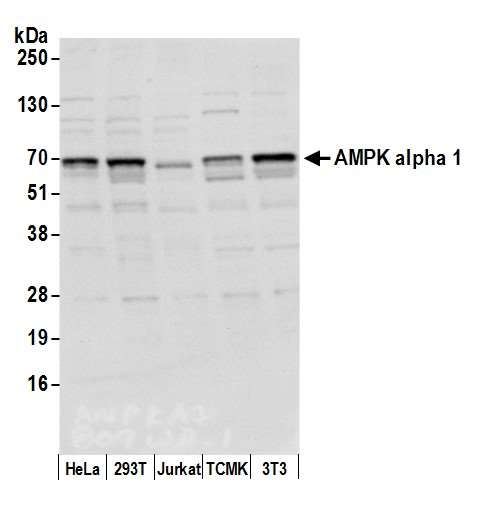 Detection of human and mouse AMPK alpha 1 by western blot. Samples: Whole cell lysate (15 µg) from HeLa, HEK293T, Jurkat, mouse TCMK-1, and mouse NIH 3T3 cells prepared using NETN lysis buffer. Antibody: Affinity purified rabbit anti-AMPK alpha 1 antibody 13008 (lot 13008-3) used for WB at 0.1 µg/ml. Detection: Chemiluminescence with an exposure time of 3 seconds.
Detection of human and mouse AMPK alpha 1 by western blot. Samples: Whole cell lysate (15 µg) from HeLa, HEK293T, Jurkat, mouse TCMK-1, and mouse NIH 3T3 cells prepared using NETN lysis buffer. Antibody: Affinity purified rabbit anti-AMPK alpha 1 antibody 13008 (lot 13008-3) used for WB at 0.1 µg/ml. Detection: Chemiluminescence with an exposure time of 3 seconds. - -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactivity Species Bovine ⋅ Human ⋅ Rat Host Species Rabbit Immunogen Synthetic peptide representing a portion of the protein encoded within exon 8 (Between 375 and 425) Product Concentration Lot Specific Formulation Tris-citrate/phosphate buffer, pH 7 to 8 containing 0.09% Sodium Azide State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by immunoaffinity chromatography Storage and Handling This antibody is stable at 2-8°C for 1 year. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunoblotting: use at 0.2-2ug/mL
Immunohistochemistry: use at 0.2- 2ug/mL. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionSpecificity This polyclonal antibody reacts with human, mouse, rat and bovine AMP activated protein kinase, alpha-1 catalytic subunit. Based on 100% sequence identity, this antibody is predicted to react with Chicken, Turkey, Dog, Horse, Rabbit, Guinea pig, Pig, Panda, Orangutan, Rhesus Monkey, Gorilla, Chimpanzee, West Indian ocean coelacanth, Medaka fish, Nile tilapia, Duckbill platypus and Three-spined stickleback. Antibody is affinity purified. Background AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a crucial enzyme in cellular energy regulation. It's a heterotrimeric protein, meaning it's composed of three different subunits: - A catalytic alpha subunit, which comes in two distinct forms, alpha1 and alpha2. The alpha1 subunit specifically acts as the serine/threonine kinase catalytic component of AMPK. - Regulatory beta and gamma subunits. AMPK plays a pivotal role in regulating key metabolic processes, including fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis. It becomes activated in response to various metabolic stresses within the cell. When cellular ATP (energy) levels are low, AMPK switches off anabolic (energy-consuming) pathways to conserve resources, acting as a master regulator of energy homeostasis. Antigen DetailsFunction Catalytic subunit of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), an energy sensor protein kinase that plays a key role in regulating cellular energy metabolism (PubMed:17307971, PubMed:17712357). In response to reduction of intracellular ATP levels, AMPK activates energy-producing pathways and inhibits energy-consuming processes: inhibits protein, carbohydrate and lipid biosynthesis, as well as cell growth and proliferation (PubMed:17307971, PubMed:17712357). AMPK acts via direct phosphorylation of metabolic enzymes, and by longer-term effects via phosphorylation of transcription regulators (PubMed:17307971, PubMed:17712357). Regulates lipid synthesis by phosphorylating and inactivating lipid metabolic enzymes such as ACACA, ACACB, GYS1, HMGCR and LIPE; regulates fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis by phosphorylating acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACACA and ACACB) and hormone-sensitive lipase (LIPE) enzymes, respectively (By similarity). Promotes lipolysis of lipid droplets by mediating phosphorylation of isoform 1 of CHKA (CHKalpha2) (PubMed:34077757). Regulates insulin-signaling and glycolysis by phosphorylating IRS1, PFKFB2 and PFKFB3 (By similarity). AMPK stimulates glucose uptake in muscle by increasing the translocation of the glucose transporter SLC2A4/GLUT4 to the plasma membrane, possibly by mediating phosphorylation of TBC1D4/AS160 (By similarity). Regulates transcription and chromatin structure by phosphorylating transcription regulators involved in energy metabolism such as CRTC2/TORC2, FOXO3, histone H2B, HDAC5, MEF2C, MLXIPL/ChREBP, EP300, HNF4A, p53/TP53, SREBF1, SREBF2 and PPARGC1A (PubMed:11554766, PubMed:11518699, PubMed:15866171, PubMed:17711846, PubMed:18184930). Acts as a key regulator of glucose homeostasis in liver by phosphorylating CRTC2/TORC2, leading to CRTC2/TORC2 sequestration in the cytoplasm (By similarity). In response to stress, phosphorylates 'Ser-36' of histone H2B (H2BS36ph), leading to promote transcription (By similarity). Acts as a key regulator of cell growth and proliferation by phosphorylating TSC2, RPTOR and ATG1/ULK1: in response to nutrient limitation, negatively regulates the mTORC1 complex by phosphorylating RPTOR component of the mTORC1 complex and by phosphorylating and activating TSC2 (PubMed:14651849, PubMed:18439900, PubMed:20160076, PubMed:21205641). In response to nutrient limitation, promotes autophagy by phosphorylating and activating ATG1/ULK1 (PubMed:21205641). In that process also activates WDR45/WIPI4 (PubMed:28561066). Phosphorylates CASP6, thereby preventing its autoprocessing and subsequent activation (PubMed:32029622). In response to nutrient limitation, phosphorylates transcription factor FOXO3 promoting FOXO3 mitochondrial import (By similarity). Also acts as a regulator of cellular polarity by remodeling the actin cytoskeleton; probably by indirectly activating myosin (PubMed:17486097). AMPK also acts as a regulator of circadian rhythm by mediating phosphorylation of CRY1, leading to destabilize it (By similarity). May regulate the Wnt signaling pathway by phosphorylating CTNNB1, leading to stabilize it (By similarity). Also has tau-protein kinase activity: in response to amyloid beta A4 protein (APP) exposure, activated by CAMKK2, leading to phosphorylation of MAPT/TAU; however the relevance of such data remains unclear in vivo (By similarity). Also phosphorylates CFTR, EEF2K, KLC1, NOS3 and SLC12A1 (PubMed:20074060, PubMed:12519745). {UniProtKB:P54645, UniProtKB:Q5EG47, PubMed:11518699, PubMed:11554766, PubMed:12519745, PubMed:14651849, PubMed:15866171, PubMed:17486097, PubMed:17711846, PubMed:18184930, PubMed:18439900, PubMed:20074060, PubMed:20160076, PubMed:21205641, PubMed:28561066, PubMed:32029622, PubMed:34077757, PubMed:17307971, PubMed:17712357}. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Enzymes References & CitationsTechnical Protocols |


