Anti-KCNQ1 K+ Channel Antibody (11510)
Anti-KCNQ1 K+ Channel Antibody (11510)
Product No.: 11510
- -
- -
Clone S37A-10 Target KCNQ1 K+ Channel Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Alternate Names IKs producing slow voltage-gated potassium channel subunitα KvLQT1, KQT-like 1, Voltage-gated potassium channel subunit Kv7.1 Isotype Mouse IgG1 Applications ICC , IF , IHC , IP , WB , AM |
Data
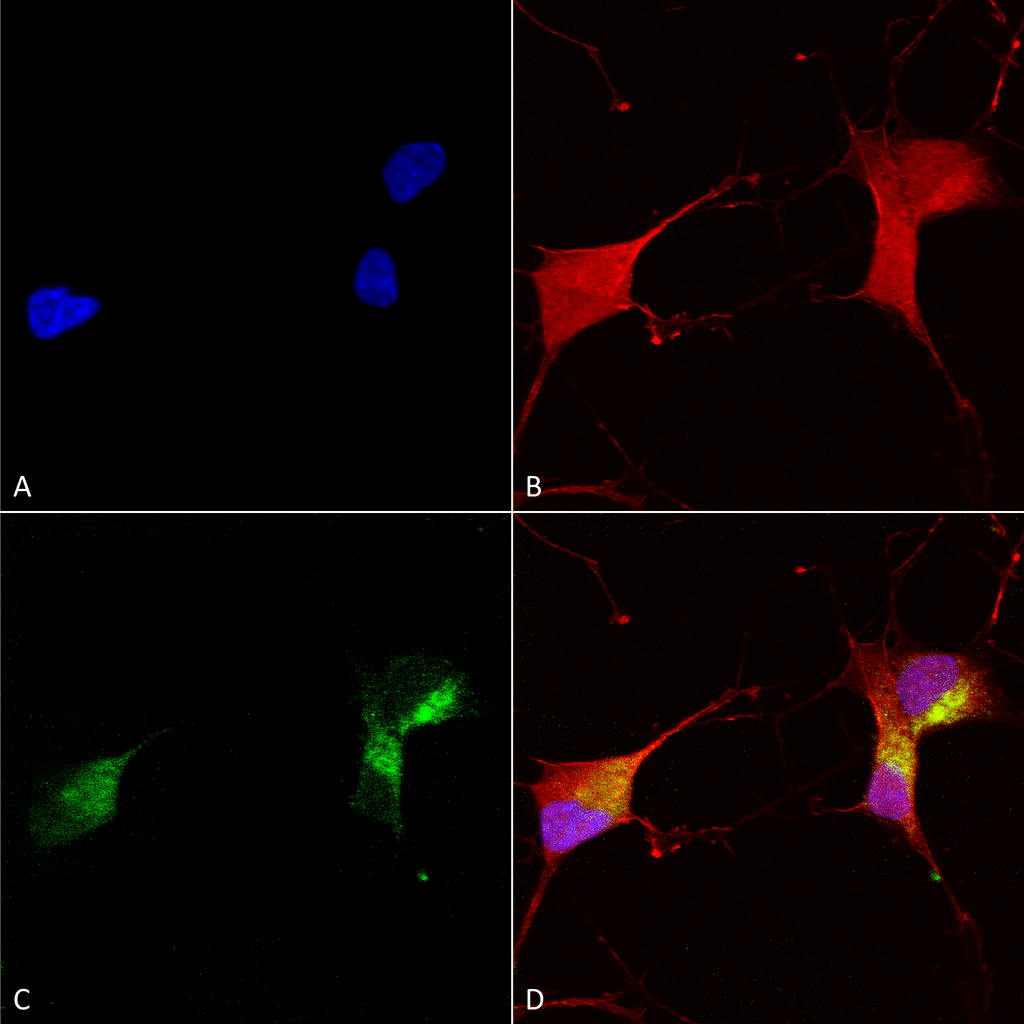 Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone N37A/10 (11510). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% PFA for 15 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody (11510) at 1:100 for overnight at 4°C with slow rocking. Secondary Antibody: AlexaFluor 488 at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain; Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain at 1:800, 1.6mM for 20 min at RT. (A) Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain. (C) KCNQ1 Antibody (D) Composite.
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone N37A/10 (11510). Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 4% PFA for 15 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody (11510) at 1:100 for overnight at 4°C with slow rocking. Secondary Antibody: AlexaFluor 488 at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain; Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain at 1:800, 1.6mM for 20 min at RT. (A) Hoechst (blue) nuclear stain. (B) Phalloidin-iFluor 647 (red) F-Actin stain. (C) KCNQ1 Antibody (D) Composite.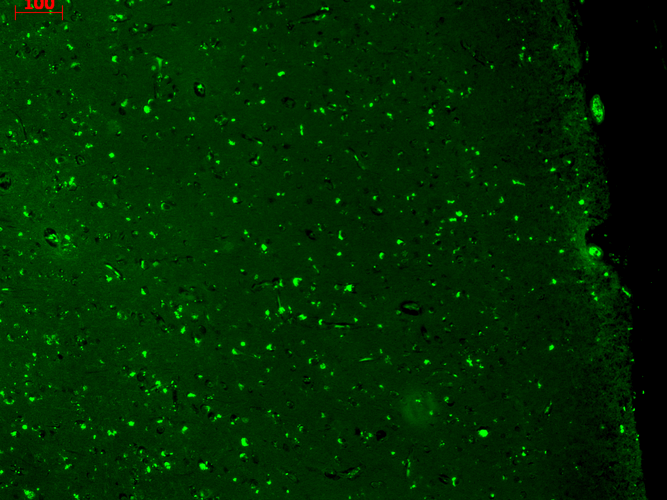 Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone N37A/10 (11510). Tissue: hippocampus. Species: Human. Fixation: Bouin’s Fixative and paraffin-embedded. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody (11510) at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Secondary Antibody: FITC Goat Anti-Mouse (green) at 1:50 for 1 hour at RT.
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone N37A/10 (11510). Tissue: hippocampus. Species: Human. Fixation: Bouin’s Fixative and paraffin-embedded. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody (11510) at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Secondary Antibody: FITC Goat Anti-Mouse (green) at 1:50 for 1 hour at RT. Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone N37A/10 (11510). Tissue: Brain Slice. Species: Mouse. Fixation: 10% Formalin Solution for 12-24 hours at RT. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody (11510) at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Secondary Antibody: HRP/DAB Detection System: Biotinylated Goat Anti-Mouse, Streptavidin Peroxidase, DAB Chromogen (brown) for 30 minutes at RT. Counterstain: Mayer Hematoxylin (purple/blue) nuclear stain at 250-500 µl for 5 minutes at RT.
Immunohistochemistry analysis using Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone N37A/10 (11510). Tissue: Brain Slice. Species: Mouse. Fixation: 10% Formalin Solution for 12-24 hours at RT. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody (11510) at 1:1000 for 1 hour at RT. Secondary Antibody: HRP/DAB Detection System: Biotinylated Goat Anti-Mouse, Streptavidin Peroxidase, DAB Chromogen (brown) for 30 minutes at RT. Counterstain: Mayer Hematoxylin (purple/blue) nuclear stain at 250-500 µl for 5 minutes at RT.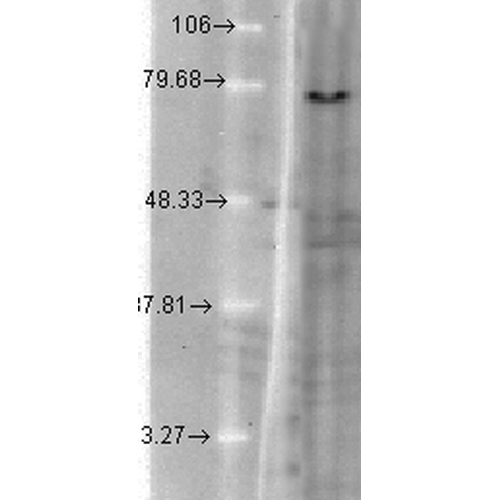 Western Blot analysis of Hamster T-CHO cell lysate showing detection of KCNQ1 protein using Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone N37A/10 (11510). Load: 15 µg. Block: 1.5% BSA for 30 minutes at RT. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody (11510) at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Sheep Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP for 1 hour at RT.
Western Blot analysis of Hamster T-CHO cell lysate showing detection of KCNQ1 protein using Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody, Clone N37A/10 (11510). Load: 15 µg. Block: 1.5% BSA for 30 minutes at RT. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-KCNQ1 Monoclonal Antibody (11510) at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Sheep Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP for 1 hour at RT. - -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactivity Species Human ⋅ Mouse ⋅ Rat Host Species Mouse Immunogen Fusion protein aa 2-101 of human KCNQ1 (K+7.1, KvLQT1, accession number P51787). Product Concentration 1.0 mg/ml Formulation PBS, pH 7.4, 50% glycerol, 0.09% sodium azide. State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Purified by Protein G affinity chromatography Storage and Handling This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Regulatory Status For in vitro investigational use only. Not for use in therapeutic or diagnostic procedures. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Immunoblotting: use at 1-10ug/mL. A band of ~75kDa is detected.Immunohistochemistry and
Immunocytochemistry: use at 0.1-1ug/mL. These are recommended concentrations; Enduser should determine optimal concentrations for their applications. Positive control: COS cell lysate transiently expressing KCNQ1. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionSpecificity This antibody recognizes human, mouse and rat KCNQ1. Background Ion channels are integral membrane proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of living cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient. –+7.1 (KvLQT1) is a potassium channel protein coded for by the gene KCNQ1. K+7.1 is present in cell membranes of cardiac muscle tissue and in inner ear neurons among other tissues. In cardiac cells, K+7.1 mediates the I. (or slow delayed rectifying K3) current that contributes to repolarization of the cell, terminating the cardiac potential and, thereby, the heart's contractions. Antigen DetailsFunction Potassium channel that plays an important role in a number of tissues, including heart, inner ear, stomach and colon (PubMed:10646604, PubMed:25441029). Associates with KCNE beta subunits that modulates current kinetics (PubMed:9312006, PubMed:9108097, PubMed:8900283, PubMed:10646604, PubMed:11101505, PubMed:19687231). Induces a voltage-dependent current by rapidly activating and slowly deactivating potassium-selective outward current (PubMed:9312006, PubMed:9108097, PubMed:8900283, PubMed:10646604, PubMed:11101505, PubMed:25441029). Promotes also a delayed voltage activated potassium current showing outward rectification characteristic (By similarity). During beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation participates in cardiac repolarization by associating with KCNE1 to form the I(Ks) cardiac potassium current that increases the amplitude and slows down the activation kinetics of outward potassium current I(Ks) (By similarity) (PubMed:9312006, PubMed:9108097, PubMed:8900283, PubMed:10646604, PubMed:11101505). Muscarinic agonist oxotremorine-M strongly suppresses KCNQ1/KCNE1 current (PubMed:10713961). When associated with KCNE3, forms the potassium channel that is important for cyclic AMP-stimulated intestinal secretion of chloride ions (PubMed:10646604). This interaction with KCNE3 is reduced by 17beta-estradiol, resulting in the reduction of currents (By similarity). During conditions of increased substrate load, maintains the driving force for proximal tubular and intestinal sodium ions absorption, gastric acid secretion, and cAMP-induced jejunal chloride ions secretion (By similarity). Allows the provision of potassium ions to the luminal membrane of the secretory canaliculus in the resting state as well as during stimulated acid secretion (By similarity). When associated with KCNE2, forms a heterooligomer complex leading to currents with an apparently instantaneous activation, a rapid deactivation process and a linear current-voltage relationship and decreases the amplitude of the outward current (PubMed:11101505). When associated with KCNE4, inhibits voltage-gated potassium channel activity (PubMed:19687231). When associated with KCNE5, this complex only conducts current upon strong and continued depolarization (PubMed:12324418). Also forms a heterotetramer with KCNQ5; has a voltage-gated potassium channel activity (PubMed:24855057). Binds with phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PubMed:25037568). {UniProtKB:P97414, UniProtKB:Q9Z0N7, PubMed:10646604, PubMed:10713961, PubMed:11101505, PubMed:12324418, PubMed:19687231, PubMed:24855057, PubMed:25037568, PubMed:8900283, PubMed:9108097, PubMed:9312006}.; [Isoform 2]: Non-functional alone but modulatory when coexpressed with the full-length isoform 1. {PubMed:9305853}. NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Ion Channels References & CitationsTechnical Protocols |


