Anti-Methylated Lysine Antibody (56499)
Data
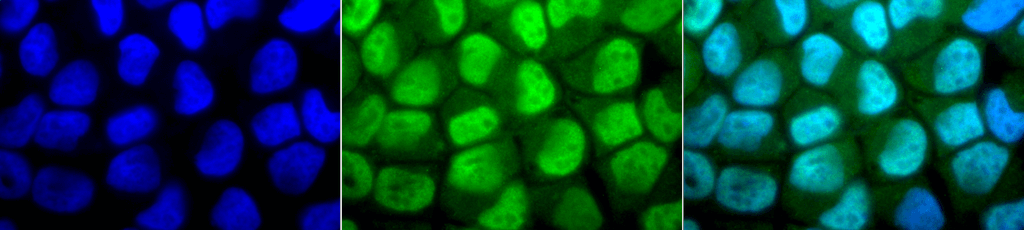 Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Rabbit Anti-Methylated Lysine Polyclonal Antibody (56499). Tissue: Cervical cancer cell line (HeLa). Species: Human. Fixation: 2% Formaldehyde for 20 min at RT. Primary Antibody: Rabbit Anti-Methylated Lysine Polyclonal Antibody (56499) at 1:50 for 12 hours at 4°C. Secondary Antibody: FITC Goat Anti-Rabbit (green) at 1:200 for 2 hours at RT. Counterstain: DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:40000 for 2 hours at RT. Localization: Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Magnification: 100x. (A) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Anti-Methylated Lysine Antibody. (C) Composite.
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Rabbit Anti-Methylated Lysine Polyclonal Antibody (56499). Tissue: Cervical cancer cell line (HeLa). Species: Human. Fixation: 2% Formaldehyde for 20 min at RT. Primary Antibody: Rabbit Anti-Methylated Lysine Polyclonal Antibody (56499) at 1:50 for 12 hours at 4°C. Secondary Antibody: FITC Goat Anti-Rabbit (green) at 1:200 for 2 hours at RT. Counterstain: DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:40000 for 2 hours at RT. Localization: Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Magnification: 100x. (A) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Anti-Methylated Lysine Antibody. (C) Composite.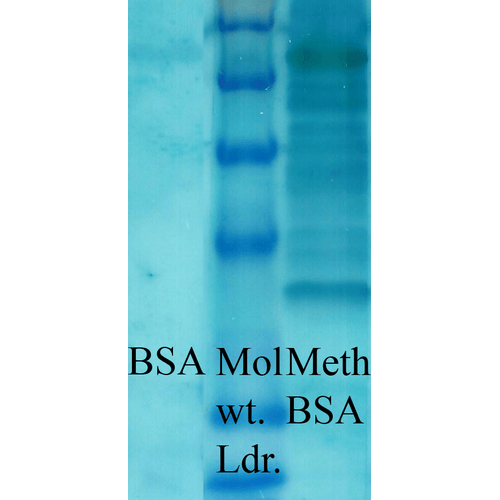 Western blot analysis of Bovine serum albumin showing detection of Methylated Lysine protein using Rabbit Anti-Methylated Lysine Polyclonal Antibody (56499). Primary Antibody: Rabbit Anti-Methylated Lysine Polyclonal Antibody (56499) at 1:1000. Methylated Lysine in BSA (Left) and Methylated BSA (Right).
Western blot analysis of Bovine serum albumin showing detection of Methylated Lysine protein using Rabbit Anti-Methylated Lysine Polyclonal Antibody (56499). Primary Antibody: Rabbit Anti-Methylated Lysine Polyclonal Antibody (56499) at 1:1000. Methylated Lysine in BSA (Left) and Methylated BSA (Right). - -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species All Host Species Rabbit Immunogen Methylated lysine-KLH conjugate. Product Concentration 1.0 mg/ml Formulation PBS, pH 7.0, and 50% glycerol. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by Protein A affinity chromatography Storage and Handling This product is stable for at least 1 year at -20°C. Freeze in multiple aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Regulatory Status For in vitro investigational use only. Not for use in therapeutic or diagnostic procedures. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunoblotting: use at 0.5-1.0ug/
mLELISA: use at 1-10ug/mL with methylated lysine-containing proteins on the solid phase. These are recommended concentrations. Enduser should determine optimal concentrations for their applications. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity This antibody recognizes proteins containing methylated lysine residues. It does not recognize non-methylated proteins. Background Post-translational modifications of proteins play critical roles in the regulation and function of many biological processes. A common post-transcriptional modification of lysine is methylation. Lysine can be methylated once, twice, or three times by lysine methyltransferases. The transfer of methyl groups from S-adenosyl methionine to histones is catalyzed by enzymes known as histone methyltransferases. Histones that are methylated on certain residues can repress or activate gene expression. Research Area Neuroscience References & CitationsTechnical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.


