Anti-GABABR2 Antibody (56311)
Anti-GABABR2 Antibody (56311)
Product No.: 56311
- -
- -
Clone https://www.leinco.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/56311.pdf Target GABA(B)R2 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Polyclonal Alternate Names GABA-B receptor 2, GABA-B-R2, GABA-BR2, GABABR2, Gb2, G-protein coupled receptor 51, HG20 Isotype Rabbit Applications WB |
Data
- -
- -
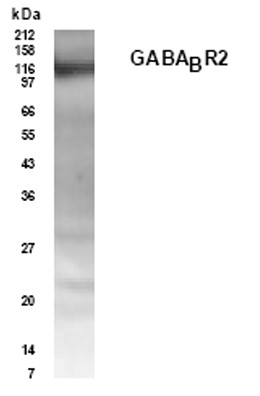
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactivity Species Human Host Species Rabbit Immunogen Synthetic peptide corresponding to aa 42-54 (TRGAPRPPPSSPP) of the rat GABABR2 subunit. Product Concentration 1.0 mg/ml Formulation PBS, pH 7.4 with 0.02% sodium azide State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by Protein A affinity chromatography Storage and Handling This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunoblotting: use at 1:250 - 1:1,000 dilution. A band of ~105kDa is detected. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionSpecificity Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody specific to GABA(B)R2 Background The GABAB receptor is the first discovered G-protein-coupled receptor whose function requires two subunits, R1 and R2, to form a functional receptor. The R1 subunit extracellular domain binds GABA, and the R2 subunit functions in G-protein activation. Antigen DetailsFunction Component of a heterodimeric G-protein coupled receptor for GABA, formed by GABBR1 and GABBR2 (PubMed:9872316, PubMed:9872744, PubMed:15617512, PubMed:18165688, PubMed:22660477, PubMed:24305054). Within the heterodimeric GABA receptor, only GABBR1 seems to bind agonists, while GABBR2 mediates coupling to G proteins (PubMed:18165688). Ligand binding causes a conformation change that triggers signaling via guanine nucleotide-binding proteins (G proteins) and modulates the activity of down-stream effectors, such as adenylate cyclase (PubMed:10075644, PubMed:10773016, PubMed:24305054). Signaling inhibits adenylate cyclase, stimulates phospholipase A2, activates potassium channels, inactivates voltage-dependent calcium-channels and modulates inositol phospholipid hydrolysis (PubMed:10075644, PubMed:9872744, PubMed:10906333, PubMed:10773016). Plays a critical role in the fine-tuning of inhibitory synaptic transmission (PubMed:9872744, PubMed:22660477). Pre-synaptic GABA receptor inhibits neurotransmitter release by down-regulating high-voltage activated calcium channels, whereas postsynaptic GABA receptor decreases neuronal excitability by activating a prominent inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) conductance that underlies the late inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (PubMed:9872316, PubMed:10075644, PubMed:9872744, PubMed:22660477). Not only implicated in synaptic inhibition but also in hippocampal long-term potentiation, slow wave sleep, muscle relaxation and antinociception (Probable). {PubMed:10075644, PubMed:10328880, PubMed:15617512, PubMed:18165688, PubMed:22660477, PubMed:24305054, PubMed:9872316, PubMed:9872744, ECO:0000305}. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Neuroscience References & CitationsTechnical Protocols |