Anti-Copper-Transporting ATPase1 Antibody (56516)
Anti-Copper-Transporting ATPase1 Antibody (56516)
Product No.: 56516
- -
- -
Clone S60-4 Target Copper-Transporting ATPase1 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Alternate Names EC 7.2.2.8, Copper pump 1, Menkes disease-associated protein Isotype Mouse IgG2b Applications ICC , IF , IHC , IP , WB |
Data
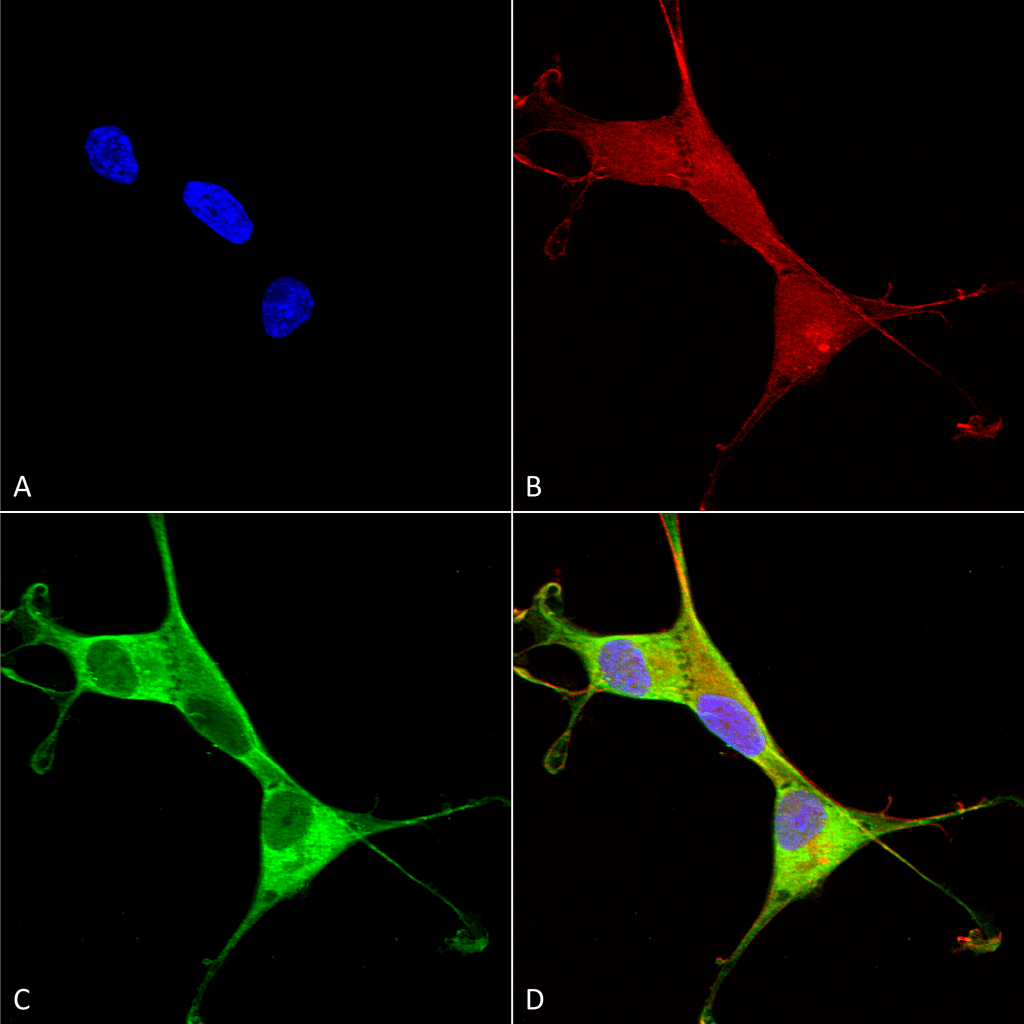 Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S60-4 (56516). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% PFA for 15 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Monoclonal Antibody (56516) at 1:100 for overnight at 4°C with slow rocking. Secondary Antibody: AlexaFluor 488 at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain; Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain at 1:800, 1.6mM for 20 min at RT. (A) Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain. (C) Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Antibody (D) Composite.
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S60-4 (56516). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% PFA for 15 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Monoclonal Antibody (56516) at 1:100 for overnight at 4°C with slow rocking. Secondary Antibody: AlexaFluor 488 at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain; Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain at 1:800, 1.6mM for 20 min at RT. (A) Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain. (C) Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Antibody (D) Composite.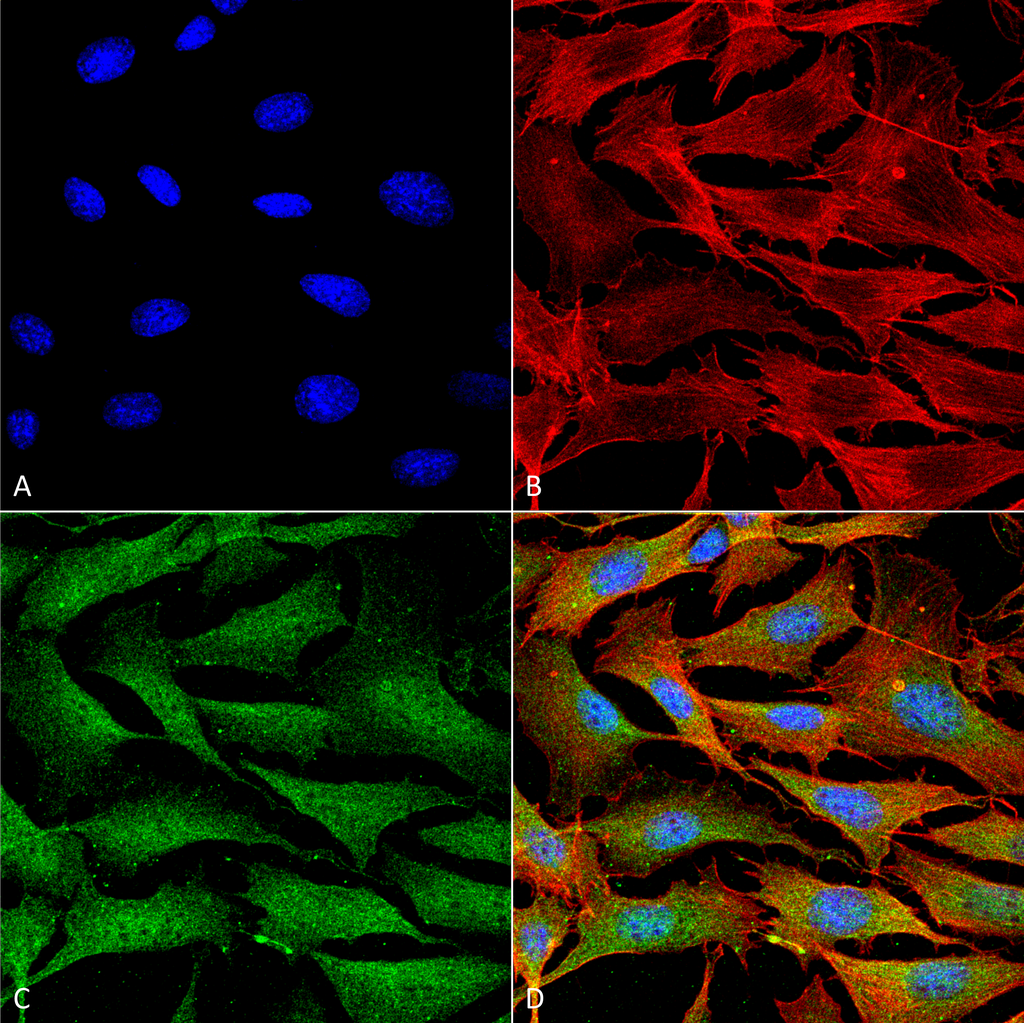 Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S60-4 (56516). Tissue: NIH 3T3 (NIH 3T3). Species: Mouse. Fixation: 4% Formaldehyde for 15 min at RT. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Monoclonal Antibody (56516) at 1:100 for 60 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse ATTO 488 at 1:200 for 60 min at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:1000, 1:5000 for 60 min at RT, 5 min at RT. Localization: Endoplasmic Reticulum, Cytoplasm, Golgi Apparatus, Trans-Golgi Network Membrane, Cell Membrane. Magnification: 60X. (A) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain. (C) Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Antibody. (D) Composite.
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S60-4 (56516). Tissue: NIH 3T3 (NIH 3T3). Species: Mouse. Fixation: 4% Formaldehyde for 15 min at RT. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Monoclonal Antibody (56516) at 1:100 for 60 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse ATTO 488 at 1:200 for 60 min at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:1000, 1:5000 for 60 min at RT, 5 min at RT. Localization: Endoplasmic Reticulum, Cytoplasm, Golgi Apparatus, Trans-Golgi Network Membrane, Cell Membrane. Magnification: 60X. (A) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin Texas Red F-Actin stain. (C) Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Antibody. (D) Composite.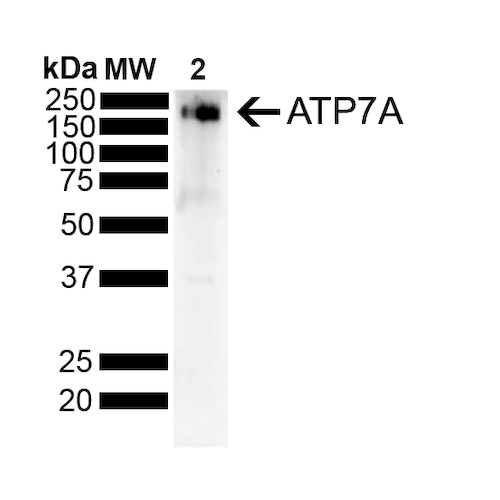 Western Blot analysis of Rat Liver showing detection of ~180 kDa Copper Transporting ATPase 1 protein using Mouse Anti-Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S60-4 (56516). Lane 1: MW Ladder. Lane 2: Rat Liver . Load: 10 ug. Block: 5% Skim Milk powder in TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Monoclonal Antibody (56516) at 1:500 for 2 hours at RT with shaking. Secondary Antibody: Goat anti-mouse IgG:HRP at 1:4000 for 1 hour at RT with shaking. Color Development: Chemiluminescent for HRP (Moss) for 5 min in RT. Predicted/Observed Size: ~180 kDa.
Western Blot analysis of Rat Liver showing detection of ~180 kDa Copper Transporting ATPase 1 protein using Mouse Anti-Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone S60-4 (56516). Lane 1: MW Ladder. Lane 2: Rat Liver . Load: 10 ug. Block: 5% Skim Milk powder in TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Copper Transporting ATPase 1 Monoclonal Antibody (56516) at 1:500 for 2 hours at RT with shaking. Secondary Antibody: Goat anti-mouse IgG:HRP at 1:4000 for 1 hour at RT with shaking. Color Development: Chemiluminescent for HRP (Moss) for 5 min in RT. Predicted/Observed Size: ~180 kDa. - -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human ⋅ Mouse ⋅ Rat Host Species Mouse Immunogen Synthetic peptide correspond- ing to aa 42-61 (cytoplasmic C-terminus) of human Copper-Transporting ATPase1 (accession no. NP_000043.3). Product Concentration 1.0 mg/ml Formulation PBS, pH 7.4, 50% glycerol, 0.09% sodium azide.Purified by Protein G affinity chromatography. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by Protein G affinity chromatography Storage and Handling This product is stable for at least 1 year at -20°C. Freeze in multiple aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Regulatory Status For in vitro investigational use only. Not for
use in therapeutic or diagnostic procedures. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunoblotting: use at 1-2ug/mL. A band of ~180kDa is detected. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity This antibody recognizes human, mouse,
and rat Copper-Transporting ATPase1. Background The copper efflux transporters ATP7A and ATP7B sequester intracellular copper into the vesicular secretory pathway for export from cells. ATP7A (also known as Copper-Transporting ATPase1) functions as a transmembrane copper-translocating P-type ATPase and plays a vital role in systemic copper absorption in the gut and copper reabsorption in the kidney. Although ATP7A is not detectable in most normal tissues, it is expressed in many common tumor types. Increased expression of ATP7A renders tumor cells resistant to cisplatin and carboplatin. Function ATP-driven copper (Cu(+)) ion pump that plays an important role in intracellular copper ion homeostasis (PubMed:10419525, PubMed:11092760, PubMed:28389643). Within a catalytic cycle, acquires Cu(+) ion from donor protein on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane and delivers it to acceptor protein on the lumenal side. The transfer of Cu(+) ion across the membrane is coupled to ATP hydrolysis and is associated with a transient phosphorylation that shifts the pump conformation from inward-facing to outward-facing state (PubMed:10419525, PubMed:19453293, PubMed:19917612, PubMed:31283225, PubMed:28389643). Under physiological conditions, at low cytosolic copper concentration, it is localized at the trans-Golgi network (TGN) where it transfers Cu(+) ions to cuproenzymes of the secretory pathway (PubMed:28389643, PubMed:11092760). Upon elevated cytosolic copper concentrations, it relocalizes to the plasma membrane where it is responsible for the export of excess Cu(+) ions (PubMed:10419525, PubMed:28389643). May play a dual role in neuron function and survival by regulating cooper efflux and neuronal transmission at the synapse as well as by supplying Cu(+) ions to enzymes such as PAM, TYR and SOD3 (PubMed:28389643) (By similarity). In the melanosomes of pigmented cells, provides copper cofactor to TYR to form an active TYR holoenzyme for melanin biosynthesis (By similarity). {UniProtKB:Q64430, PubMed:10419525, PubMed:11092760, PubMed:19453293, PubMed:19917612, PubMed:28389643, PubMed:31283225}. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Neuroscience References & CitationsTechnical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |


