Anti-4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (56611)
Anti-4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (56611)
Product No.: 56611
- -
- -
Clone 6F10 Target 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Alternate Names 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal (4-HHE), 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal, 4-HHE, MG, MG-modified protein, 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal-modified , 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal, 4-hydroxy Hexenal, HHE, 4-HHE Isotype Mouse IgG2b Applications ELISA , FACS , ICC , IF , WB , FCM |
Data
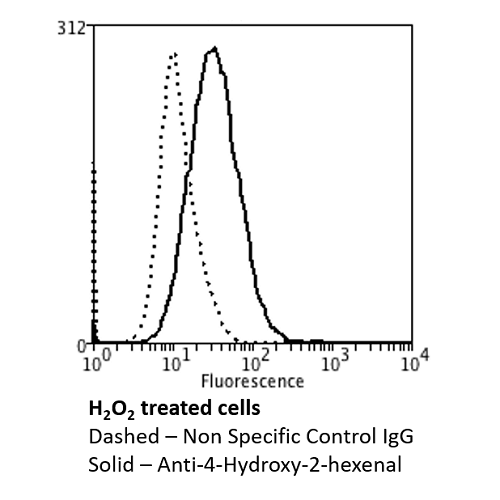 Flow Cytometry analysis using Mouse Anti-4-hydroxy-2-hexenal Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 6F10 . Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 90% Methanol. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-4-hydroxy-2-hexenal Monoclonal Antibody at 1:50 for 30 min on ice. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse: PE at 1:100 for 20 min at RT. Isotype Control: Non Specific IgG. Cells were subject to oxidative stress by treating with 250 µM H2O2 for 24 hours.
Flow Cytometry analysis using Mouse Anti-4-hydroxy-2-hexenal Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 6F10 . Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 90% Methanol. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-4-hydroxy-2-hexenal Monoclonal Antibody at 1:50 for 30 min on ice. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse: PE at 1:100 for 20 min at RT. Isotype Control: Non Specific IgG. Cells were subject to oxidative stress by treating with 250 µM H2O2 for 24 hours.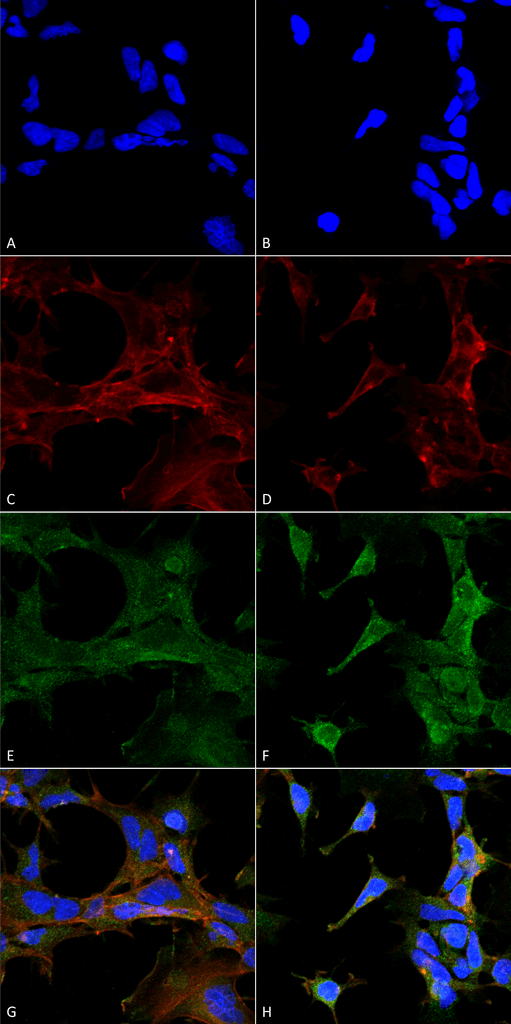 Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 6F10 . Tissue: Embryonic kidney epithelial cell line (HEK293). Species: Human. Fixation: 5% Formaldehyde for 5 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal Monoclonal Antibody at 1:400 for 30-60 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse Alexa Fluor 488 at 1:1500 for 30-60 min at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin Alexa Fluor 633 F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:250, 1:50000 for 30-60 min at RT. Magnification: 20X (2X Zoom). (A,C,E,G) – Untreated. (B,D,F,H) – Cells cultured overnight with 50 µM H2O2. (A,B) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (C,D) Phalloidin Alexa Fluor 633 F-Actin stain. (E,F) 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal Antibody. (G,H) Composite. Courtesy of: Dr. Robert Burke, University of Victoria.
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 6F10 . Tissue: Embryonic kidney epithelial cell line (HEK293). Species: Human. Fixation: 5% Formaldehyde for 5 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal Monoclonal Antibody at 1:400 for 30-60 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse Alexa Fluor 488 at 1:1500 for 30-60 min at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin Alexa Fluor 633 F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:250, 1:50000 for 30-60 min at RT. Magnification: 20X (2X Zoom). (A,C,E,G) – Untreated. (B,D,F,H) – Cells cultured overnight with 50 µM H2O2. (A,B) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (C,D) Phalloidin Alexa Fluor 633 F-Actin stain. (E,F) 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal Antibody. (G,H) Composite. Courtesy of: Dr. Robert Burke, University of Victoria.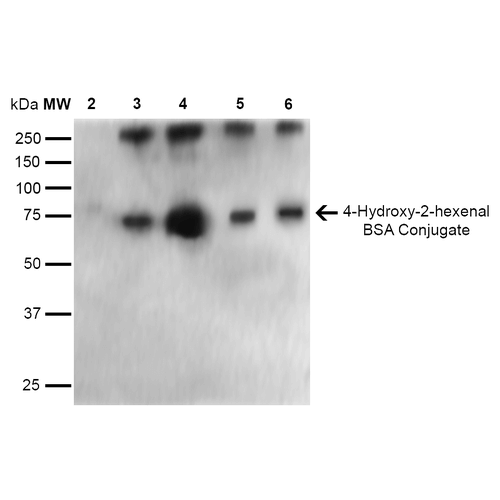 Western Blot analysis of 4-hydroxy-2-hexanal-BSA Conjugate showing detection of 67 kDa 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal protein using Mouse Anti-4-hydroxy-2-hexenal Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 6F10 . Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder (MW). Lane 2: BSA (0.5 µg). Lane 3: 4-hydroxyl nonenal-BSA (0.5 µg). Lane 4: 4-hydroxy nonenal-BSA (2.0 µg). Lane 5: 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal (0.5 µg). Lane 6: 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal (2.0 µg). Block: 5% Skim Milk in TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-4-hydroxy-2-hexenal Monoclonal Antibody at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP at 1:2000 for 60 min at RT. Color Development: ECL solution for 5 min in RT. Predicted/Observed Size: 67 kDa.
Western Blot analysis of 4-hydroxy-2-hexanal-BSA Conjugate showing detection of 67 kDa 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal protein using Mouse Anti-4-hydroxy-2-hexenal Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 6F10 . Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder (MW). Lane 2: BSA (0.5 µg). Lane 3: 4-hydroxyl nonenal-BSA (0.5 µg). Lane 4: 4-hydroxy nonenal-BSA (2.0 µg). Lane 5: 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal (0.5 µg). Lane 6: 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal (2.0 µg). Block: 5% Skim Milk in TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-4-hydroxy-2-hexenal Monoclonal Antibody at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP at 1:2000 for 60 min at RT. Color Development: ECL solution for 5 min in RT. Predicted/Observed Size: 67 kDa. - -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactivity Species Species Independent Host Species Mouse Immunogen Synthetic 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal modified Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KLH). Product Concentration 1 mg/mL Formulation PBS pH 7.4, 50% glycerol, 0.09% Sodium azide State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Protein G Purified Storage and Handling This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Regulatory Status Research Use Only Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco WB (1:1000); ICC/IF (1:50); ELISA (1:1000); FACS (1:50); FCM (1:50); Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionSpecificity Specific for 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal (4-HHE) and 4-Hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) modified proteins. Does not detect free 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal (4-HHE) or 4-Hydroxynonenal (4-HNE). Does not cross-react with Acrolein, Crotonaldehyde, Hexanoyl Lysine, Malondialdehyde, or Methylglyoxal modified proteins. Background Lipid peroxidation occurs when oxidizing agents attack carbon-carbon double bonds found in unsaturated lipids. In addition to membrane degradation, oxidation end-products have been found to damage cell viability through their mutagenic and toxic properties. These downstream functional consequences facilitate the development of disease and premature aging. 4-hydroxy-2-hexenal (4-HHE) is a major alpha,beta-unsaturated aldehyde product of n-3 PUFA oxidation resulting from lipid peroxidation. High levels of HHE are found in disease states (1). 4-HHE reacts with histidine residues to form Michael-addition type adducts. Antigen DetailsResearch Area Cancer . Lipid peroxidation . Oxidative Stress References & CitationsTechnical Protocols |
Formats Available
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.


