Anti-Ubiquitin Antibody
Data
- -
- -
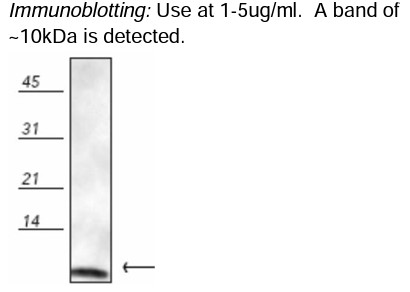
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species E. coli ⋅ Bovine ⋅ Canine ⋅ Chicken ⋅ Drosophila ⋅ Fish ⋅ Guinea Pig ⋅ Hamster ⋅ Human ⋅ Monkey ⋅ Mouse ⋅ Porcine ⋅ Rabbit ⋅ Rat ⋅ Sheep ⋅ Xenopus ⋅ Yeast Host Species Rabbit Immunogen Native bovine ubiquitin conjugated to KLH. Product Concentration Lot Specific Formulation PBS, pH 7.2, 50% glycerol, 0.09% sodium azide. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by protein A affinity chromatography Storage and Handling This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Store in appropriate aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Regulatory Status Research Use Only Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunoblotting: Use at 1-5ug/mL. A band of ~10kDa is detected.
Immunohistochemistry: use at 1-10ug/mL. These are recommended concentrations. Endusers should determine optimal concentrations for their applications. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity This antibody recognizes free ubiquitin as well as ubiquinated proteins in immunoblots. It recognizes human, monkey, mouse, rat, hamster, rabbit, Guinea pig, bovine, porcine, canine, sheep, chicken, Xenopus, yeast, Drosophila, and fish ubiquitin. Background Ubiquitin is a small, highly conserved 76-amino acid polypeptide found in all eukaryotic cells. The process of ubiquitination tags cytosolic and nuclear proteins for degradation by the proteasome, playing a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis. This regulated pathway relies on a sequential cascade of enzymes: ubiquitin-activating enzymes (E1s), ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s or Ubcs), and ubiquitin-protein ligases (E3s), which together attach ubiquitin molecules to target proteins. Beyond proteasomal degradation, ubiquitination is also involved in the internalization and lysosomal degradation of membrane proteins—such as T cell receptor subunits—while they remain associated with the endoplasmic reticulum. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org P0CG53 Research Area Apoptosis . Cell Biology . Neuroscience References & Citations1. Li, B., Li, M., et al. Aging (Albany NY) . 2019 Dec 26 11(24):12546-12567 2. Garcia-Jove Navarro, M., Basset, C., et al. PLoS One . 2013 Aug 7 8(8):e71443 3. Ribeiro, J. R., Lovasco, L. A., et al. Front Oncol . 2014 Mar 11 4:45 4. Bouwman, R. D., Palser, A., et al.Retrovirology. 2014 Jul 3 11:53 5. Leonard, A., Paton, A. W., et al. PLoS One . 2014 Oct 30 9(10):e110949 6. Kang, K. A., Piao, M. J., et al. Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 28 7(26):40594-40620 7. Cai, T., Sun, D., et al. J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Mar 22(3):1684-1695 8. López de la Oliva, A. R., Campos-Sandoval, J. A., et al.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 10 10(1):2259 9. Lei, W., Duron, D. I., et al.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Nov 29 12:294 Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |