Anti-Human EGFR (Necitumumab) [Clone IMC-11F8]
Anti-Human EGFR (Necitumumab) [Clone IMC-11F8]
Product No.: LT610
Product No.LT610 Clone IMC-11F8 Target EGFR Product Type Biosimilar Recombinant Human Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names Epidermal growth factor receptor, ErbB1, Anti-Human EGFR, 906805-06-9, IMC-11F8 Isotype Human IgG1κ Applications ELISA , FA , FC , IP , WB |
Data
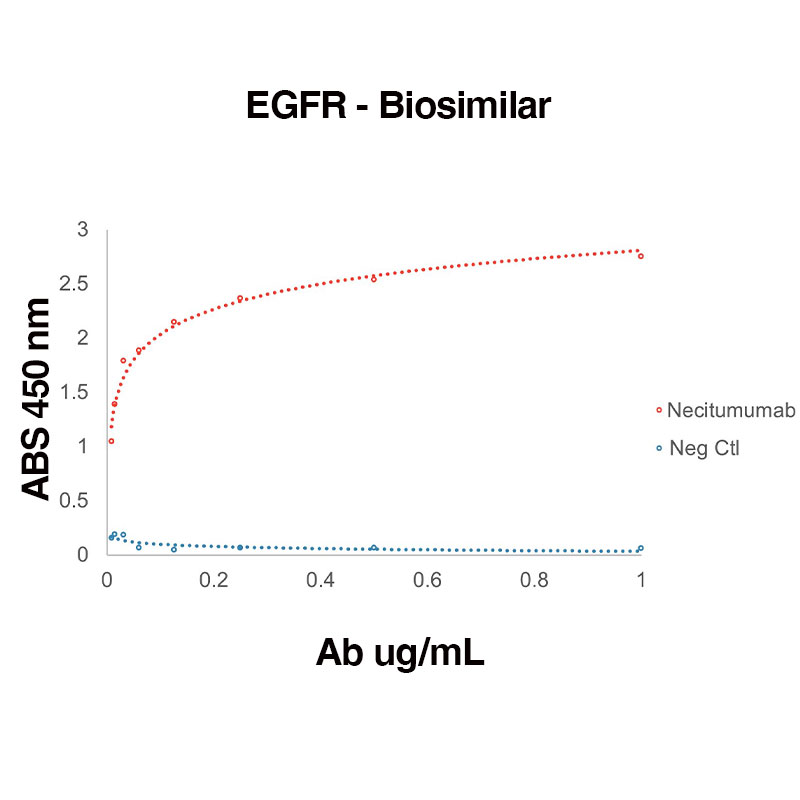 Direct binding of Human Recombinant EGFR (Leinco Prod. No.: E309) to anti-Human EGFR Necitumumab (Leinco Prod. No.: LT610)
Direct binding of Human Recombinant EGFR (Leinco Prod. No.: E309) to anti-Human EGFR Necitumumab (Leinco Prod. No.: LT610)
Binding was measured by ELISA. Recombinant Human EGFR was immobilized at 1 µg/mL. Necitumumab antibody was titrated.
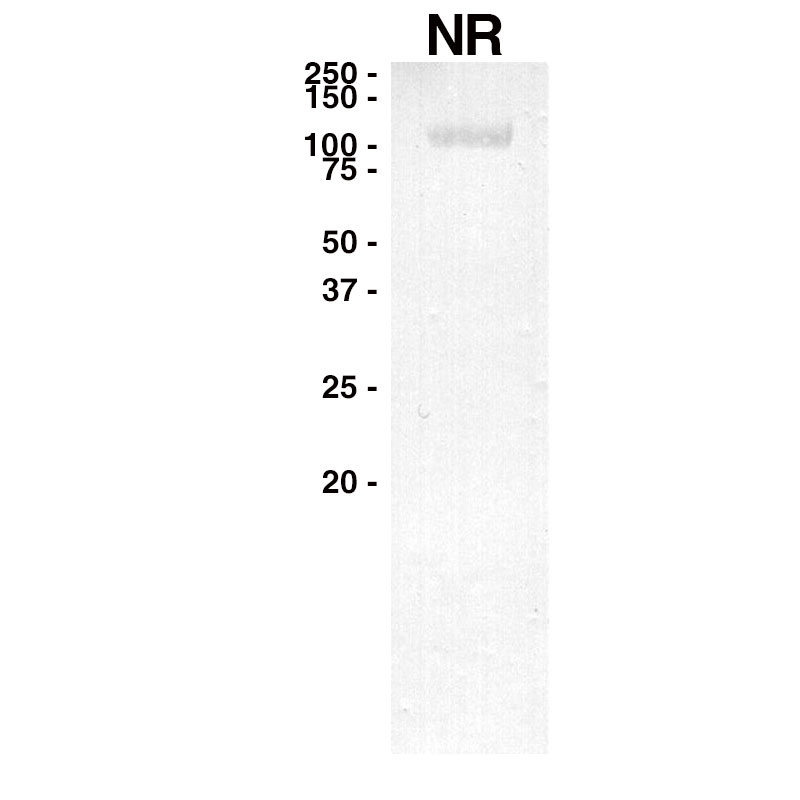 WESTERN
WESTERN
Purified recombinant human EGFR (Leinco Prod. No.: E309) was separated on SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions and probed with Necitumumab (Leinco Prod. No.: LT610).
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Human Host Species Human Expression Host HEK-293 Cells FC Effector Activity Active Immunogen Human EGFR/ErbB1 Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level < 1.0 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥95% by SDS Page ⋅ ≥95% monomer by analytical SEC Formulation This biosimilar antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Recombinant biosimilar antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using only in vitro protein free cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Pathogen Testing To protect mouse colonies from infection by pathogens and to assure that experimental preclinical data is not affected by such pathogens, all of Leinco’s recombinant biosimilar antibodies are tested and guaranteed to be negative for all pathogens in the IDEXX IMPACT I Mouse Profile. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Regulatory Status Research Use Only (RUO). Non-Therapeutic. Country of Origin USA Shipping 2-8°C Wet Ice Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco FA, ELISA, WB Additional Applications Reported In Literature ? FC, IP, Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity This non-therapeutic biosimilar antibody uses the same variable region sequence as the therapeutic antibody Necitumumab. This product is for research use only. Necitumumab activity is directed against human EGFR. Background Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR, also known as ErbB1 or HER-1) belongs to the receptor tyrosine kinase superfamily and is a transmembrane glycoprotein that activates various signaling pathways fundamental to cellular proliferation, differentiation, and survival1, 2. EGFR plays important roles during embryogenesis, organogenesis, and in the growth, differentiation, maintenance, and repair of adult tissues2, including autophagy3. EGFR is also a host factor that facilitates viral entry for hepatitis B4, hepatitis C5, and gastroenteritis6 and plays a role in SARS-CoV-2 infection7, 8, 9. Dysregulation, somatic mutation, and/or altered signaling of EGFR are associated with disease (Parkinson’s2, Alzheimer’s1,2, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis2) and various cancers (lung, glioblastoma, brain, breast, colorectal, ovarian)3. Additionally, in cancer, aberrant activation of EGFR is associated with increased cell proliferation, invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, and decreased apoptosis10. As such, EGFR is the target of multiple cancer therapies, including monoclonal humanized antibodies, such as necitumumab, as well as selective small molecule inhibitors.
Necitumumab inhibits EGFR-dependent tumor cell proliferation and metastasis11 by acting as an EGFR antagonist that binds specifically and with high affinity to human EGFR, thereby blocking ligand binding and neutralizing ligand-induced EGFR phosphorylation and downstream signaling pathways10, 11, 12. Anti-tumor activity has been demonstrated in vitro and in vivo 10, and necitumumab is FDA approved for treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic EGFR-expressing squamous non-small cell lung cancer11. In vitro studies have shown that necitumumab induces internationalization and degradation of EGFR, leading to antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in EGFR-expressing cells10, 11. Necitumumab was generated from the Dyax Corp proprietary phage display library by ImClone Systems, a wholly owned subsidiary of Eli Lilly10. Antigen Distribution EGFR is overexpressed on the cell surfaces of various tumor cell types and is also found in the plasma membranes, cytoplasm, and cell junctions of many healthy tissues, including those associated with the Skin – Epidermis development cluster of The Human Protein Atlas. EGFR is also found in the blood secretome. Ligand/Receptor Epidermal growth factor receptor PubMed NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Biosimilars . Cancer . Cell Biology . Immuno-Oncology . Immunology Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Research-grade Necitumumab biosimilars can be used as calibration standards or reference controls in pharmacokinetic (PK) bridging ELISA assays to quantitatively measure drug concentrations in serum samples. In a PK bridging ELISA for biosimilar development:
Essential context and key steps:
In summary, research-grade Necitumumab biosimilars serve as highly characterized calibration standards and reference controls in PK bridging ELISA assays, enabling precise and equivalent quantification of drug concentrations for clinical and nonclinical bioequivalence studies. Primary Models for Studying Anti-EGFR Antibodies and Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes (TILs) To study the effects of anti-EGFR antibodies on tumor growth inhibition and characterize TILs, researchers often employ syngeneic or humanized mouse models. Here are the primary models used: 1. Murine Syngeneic Models
2. Humanized Mouse Models
3. Specific Example: Athymic (Nude) Mice with Xenografts
Characterizing TILsIn both syngeneic and humanized models, researchers can analyze TILs to understand how anti-EGFR therapies affect the tumor microenvironment. This includes examining the types and functions of immune cells present in the tumor, such as T cells and macrophages, which can provide insights into how these therapies modulate immune responses against tumors. Based on the available search results, there is limited specific information about researchers using necitumumab biosimilars in conjunction with other checkpoint inhibitors to study synergistic effects. However, I can provide insights into the current research landscape and methodological approaches being explored in this area. Current State of Necitumumab ResearchNecitumumab is an anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody that has been established as a standard therapy component for advanced lung squamous cell carcinoma when combined with gemcitabine and cisplatin. The drug works by binding to EGFR with high affinity and blocking signal transmission, inhibiting tumor growth. Clinical studies like the international SQUIRE trial and the Japanese JFCM study have demonstrated significant improvements in overall survival when necitumumab is added to chemotherapy regimens. Combination Immunotherapy StrategiesThe field of immune-oncology is actively exploring combination strategies that target multiple immune checkpoints simultaneously. The rationale behind combining different checkpoint inhibitors stems from their distinct mechanisms of action - for example, anti-CTLA-4 agents primarily act in lymph node compartments to restore T cell activation and proliferation, while anti-PD-1/PD-L1 agents work at the tumor periphery to prevent cytotoxic T cell neutralization. Research Methodologies for Studying Synergistic EffectsResearchers are employing several approaches to study combination effects: Preclinical Models: Multiple preclinical studies are investigating combinations of immune checkpoint inhibitors with various therapeutic agents. These models help establish the mechanistic basis for beneficial therapeutic interactions before advancing to clinical trials. Clinical Trial Designs: Early-phase clinical studies are being conducted to evaluate combination strategies. For instance, there are ongoing phase Ib/II trials examining necitumumab in combination with other targeted therapies like trastuzumab and osimertinib for EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Real-World Evidence Studies: Researchers are conducting multicenter retrospective studies to assess the efficacy and tolerability of combination regimens in real-world settings, particularly examining how treatments perform after patients have received prior immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Challenges and ConsiderationsThe major limitation of combination immunotherapy approaches is the increased risk of grade 3 or grade 4 toxicities. This necessitates careful dose optimization and patient selection strategies. Additionally, the efficacy of combination approaches may vary based on biomarker status - for example, patients with PD-L1-negative tumors may benefit more from combination therapy than those with PD-L1-positive tumors. While the search results do not provide specific details about necitumumab biosimilar combinations with anti-CTLA-4 or anti-LAG-3 inhibitors, the general approach to studying such combinations would likely involve preclinical immune-oncology models followed by carefully designed early-phase clinical trials with appropriate safety monitoring and biomarker-driven patient selection strategies. A Necitumumab biosimilar can be used as a reagent in a bridging anti-drug antibody (ADA) ELISA to detect patient immune responses (ADAs) against Necitumumab or its biosimilar by exploiting the antibody’s ability to "bridge" two forms of the drug: one immobilized on the plate (capture) and one labeled for detection. Context and Explanation:
Summary Table: Necitumumab Biosimilar in Bridging ADA ELISA
Key Point: If you need specific labeling or procedural details for a particular platform or regulatory guidance, please clarify, as protocols may vary depending on assay design and regulatory requirements. References & Citations1. Jayaswamy PK, Vijaykrishnaraj M, Patil P, et al. Ageing Res Rev. 83:101791. 2023.
2. Romano R, Bucci C. Cells. 9(8):1887. 2020. 3. Sigismund S, Avanzato D, Lanzetti L. Mol Oncol. 12(1):3-20. 2018. 4. Iwamoto M, Saso W, Sugiyama R, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 116(17):8487-8492. 2019. 5. Lupberger J, Zeisel MB, Xiao F, et al. Nat Med. 17(5):589-595. 2011. 6. Hu W, Zhang S, Shen Y, et al. Virology. 521:33-43. 2018. 7. Klann K, Bojkova D, Tascher G, et al. Mol Cell. 80(1):164-174.e4. 2020. 8. Xu G, Li Y, Zhang S, et al. Cell Res. 31(12):1230-1243. 2021. 9. Wang S, Qiu Z, Hou Y, et al. Cell Res. 31(2):126-140. 2021. 10. Garnock-Jones KP. Drugs. 76(2):283-289. 2016. 11. Fala L. Am Health Drug Benefits. 9(Spec Feature):119-122. 2016. 12. https://www.cancer.gov/publications/dictionaries/cancer-drug/def/necitumumab?redirect=true Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Formats Available
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
LT610 | |
LT615 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.


