Anti-Mouse CTLA-4 [Clone 9D9] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse CTLA-4 [Clone 9D9] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Product No.: C2855
Clone 9D9 Target CTLA-4 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names CD152, Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte-Associated Antigen-4, Ly-56 Isotype Mouse IgG2b Applications FA , in vivo , WB |
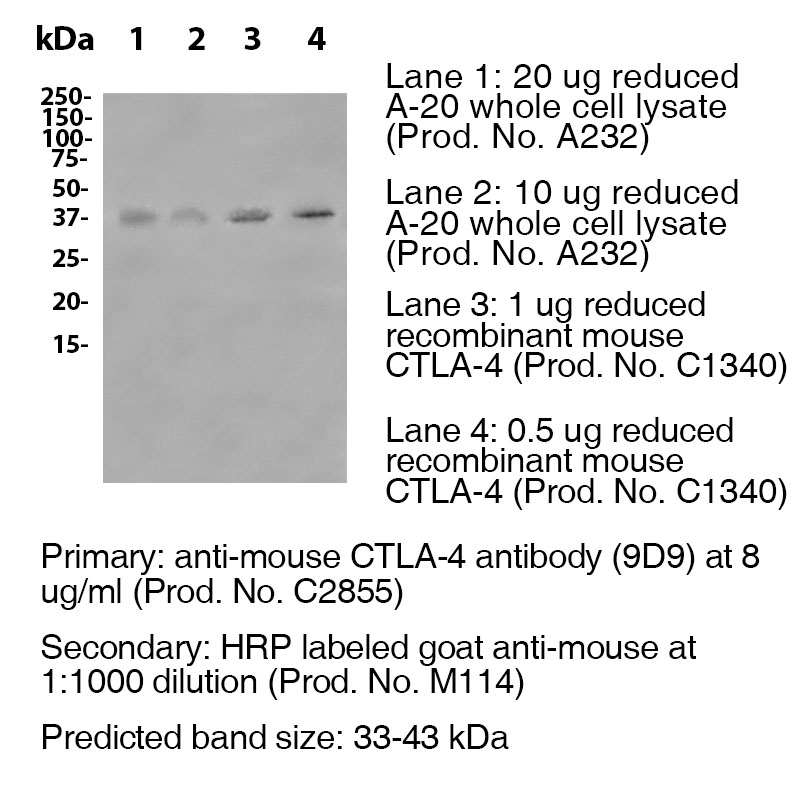
Data
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Mouse Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Dilution Buffer Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level < 1.0 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥95% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2737474 Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Clone 9D9 recognizes an epitope on mouse CTLA-4. Background CTLA-4 is a 33 kD member of the Ig superfamily similar to CD28 in amino acid sequence, structure, and genomic organization. CTLA-4 is a protein receptor that functions as an immune checkpoint and downregulates immune responses. It is involved in the development of protective immunity and thymocyte regulation, in addition to the induction and maintenance of immunological tolerance. CTLA-4 has therapeutic potential both as an agonist to reduce immune activity, and an antagonist to increase immune activity. Antigen Distribution CTLA-4 is expressed on activated T and B lymphocytes. Ligand/Receptor CD80 (B7.1), CD86 (B7.2) NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Immunology . Inhibitory Molecules Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Clone 9D9, a monoclonal antibody targeting mouse CTLA-4 (CD152), is commonly used in in vivo applications for cancer immunotherapy research in mice. Here are some of its primary applications:
For in vivo studies, clone 9D9 is typically administered via intraperitoneal injection, with a recommended dose range of 100-250 μg per mouse, and dosing is usually performed every 3 days. In the literature, 9D9, a monoclonal antibody specific to mouse CTLA-4, is often used alone for CTLA-4 checkpoint blockade studies. However, it is compared or mentioned alongside other CTLA-4 targeting antibodies, such as:
For broader immune checkpoint studies, while not specifically paired with 9D9, other antibodies targeting different pathways, such as PD-1/PD-L1, are commonly used in cancer immunotherapy research. There is limited direct mention of other specific antibodies or proteins used in combination with 9D9 in the literature, but it is often used as a surrogate in mouse models to study CTLA-4 blockade mechanisms. Clone 9D9, an anti-mouse CTLA-4 antibody, has emerged as a pivotal tool in cancer immunotherapy research, with scientific literature revealing its multifaceted mechanisms and therapeutic potential. This antibody operates through dual mechanisms that distinguish it from other CTLA-4-targeting agents, making it particularly valuable for preclinical studies. Dual Mechanism of ActionClone 9D9 functions through two primary mechanisms that work synergistically to enhance anti-tumor immunity. The antibody blocks CTLA-4, a negative regulator of T cell activation, while simultaneously depleting intratumoral regulatory T cells (Tregs). This dual action sets it apart from other anti-CTLA-4 clones and contributes to its robust therapeutic efficacy. The CTLA-4 blockade component works by preventing negative signaling and reducing B7 transendocytosis, which enhances T cell priming in tumor-draining lymph nodes. Within just 3 days of treatment, 9D9 increases the percentage of CD4+ and CD8+ effector T cells expressing proliferation marker Ki67 and activation marker PD-1 in these lymph nodes. Impact on Tumor MicroenvironmentStudies demonstrate that 9D9 profoundly alters the tumor microenvironment in ways that favor anti-tumor immunity. The antibody increases global lymphocyte infiltration (CD3+ cells) as well as CD8+ T cell infiltration specifically. These infiltrating CD8+ T cells display heightened activation, expressing elevated levels of CD44, CD69, and PD1. Critically, tumors treated with 9D9 exhibit a significantly lower proportion of regulatory T cells (CD4+/CD25+/FoxP3+), reflecting the antibody's Treg-depleting capacity. This reduction in immunosuppressive Tregs within the tumor creates a more permissive environment for effector T cell function. Therapeutic EfficacyThe therapeutic potential of 9D9 has been validated across multiple tumor models and treatment settings. In the CT26 tumor model, 9D9 demonstrated effectiveness in a therapeutic setting when administration began 3 days after tumor implantation, inducing tumor clearance in 8 out of 10 mice. The antibody has proven versatile across different mouse strains and tumor types, consistently showing tumor regression capabilities. However, research indicates that both CTLA-4 antagonism and intratumoral Treg depletion are essential for maximum efficacy. Studies comparing 9D9 to modified versions with silenced Fc regions revealed that antagonism alone is insufficient—the Fc-silenced version resulted in survival similar to control mice. Conversely, constructs that depleted Tregs but lacked antagonistic properties also proved less effective than wild-type 9D9, with only the full 9D9 showing signs of enhanced T cell activation. Limitations and Treg ExpansionDespite its efficacy, 9D9 cured less than 50% of mice in some studies, a limitation attributed to nonspecific T cell priming in tumor-draining lymph nodes. An important consequence of CTLA-4 antagonism is that nodal Tregs, which express lower levels of CTLA-4 than intratumoral Tregs, experience enhanced costimulation and subsequent expansion rather than depletion. This proliferative Treg response may allow immunosuppressive functions to dominate the anti-tumor immune response, potentially limiting overall therapeutic benefit. DNA-Encoded Antibody PlatformRecent innovations have explored delivering 9D9 through synthetic DNA-encoded monoclonal antibodies (DMAbs). Initial designs produced relatively low antibody levels (~660ng/mL in vitro and ~1.2μg/mL in serum), but framework modifications improved expression nearly 10-fold without altering binding to mouse CTLA-4 protein. The optimized DMAb version (mod #4) achieved serum levels of approximately 7.9μg/mL, representing over 6-fold improvement while maintaining similar IC50 values (36.105–44.25ng/mL) compared to recombinant 9D9. These findings establish clone 9D9 as a cornerstone tool in mouse cancer immunotherapy research, valued for its ability to simultaneously block CTLA-4 signaling and deplete intratumoral Tregs, though its therapeutic ceiling remains constrained by nodal Treg expansion dynamics. Dosing regimens of clone 9D9 in mouse models generally use 100–250 μg per mouse, administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) every 3 days, but can vary depending on the specific study design, application, and sometimes route of administration. Key points on variation across different mouse models:
Summary Table: Clone 9D9 Dosing Regimens in Mouse Models
In summary: While the core regimen for clone 9D9 across mouse models remains 100–250 μg i.p. every 3 days, model-specific adjustments (e.g., route, formulation, or frequency) are made based on experimental needs, such as pharmacokinetic profiling, gene delivery, or combination immunotherapy. References & CitationsTechnical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
S211 | |
R1364 | |
I-119 | |
M1188 | |
C247 | |
F1175 | |
S571 |
Formats Available
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.