Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (56610)
Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Mouse Monoclonal Antibody (56610)
Product No.: 56610
- -
- -
Clone 5E8 Target Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Alternate Names Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct, HEL (Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct), HEL, HEL Adduct, Hexanoyl-Lys adduct, Hexanoyl-Lys, Hexanoyl-Lysine (HEL) adduct, Hexanoyl-Lys (HEL), Hexanoyl Lysine adduct, Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct-modified protein, Hexanoyl-Lysine Adduct (HEL) Isotype Mouse IgG1 Applications ELISA , FACS , ICC , IF , WB , FCM |
Data
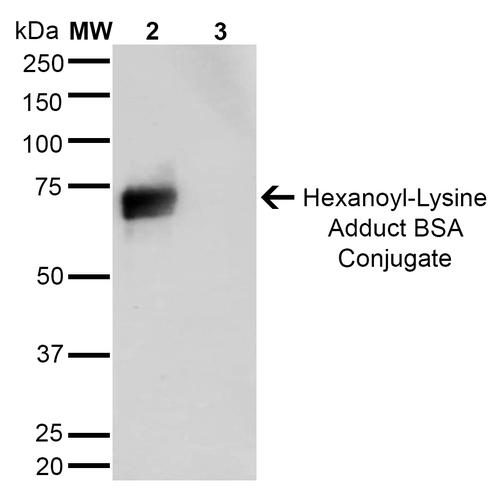 Western Blot analysis of Hexanoyl Lysine-BSA Conjugate showing detection of 67 kDa Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct protein using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5E8 . Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder (MW). Lane 2: Hexanoyl Lysine-BSA. Lane 3: BSA. Load: 0.5 µg. Block: 5% Skim Milk in TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP at 1:2000 for 60 min at RT. Color Development: ECL solution for 5 min in RT. Predicted/Observed Size: 67 kDa.
Western Blot analysis of Hexanoyl Lysine-BSA Conjugate showing detection of 67 kDa Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct protein using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5E8 . Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder (MW). Lane 2: Hexanoyl Lysine-BSA. Lane 3: BSA. Load: 0.5 µg. Block: 5% Skim Milk in TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP at 1:2000 for 60 min at RT. Color Development: ECL solution for 5 min in RT. Predicted/Observed Size: 67 kDa.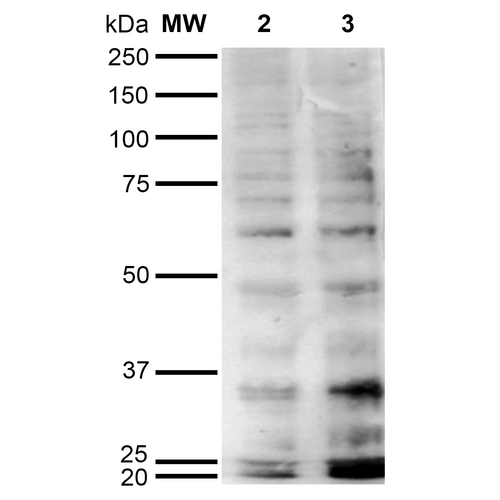 Western Blot analysis of Human Cervical cancer cell line (HeLa) lysate showing detection of Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct protein using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5E8 . Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder (MW). Lane 2: HeLa cell lysate. Lane 3: H2O2 treated HeLa cell lysate. Load: 12 µg. Block: 5% Skim Milk in TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP at 1:2000 for 60 min at RT. Color Development: ECL solution for 5 min in RT.
Western Blot analysis of Human Cervical cancer cell line (HeLa) lysate showing detection of Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct protein using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5E8 . Lane 1: Molecular Weight Ladder (MW). Lane 2: HeLa cell lysate. Lane 3: H2O2 treated HeLa cell lysate. Load: 12 µg. Block: 5% Skim Milk in TBST. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody at 1:1000 for 2 hours at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse IgG: HRP at 1:2000 for 60 min at RT. Color Development: ECL solution for 5 min in RT.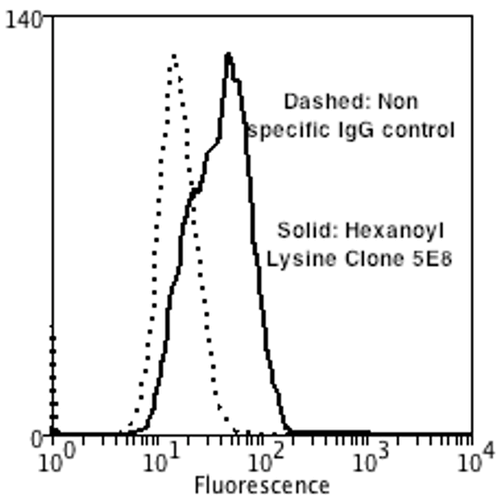 Flow Cytometry analysis using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5E8 . Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 90% Methanol. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody at 1:50 for 30 min on ice. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse: PE at 1:100 for 20 min at RT. Isotype Control: Non Specific IgG.
Flow Cytometry analysis using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5E8 . Tissue: Neuroblastoma cells (SH-SY5Y). Species: Human. Fixation: 90% Methanol. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody at 1:50 for 30 min on ice. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse: PE at 1:100 for 20 min at RT. Isotype Control: Non Specific IgG.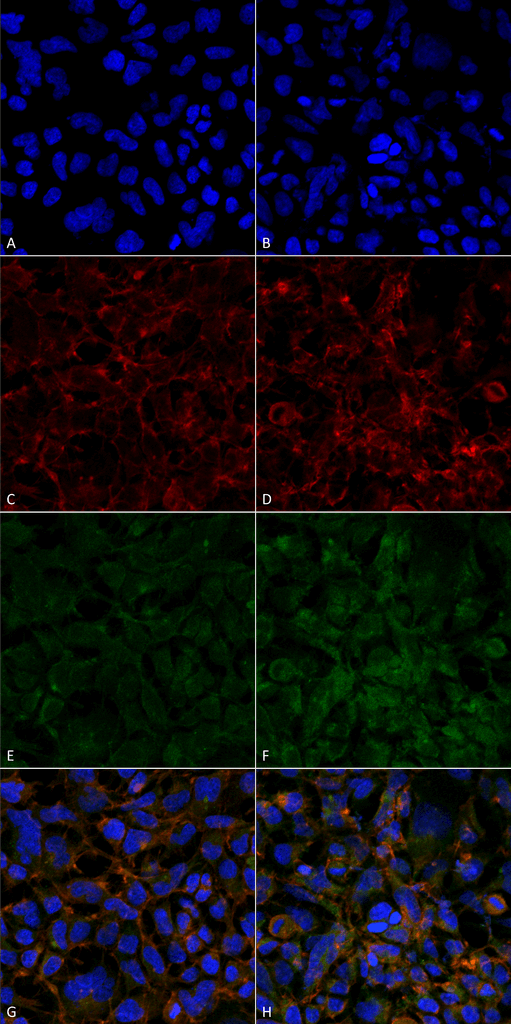 Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5E8 . Tissue: Embryonic kidney epithelial cell line (HEK293). Species: Human. Fixation: 5% Formaldehyde for 5 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody at 1:50 for 30-60 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse Alexa Fluor 488 at 1:1500 for 30-60 min at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin Alexa Fluor 633 F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:250, 1:50000 for 30-60 min at RT. Magnification: 20X (2X Zoom). (A,C,E,G) – Untreated. (B,D,F,H) – Cells cultured overnight with 50 µM H2O2. (A,B) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (C,D) Phalloidin Alexa Fluor 633 F-Actin stain. (E,F) Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Antibody. (G,H) Composite. Courtesy of: Dr. Robert Burke, University of Victoria.
Immunocytochemistry/Immunofluorescence analysis using Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody, Clone 5E8 . Tissue: Embryonic kidney epithelial cell line (HEK293). Species: Human. Fixation: 5% Formaldehyde for 5 min. Primary Antibody: Mouse Anti-Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Monoclonal Antibody at 1:50 for 30-60 min at RT. Secondary Antibody: Goat Anti-Mouse Alexa Fluor 488 at 1:1500 for 30-60 min at RT. Counterstain: Phalloidin Alexa Fluor 633 F-Actin stain; DAPI (blue) nuclear stain at 1:250, 1:50000 for 30-60 min at RT. Magnification: 20X (2X Zoom). (A,C,E,G) – Untreated. (B,D,F,H) – Cells cultured overnight with 50 µM H2O2. (A,B) DAPI (blue) nuclear stain. (C,D) Phalloidin Alexa Fluor 633 F-Actin stain. (E,F) Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct Antibody. (G,H) Composite. Courtesy of: Dr. Robert Burke, University of Victoria. - -
- -
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactivity Species Species Independent Host Species Mouse Immunogen Synthetic Hexanoyl modified Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KLH). Product Concentration 1 mg/mL Formulation PBS pH 7.4, 50% glycerol, 0.09% Sodium azide State of Matter Liquid Product Preparation Protein G Purified Storage and Handling This antibody is stable for at least one (1) year at -20°C. Avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Regulatory Status Research Use Only Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco WB (1:1000); ICC/IF (1:50); ELISA (1:1000); FACS (1:50); FCM (1:50); Optimal dilutions for assays should be determined by the user. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionSpecificity Specific for Hexanoyl-Lysine adduct (HEL) modified peptides and proteins. Does not detect free Hexanoyl-Lysine. Does not cross-react with Acrolein, Crotonaldehyde, 4-Hydroxy-2-hexenal, 4-Hydroxy nonenal, Malondialdehyde, or Methylglyoxal modified proteins. Background Hexanoyl-lysine adduct (HEL) is a lysine adduct of 13-HPODE and is produced by the oxidation of omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids (1). It is a biomarker for the initial stage of lipid peroxidation. Lipid peroxidation end-products have been found to damage cell viability through their mutagenic and toxic properties. These downstream functional consequences facilitate the development of disease and premature aging. Antigen DetailsResearch Area Cancer . Lipid peroxidation . Oxidative Stress References & CitationsTechnical Protocols |


