Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1) [Clone 29F.1A12] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1) [Clone 29F.1A12] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade
Product No.: P378
Clone 29F.1A12 Target PD-1 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names PD1, Programmed Death-1, CD279 Isotype Rat IgG2a Applications B , CyTOF® , FC , IHC FF , in vivo , PhenoCycler® , WB |
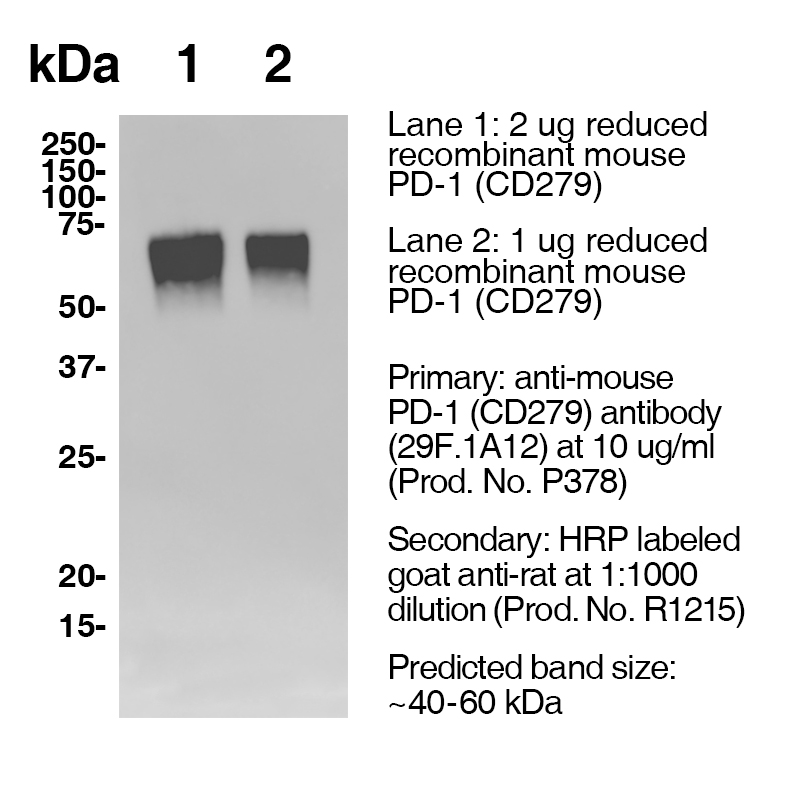
Data
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Rat Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Dilution Buffer Immunogen PD-1 cDNA followed by PD-1-Ig fusion protein Product Concentration 2.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level <0.5 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥98% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Pathogen Testing To protect mouse colonies from infection by pathogens and to assure that experimental preclinical data is not affected by such pathogens, all of Leinco’s Purified Functional PLATINUM™ antibodies are tested and guaranteed to be negative for all pathogens in the IDEXX IMPACT I Mouse Profile. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2831652 Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco FC WB Additional Applications Reported In Literature ? CyTOF® PhenoCycler-Fusion (CODEX)® IHC FF B Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Clone 29F.1A12 recognizes an epitope on mouse PD-1. Background PD-1 is a 50-55 kD member of the B7 Ig superfamily. PD-1 is also a member of the extended CD28/CTLA-4 family of T cell regulators and is suspected to play a role in lymphocyte clonal selection and peripheral tolerance. The ligands of PD-1 are PD-L1 and PD-L2, and are also members of the B7 Ig superfamily. PD-1 and its ligands negatively regulate immune responses. PD-L1, or B7-Homolog 1, is a 40 kD type I transmembrane protein that has been reported to costimulate T cell growth and cytokine production. The interaction of PD-1 with its ligand PD-L1 is critical in the inhibition of T cell responses that include T cell proliferation and cytokine production. PD-L1 has increased expression in several cancers. Inhibition of the interaction between PD-1 and PD-L1 can serve as an immune checkpoint blockade by improving T-cell responses In vitro and mediating preclinical antitumor activity. Within the field of checkpoint inhibition, combination therapy using anti-PD1 in conjunction with anti-CTLA4 has significant therapeutic potential for tumor treatments. PD-L2 is a 25 kD type I transmembrane ligand of PD-1. Via PD-1, PD-L2 can serve as a co-inhibitor of T cell functions. Regulation of T cell responses, including enhanced T cell proliferation and cytokine production, can result from mAbs that block the PD-L2 and PD-1 interaction. Antigen Distribution PD-1 is expressed on a subset of CD4-CD8- thymocytes, and on activated T and B cells. Ligand/Receptor B7-H1 (PD-L1) & B7-DC (PD-L2) Function Lymphocyte clonal selection, peripheral tolerance NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. In Vivo Applications of Clone 29F.1A12 in MiceClone 29F.1A12 is a rat monoclonal antibody raised against mouse programmed death-1 (PD-1), also known as CD279. This clone is widely utilized in preclinical mouse models for immune checkpoint blockade studies, especially in the context of cancer immunotherapy. Major In Vivo Uses
Technical Considerations
Comparative Context29F.1A12 is one of the three most commonly used anti-mouse PD-1 clones for in vivo research, alongside RMP1-14 and J43. The choice among these clones depends on the specific research question, desired affinity, and compatibility with the experimental setup. Summary Table: Key Features of 29F.1A12 In Vivo Use
ConclusionClone 29F.1A12 is a cornerstone tool for in vivo PD-1 blockade studies in mice, especially in cancer immunotherapy research. Its high blocking affinity, specificity, and suitability for combinatorial approaches make it a preferred choice for mechanistic and therapeutic investigations in preclinical models. The anti-PD-1 antibody 29F.1A12 is commonly used in conjunction with several other antibodies or proteins in the literature, especially those targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis. Frequently paired and comparative antibodies include:
Additional proteins and controls commonly used include:
These combinations allow researchers to analyze:
In summary, 29F.1A12 is routinely used with anti-PD-1 clones like RMP1-30, RMP1-14, J43, and anti-PD-L1 clones like 10F.9G2, MIH6, as well as recombinant PD-L1 and various isotype controls for rigorous experimental design in immunology and preclinical cancer research. Clone 29F.1A12 is a widely used monoclonal antibody specific for mouse PD-1 (CD279), and its citations in scientific literature highlight several key findings relevant to both mechanistic immunology and preclinical therapy development:
Summary Table: Key Properties of 29F.1A12
Researchers using clone 29F.1A12 should consider its potent blocking ability, strong detection of live-cell PD-1, cross-reactivity concerns with dead cells, and context-dependent therapeutic effects in preclinical models. Proper experimental controls and awareness of clone interactions are essential for accurate data interpretation. Dosing regimens of clone 29F.1A12 (anti-mouse PD-1 antibody) in mouse models commonly range from 100–200 μg per mouse via intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection every 3 days for three doses, but both the dose and schedule are frequently adjusted based on model and experimental goals. In some studies, doses as low as 10 μg or as high as 7.5 mg/kg are used, and the injection interval can be varied (twice weekly, every 3–4 days, or weekly). Key variations in dosing regimens include:
Applications covered by these regimens include:
Summary Table: Dosing Regimen Variations for 29F.1A12
In summary, clone 29F.1A12 is administered using a flexible dosing strategy with a core range of 100–200 μg/mouse i.p. every 3 days, but regimens vary with the mouse model, experimental objective, and combination therapies. References & Citations1.) Ardolino, M. et al. (2018) J Clin Invest. 128(10):4654-4668. PubMed 2.) Schreiber, RD. et al. (2017) Cancer Immunol Res. 5(2):106-117. 3.) Honjo, T. et al. (1992) EMBO J. 11:3887. 4.) Wurster S. et al. (2020) The Journal of Infectious Diseases 222(6):1989–994 Journal Link 5.) Lo, R. et al. (2021) Cancer Cell 39(10):1375-1387.e6 Journal Link Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
S211 | |
R1364 | |
I-1177 | |
C247 | |
F1175 | |
R1214 | |
S571 |
Formats Available
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
P377 | |
P383 | |
P384 | |
P501 | |
P378 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
![Anti-Mouse CD279 (PD-1) [Clone 29F.1A12] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade, Parent vial — Leinco Prod. No. P378](https://www.leinco.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/P378-Anti-Mouse-CD279-PD-1-Clone-29F.1A12-PLAT-Parent-Vial-500x500.jpg)