Anti-Influenza B Neuraminidase Antibody (19601)
Anti-Influenza B Neuraminidase Antibody (19601)
Product No.: 19601
- -
- -
Clone B3 Target Influenza B Neuraminidase Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Alternate Names EC 3.2.1.18 Isotype Mouse IgG2a Applications ELISA , N |
Data
- -
- -
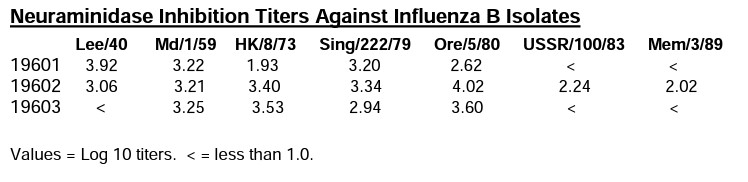
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Influenza B Neuraminidase Host Species Mouse Immunogen Influenza B Lee/40 Product Concentration Lot Specific Formulation PBS, pH 7.4. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by Protein G affinity chromatography Storage and Handling These antibodies are stable for at least one (1) year at -20 to-70°C. Store product in appropriate aliquots to avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco These antibodies may be used in immunoassays to detect and quantitate Influenza B neuraminidase and in neuraminidase inhibition assays. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionSpecificity Mouse Monoclonal Antibody specific to Influenza B Neuraminidase Function Catalyzes the removal of terminal sialic acid residues from viral and cellular glycoconjugates. Cleaves off the terminal sialic acids on the glycosylated HA during virus budding to facilitate virus release. Additionally helps virus spread through the circulation by further removing sialic acids from the cell surface. These cleavages prevent self-aggregation and ensure the efficient spread of the progeny virus from cell to cell. Otherwise, infection would be limited to one round of replication. Described as a receptor-destroying enzyme because it cleaves a terminal sialic acid from the cellular receptors. May facilitate viral invasion of the upper airways by cleaving the sialic acid moieties on the mucin of the airway epithelial cells. Likely to plays a role in the budding process through its association with lipid rafts during intracellular transport. May additionally display a raft-association independent effect on budding. Plays a role in the determination of host range restriction on replication and virulence. Sialidase activity in late endosome/lysosome traffic seems to enhance virus replication. {HAMAP-Rule:MF_04071}. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Infectious Disease . IVD Raw Material References & CitationsG.M. Air et al. (1990) Virology 177: 578. (Catalog no. 19601 = MAb B3, 19602 = MAb B14, 19603 = MAb B19). Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |