Anti-Chikungunya E2 Protein [Clone CHK152] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Anti-Chikungunya E2 Protein [Clone CHK152] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Product No.: C450
Clone CHK152 Target Chikungunya E2 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Hybridoma Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names CHIKV, Chikungunya virus, VLPs, Chikungunya virus-like particles Isotype Mouse IgG2a k Applications ELISA , IHC , in vivo , N |
Data
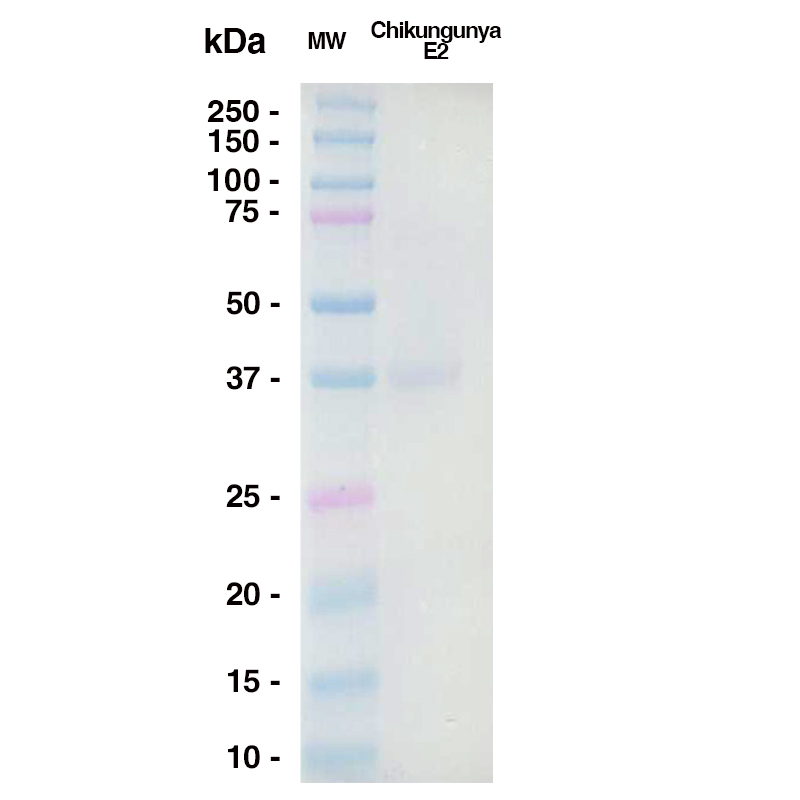 Western Blot
Western Blot
A 5ug sample of Chikungunya E2 was loaded onto an SDS-PAGE gel under reducing conditions and probed with CHK-152 @ 10ug/mL (Leinco Prod. No.: C450), Goat Anti-Human IgG secondary antibody 1:2500 dilution (Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) adsorbed against ms HRP Leinco Prod. No.: M114)
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Mouse Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Dilution Buffer Immunogen Chikungunya E2 protein Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level <1.0 EU/µg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥95% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Storage and Handling This antibody may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Additional Applications Reported In Literature ? NELISA Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Clone CHK152 binds to and shows mechanisms of neutralizing1 of the Chikungunya E2 protein. Background Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is a mosquito-transmitted alphavirus that causes epidemics globally and has been declared a notable disease by the CDC 1,2 . Symptoms include high fever, myalgia,
rash, and severe polyarthritis which can persist for long after acute infection. CHIKV is an enveloped virus with an 11.8-kb single-stranded, positive-sense RNA genome with two open reading frames 3,4. There are three main genotypes, having 95.2 to 99.8% amino acid identity: Asian, West African, and East/Central/South African (ECSA). The mature CHIKV virion is comprised of a nucleocapsid protein C and two glycoproteins, E1 and E2 5. E1 participates in
virus fusion. E2 functions in attachment to cells. E1 and E2 form 80 trimeric spikes on the virus surface 6.
Co-circulation of CHIKV with other arboviruses, such as dengue, Zika, Mayaro, and yellow fever, occurs in many countries, posing significant difficulties for diagnosis 2. Monoclonal antibodies (MAb) can be used both for diagnosis 7 and as a therapeutic agent 5,8,9. CHIKV can be rapidly detected by an immunochromatographic assay using MAbs against the CHIKV envelope protein 7. Additionally, MAb CHK-152 has been successfully used as a therapeutic agent in mouse 5 and macaque 9. CHK-152 activity is directed against the A domain of CHIKV E2 5 and likely neutralizes infectivity by inhibiting fusion 10. MAb CHK-152 protects immunocompromised mice and macaque against CHIKV-induced mortality and disease, inhibiting all three CHIKV genotypes 5, 9. Viral loads are markedly reduced in serum, spleen, liver, muscle, and brain relative to controls and joint tissue appears normal 5, 8. Combination MAb therapy (CHK-102+CHK-152 or CHK-166+CHK-152), avoids the emergence of viral resistance (dominant single-mutation escape) in both mouse 5 and macaque models 9 and the treatment window is extended 5 . When humanized, hu-CHK-152 neutralizing activity and affinity for pE2-E1 are similar to mouse CHK-152 5. Antigen Distribution The E2 Envelope protein is expressed on the surface of the Chikungunya Virus Research Area Category B Pathogens . Chikungunya . Infectious Disease . Viral . IVD Raw Material Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Clone CHK152 is primarily used in vivo in mice for protecting against Chikungunya virus (CHIKV)-induced mortality, disease, and viremia. The antibody functions as a potent neutralizer of CHIKV by targeting the viral E2 protein, thereby blocking viral fusion and preventing infection. Key in vivo applications in mice include:
Typical endpoints in these mouse studies include:
In summary, clone CHK152 is a gold-standard tool for modeling antibody-mediated protection, therapy, and resistance mechanisms for Chikungunya virus infection in mice. Other antibodies most commonly used with CHK152 in the literature are CHK-102, CHK-166, and CHK-263, typically in combination for enhanced neutralization and protection against Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) infection. These monoclonal antibodies target different epitopes on the viral E1 and E2 surface glycoproteins:
In laboratory assays, these antibodies are applied together to:
Other proteins briefly mentioned in broader literature for CHIKV research include:
In summary, CHK-102, CHK-166, and CHK-263 are the most commonly referenced antibodies in combination with CHK-152 for both mechanistic studies and therapeutic applications in CHIKV literature. Key Findings on Clone CHK152 (Anti-Chikungunya Virus E2 Monoclonal Antibody)Highly Protective In Vivo Mechanism of Neutralization and Fusion Blockade Epitope and Neutralization Escape Mutants Combination Therapy and Resistance Fitness of Escape Variants Conservation of Targeted Residues Summary Table: Major Properties and Findings for CHK-152
ConclusionCHK-152 is a potent, E2-targeting monoclonal antibody with demonstrated efficacy in animal models of CHIKV infection. Its therapeutic potential is maximized in combination with other MAbs to prevent viral escape, and the targeted epitope is highly conserved, reducing the likelihood of natural resistance. Escape mutants, while retaining fitness, are clinically attenuated, which may have implications for viral evolution under antibody pressure. Dosing regimens of clone CHK152 vary widely depending on the mouse model used, including differences in dose amounts, timing (prophylaxis or treatment), and whether CHK152 is given as monotherapy or in combination therapy. Key variations in dosing regimens:
Example dosing regimens across mouse models:
Additional considerations:
Summary: References & Citations1. Petersen, L. R., & Epstein, J. S. (2014). Transfusion, 54(8), 1911–1915. 2. Silva, JVJ Jr., Ludwig-Begall, LF., Oliveira-Filho, EF. et al. (2018) Acta Trop. 188:213-224. 3. Powers, AM., Brault, AC., Tesh, RB. et al. (2000) J. Gen. Virol. 81:471–479. 4. Arankalle, VA., Shrivastava, S., Cherian, S. et al. (2007) J. Gen. Virol. 88:1967–1976. 5. Pal, P., Dowd, KA., Brien, JD. et al. (2013)PLoS Pathog. 9(4):e1003312. 6. Mukhopadhyay, S., Zhang, W., Gabler, S. et al. (2006) Structure. 14(1):63-73. 7. Okabayashi, T., Sasaki, T., Masrinoul, P. et al. (2015) J Clin Microbiol. 53(2):382-388. 8. Hawman, DW., Stoermer, KA., Montgomery, SA. et al. (2013) J Virol. 87(24):13878-13888. 9. Pal, P, Fox, JM., Hawman, DW. et al. (2014) J Virol. 88(15):8213-8226. 10. Sun, S., Xiang, Y., Akahata, W. et al. (2013) Elife. 2:e00435. Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
Formats Available
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
C450 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.


