Recombinant Human FGF-Basic (146 aa)
Recombinant Human FGF-Basic (146 aa)
Product No.: F1105
Alternate Names Fibroblast Growth Factor-Basic, B-FGF, FGF-2, FGF-β, FGFB, Prostatropin, NUDT6 Product Type Recombinant Protein Expression Host E. coli Cells Species Human Applications ELISA Cap ⋅ FC |
Data
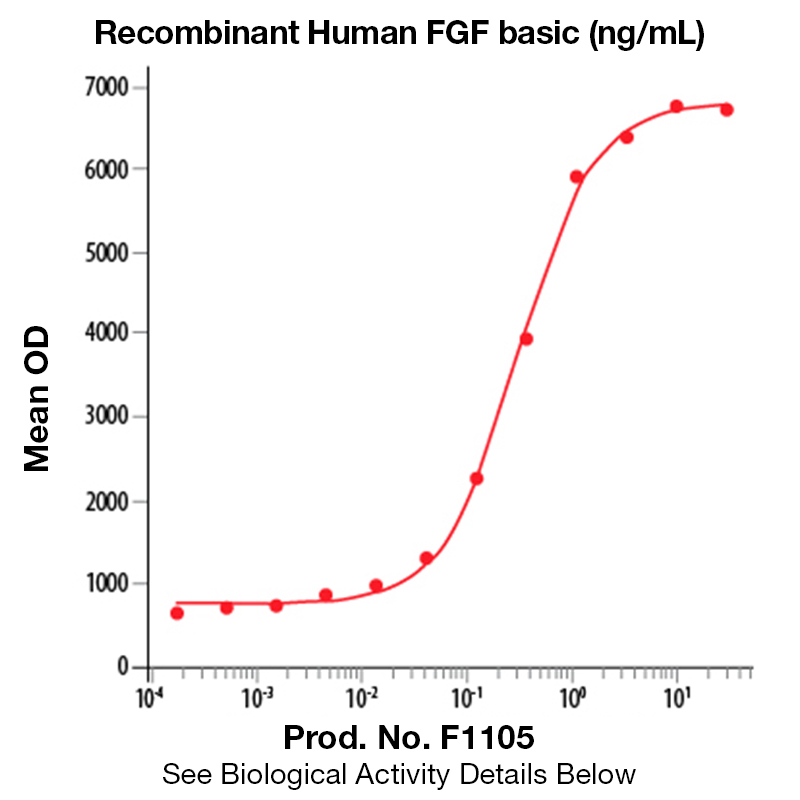
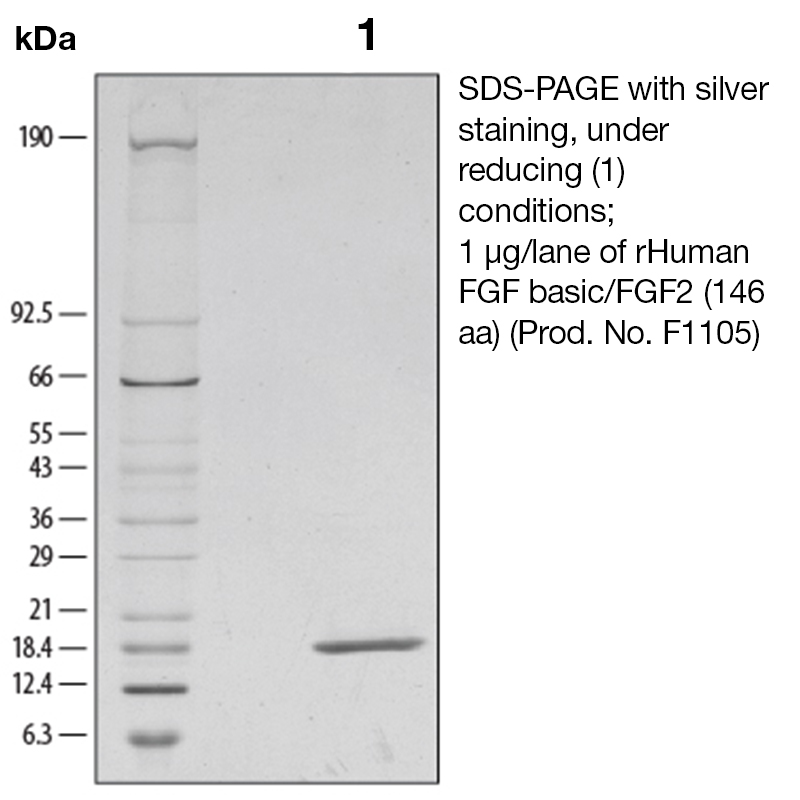
BackgroundBasic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), also known as FGF-2 and FGF-β, is a non-glycosylated heparin binding growth factor and member of the FGF family of mitogenic proteins. Members of this family play a central role during prenatal development, postnatal growth and regeneration of a variety of tissues, by promoting cellular proliferation and differentiation (1). bFGF is expressed in the brain, pituitary, kidney, retina, bone, testis, adrenal gland, liver, placenta, and monocytes, epithelial and endothelial cells. It is secreted by mechanisms other than the classical protein secretion pathway due to the lack of a signal peptide. Acidic FGF (aFGF) and bFGF bind to the same high affinity receptors (2). Binding of bFGF to heparin or cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans is a prerequisite for ligation of bFGF to these receptors. aFGF and BFGF have a similar range of biological activities which are implicated in several important physiological and pathological processes, such as embryonic development and differentiation, morphogenesis, angiogenesis, and wound healing (3-4). Protein DetailsPurity >97% by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by silver stain. Endotoxin Level <0.1 EU/µg as determined by the LAL method Biological Activity The biological activity of Human FGF basic (146 a.a.) was determined in a cell proliferation assay using NR6R3T3 mouse fibroblasts. The ED<sub>50</sub> for this effect is typically 0.5-2.5 ng/ml. Protein Accession No. Amino Acid Sequence palpedgg sgafppghfk dpkrlyckng gfflrihpdg rvdgvreksd phiklqlqae ergvvsikgv canrylamke dgrllaskcv tdecffferl esnnyntyrs rkytswyval krtgqyklgs ktgpgqkail flpmsaks
N-terminal Sequence Analysis Ala-Pro143 State of Matter Lyophilized Predicted Molecular Mass The predicted molecular weight of Recombinant Human FGF-Basic is Mr 16.0 kDa. However, the actual molecular weight as observed by migration on SDS-PAGE is Mr 17 kDa. Predicted Molecular Mass 16.0 Formulation This recombinant protein was 0.2 µm filtered and lyophilized from a sterile solution containing 20 mM Tris, 1000 mM NaCl pH 7.0. Storage and Stability This lyophilized protein is stable for six to twelve months when stored desiccated at -20°C to -70°C. After aseptic reconstitution, this protein may be stored at 2°C to 8°C for one month or at -20°C to -70°C in a manual defrost freezer. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. See Product Insert for exact lot specific storage instructions. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day Ambient NCBI Gene Bank Applications and Recommended Usage ? (Quality Tested by Leinco) ELISA Sandwich: This antibody is useful as the capture antibody in a sandwich ELISA. The suggested coating concentration is 5 µg/ml (100 µl/well) µg/ml. Flow Cytometry: PN:A106 Flow Cytometry: It is recommended to use the indirect method for signal enhancement when enumerating cells expressing CXCR5. A suggested method would be to stain cells expressing CXCR5 with approximately 10 µl per test. A typical test sample constitutes approximately 50 µl of packed whole blood or 1 x 105 continuous passage or activated cell cultures that have been centrifuged at 500 X g for five minutes. Labeling of the cells with the biotin conjugate should be followed by PN:A104, resuspended in 200-400 µl of 1X PBS. Leinco Protein AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Recombinant Human FGF-Basic (146 aa) is widely used in research due to its potent mitogenic and angiogenic activities, making it essential for studies involving cell proliferation, tissue regeneration, and developmental biology. FGF-Basic (also known as FGF-2 or bFGF) is a member of the fibroblast growth factor family and is involved in several key biological processes:
Technical Advantages:
Common Applications:
Best Practices:
In summary, Recombinant Human FGF-Basic (146 aa) is a versatile and essential growth factor for research in cell biology, regenerative medicine, developmental biology, and disease modeling due to its broad spectrum of biological activities and technical reliability. Yes, recombinant human FGF-Basic (146 aa) can be used as a standard for quantification and calibration in ELISA assays. This is one of the primary recommended applications for this protein formulation. Formulation Selection for ELISAWhen using recombinant FGF-Basic for ELISA standardization, you should select the formulation with BSA (Bovine Serum Albumin) as a carrier protein. The carrier protein enhances protein stability, increases shelf-life, and allows the recombinant protein to be stored at more dilute concentrations—all critical factors for maintaining standard integrity across multiple assay runs. Alternatively, if you require a carrier-free formulation, this option is available for applications where the presence of BSA could interfere with your specific assay design. Protein SpecificationsThe 146 amino acid variant has the following characteristics relevant to ELISA applications:
Recommended Dilution RangeFor ELISA applications, typical working dilutions range from 0.2 to 0.4 ng/well, depending on your specific assay optimization requirements. Important ConsiderationNote that ELISA standard formulations are specifically validated for quantification purposes and should not be used interchangeably with bioassay-grade recombinant proteins, as ELISA standards are not tested for cell proliferation or functional bioassay applications. Research Applications of Recombinant Human FGF-Basic (146 aa)Recombinant human FGF-basic (146 aa) has been validated across a diverse range of research applications in published literature, reflecting its broad biological activity and utility in multiple experimental contexts. Stem Cell Biology and DifferentiationFGF-basic (146 aa) has demonstrated significant utility in stem cell research. The protein supports neural stem cell expansion, with documented use at 20 ng/mL concentrations achieving 100-fold expansion of rat and mouse cortical stem cells over multiple passages. In pluripotent stem cell applications, the protein has been employed for directed differentiation into specialized cell types, including lung-specific mesenchyme, Schwann cells, and germ-like cells. The protein also supports the development of functional human pluripotent stem cell-derived Kupffer cells in hepatic organoid systems. Cell Proliferation and BioassaysThe primary validated application involves cell proliferation assays, where recombinant human FGF-basic (146 aa) induces dose-dependent proliferation of NIH/3T3 mouse fibroblasts. This bioassay application has been extensively utilized across numerous published studies examining cellular responses to growth factor signaling. The protein stimulates proliferation of cells derived from mesodermal, neuroectodermal, ectodermal, and endodermal origins. Organoid Development and Tissue EngineeringFGF-basic (146 aa) has been validated for use in regenerative human liver organoid (HLO) development for hepatotoxicity assays. The protein supports organoid formation and maturation in perfusion-based culture systems, enabling functional tissue modeling. Neurobiological ResearchThe protein has been applied in studies examining neuronal differentiation, survival, and regeneration. Published research has utilized FGF-basic in investigations of neural development, neurodegeneration, and disease modeling in neurological conditions. Disease Modeling ApplicationsFGF-basic (146 aa) has been validated in multiple disease modeling contexts, including studies of Parkinson's disease, glioblastoma, synovial sarcoma, skeletal dysplasia, and Hirschsprung's disease. The protein supports the generation and maintenance of disease-relevant cell populations for mechanistic studies and therapeutic screening. Tissue Culture and MaintenanceThe protein is used to supplement tissue culture media for supporting growth of specialized cell populations, including human and canine chondrocyte-like cells. To reconstitute and prepare Recombinant Human FGF-Basic (146 aa) protein for cell culture experiments, dissolve the lyophilized protein at 100–250 μg/mL in sterile PBS containing at least 0.1% human or bovine serum albumin (BSA or HSA). This carrier protein is essential to stabilize FGF-Basic and prevent adsorption to surfaces and loss of activity. Step-by-step protocol:
Additional notes:
Summary Table:
This protocol ensures optimal stability and bioactivity of FGF-Basic for cell culture experiments. References & Citations1. Swain, JL. et al. (1991) Developement 111: 741 2. Grevers, G. et al. (1997) Laryngorhinootologie 76: 421 3. Bühring, HJ. et al. (2007) Differentiation. 75(4):279-91 Technical ProtocolsCertificate of AnalysisIMPORTANT Use lot specific datasheet for all technical information pertaining to this recombinant protein. |
Related Products
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
F149 | |
F1105 | |
F107 | |
F110 | |
F1022 | |
F1027 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.