Anti-Mouse IFNγ [Clone H22] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse IFNγ [Clone H22] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade
Product No.: I-1190
Clone H22 Target IFNγ Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names Immune Interferon, Type II Interferon, T Cell Interferon, MAF, IFNG, IFG, IFNy Isotype IgG Applications ELISA , IF , in vivo , IP , N , WB |
Data
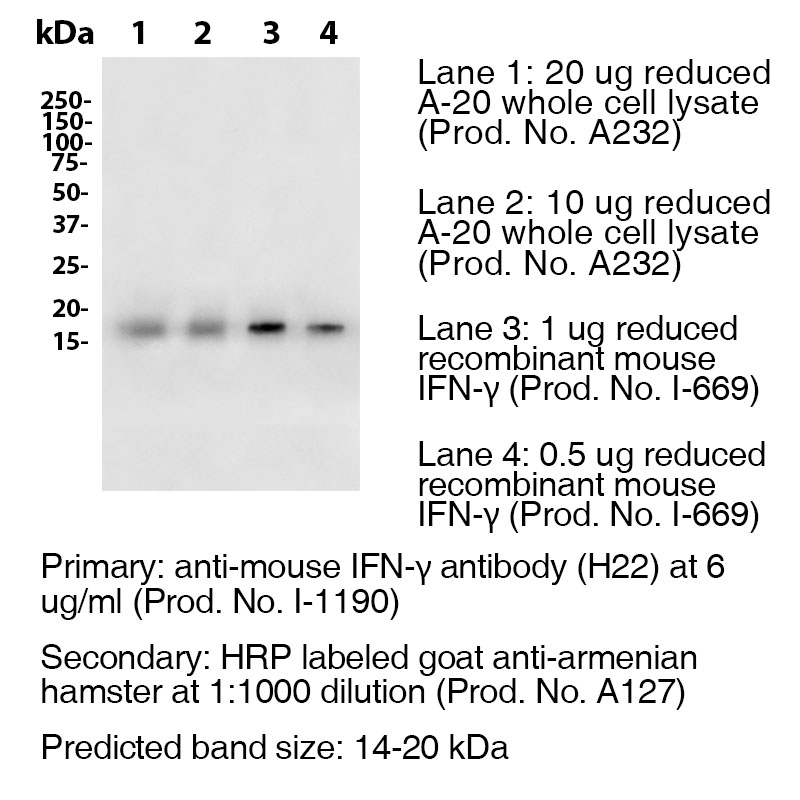
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Armenian Hamster Recommended Dilution Buffer Immunogen Purified Recombinant Mouse IFN-γ (>98%) Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level <0.5 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥98% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Pathogen Testing To protect mouse colonies from infection by pathogens and to assure that experimental preclinical data is not affected by such pathogens, all of Leinco’s Purified Functional PLATINUM™ antibodies are tested and guaranteed to be negative for all pathogens in the IDEXX IMPACT I Mouse Profile. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2830520 Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco WB The suggested concentration for this clone H22 antibody for use in western blotting is 0.5 μg/ml. Additional Applications Reported In Literature ? N ELISA IF IP For specific conjugates of this clone, review literature for suggested application details. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Armenian Hamster Anti-Mouse Interferon Gamma (IFN-γ) (Clone H22) recognizes an epitope on Mouse IFN-γ. This antibody was also pathogen tested and third-party certified by IDEXX BioReseach to meet the lowest mycoplasma specification and free of any viral pathogens of concern. Background Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) or type II interferon is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons.3 It is a cytokine critical for innate and adaptive immunity against viral and intracellular bacterial infections and for tumor control. IFNG is produced predominantly by natural killer (NK) and natural killer T (NKT) cells as part of the innate immune response, and by CD4 and CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) effector T cells once antigen-specific immunity develops.4 IFN-γ has antiviral, immunoregulatory, and anti-tumour properties.5 Ligand/Receptor IFN-γRα (CDw119) dimerized with IFN-γRβ (AF-1) NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Immunology . Other Molecules Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Clone H22 has distinct applications in mice, depending on its context:
In summary, clone H22 as a monoclonal antibody is used for immunological studies, while the H22 cell line is used in cancer research. Based on the literature, several commonly used antibodies and proteins are associated with H22, depending on the specific context: Anti-CD64 ApplicationsWhen H22 refers to the anti-CD64 antibody, it is frequently used alongside anti-TNF monoclonal antibodies such as infliximab and adalimumab. The H22(scFv) fragment specifically blocks CD64 (FcγRI) to prevent the capture of these anti-TNF therapeutics by immune cells. Additionally, anti-His tag antibodies and various cell surface markers are commonly employed with H22 in experimental settings. The bispecific antibody MDX-H210 represents another important application, where H22 is chemically crosslinked with mAb 520C9 (which targets HER-2/neu) to create a therapeutic construct that can trigger FcγRI-mediated cellular responses. Detection and Blocking StudiesIn CD64 research, anti-human CD64 clone 10.1 (FITC-labeled) is frequently used to measure CD64 blocking by H22(scFv). Researchers also utilize fusion constructs incorporating toxins or cell-penetrating peptides like 9R when working with H22-based therapeutics. Anti-IFNγ ContextWhen H22 refers to the anti-mouse IFNγ monoclonal antibody clone, it is primarily used in immunological assays including ELISA, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation applications for studying interferon-gamma in mouse models. The specific antibodies and proteins used with H22 ultimately depend on whether the reference is to the anti-CD64 antibody, the anti-IFNγ clone, or other H22 variants in the literature. The scientific literature reveals that "clone H22" refers to multiple distinct biological entities across different research contexts, each with significant findings in their respective fields. H22 Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell LineThe murine H22 hepatoma cell line serves as a widely used model in liver cancer research. Studies have demonstrated its utility in evaluating anti-tumor immune responses and angiogenesis inhibition. Research involving DNA vaccines targeting domains 1-3 of flk-1 (VEGFR-2) showed that these vaccines could induce immune responses capable of blocking H22 tumor growth in mice by inhibiting angiogenesis. Additionally, investigations into nm23 mRNA expression in H22 clones revealed associations between nm23 mRNA levels and metastatic potential in murine ascites hepatoma. H22 Anti-IFNγ Monoclonal AntibodyIn immunology research, clone H22 functions as a monoclonal antibody targeting interferon-gamma (IFNγ). This antibody has proven valuable in studies examining IFNγ function, which includes antiviral activity, tumor antiproliferative effects, induction of class I and II MHC molecules, and macrophage activation. The H22 clone enables researchers to neutralize or block IFNγ activity in experimental models, facilitating investigations into immune responses and inflammatory processes. H22(scFv) CD64-Blocking FragmentA recombinant single-chain variable fragment derived from the original murine mAb22, designated H22(scFv), demonstrates potent and specific blocking of CD64. This fragment prevents the capture of anti-TNF monoclonal antibodies by selectively binding to CD64 without inducing receptor activation or pro-inflammatory cytokine expression. The blocking effect correlates quantitatively with reduced anti-TNF mAb capture, with approximately 100 nM of H22(scFv) sufficient to block all CD64 molecules on cell surfaces. Importantly, H22(scFv) binding occurs at an epitope outside the Fcγ domain binding site, allowing it to function effectively even in the presence of human serum. Distinct Research ApplicationsThese different H22 entities serve separate but important roles: the hepatoma cell line advances cancer immunotherapy research, the anti-IFNγ antibody enables cytokine pathway studies, and the H22(scFv) fragment offers therapeutic potential for chronic inflammatory diseases by preventing unwanted anti-TNF antibody clearance. References & Citations1.) Schreiber, RD. et al. (2017) Cancer Immunol Res. 5(2):106-117. PubMed 2.) Schreiber, RD. et al. (2015) PLoS One.10(5):e0128636. PubMed 3.) Goeddel, DV. et al. (1982) Nature 298: 859 4.) Wilson, CB. et al. (2007) Adv. Immunol. 96: 41 5.) Hume, DA. et al. (2004) J Leukoc Biol. 75: 163 6.) Karki et al. (2021) Cell. 184:149–168 Journal Link Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Formats Available
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.