Anti-Mouse CD54 (ICAM-1) [Clone YN1/1.7.4] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse CD54 (ICAM-1) [Clone YN1/1.7.4] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade
Product No.: C6391
Clone YN1/1.7.4 Target CD54 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names Ly-47, ICAM-1 Isotype Rat IgG2b κ Applications CyTOF® , FA , FC , IHC FF , in vivo , IP , PhenoCycler® , WB |
Data
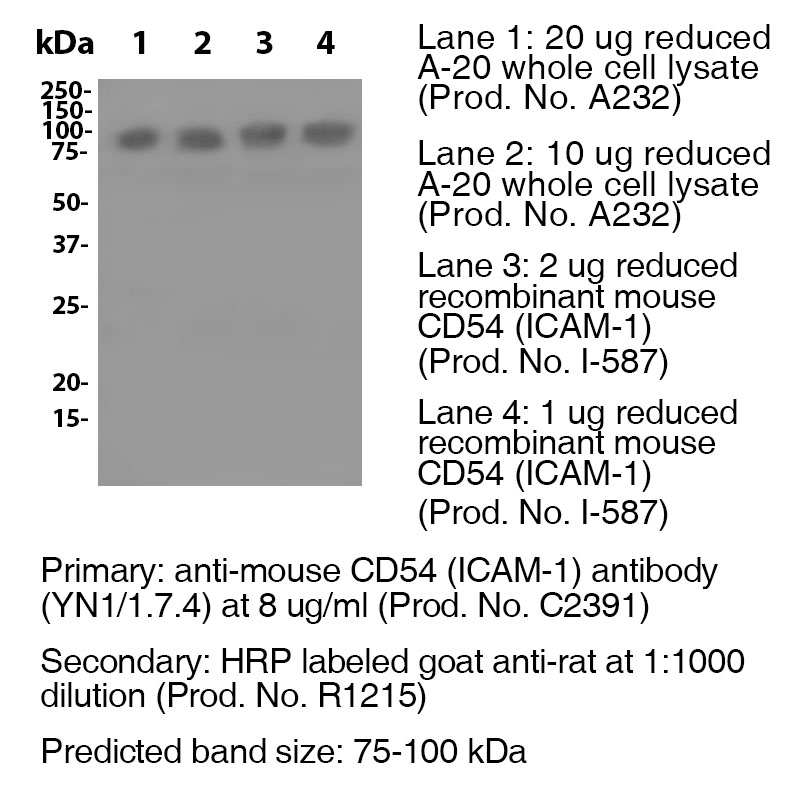
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Rat Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Dilution Buffer Immunogen Mouse NS-1 cells Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level <0.5 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥98% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Pathogen Testing To protect mouse colonies from infection by pathogens and to assure that experimental preclinical data is not affected by such pathogens, all of Leinco’s Purified Functional PLATINUM™ antibodies are tested and guaranteed to be negative for all pathogens in the IDEXX IMPACT I Mouse Profile. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2829795 Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco FC The suggested concentration for this YN1/1.7.4 antibody for staining cells in flow cytometry is ≤ 0.25 μg per 106 cells in a volume of 100 μl. Titration of the reagent is recommended for optimal performance for each application. WB The suggested concentration for this YN1/1.7.4 antibody for use in western blotting is 1-10 μg/ml. Additional Applications Reported In Literature ? PhenoCycler-Fusion (CODEX)® CyTOF® IP Additional Reported Applications For Relevant Conjugates ? B IHC (Frozen) For specific conjugates of this clone, review literature for suggested application details. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Clone YN1/1.7.4 recognizes an epitope on mouse CD54. Background ICAM-1 is a 55 kDa glycoprotein that is part of the Ig superfamily. It is heavily glycosylated to form 75 kDa to 115 kDa. ICAM-1 is known to be an adhesion and viral entry molecule, and its long suspected involevement in signal transduction is being elucidated. The signal-transducing functions of ICAM-1 appear to be mainly associated with proinflammatory pathways. Furthermore, ICAM-1 signaling appears to act as a beacon for inflammatory immune cells such as macrophages and granulocytes bringing about inflammation via lymphocyte trafficking. ICAM-1 is essential for the transmigration of leukocytes out of blood vessels and into tissues, and is a marker of endothelial dysfunction leading to damaging vascular disorders in umbilical and placental vascular tissue of gestational pregnancies. ICAM-1 is the receptor for rhinoviruses (the cause of most common colds) and malaria, and plays an inflammatory role in ocular allergies. Antigen Distribution CD54 is present on endothelial cells, lymphocytes, epithelial cells, dendritic cells and keratinocytes. Ligand/Receptor CD11a/CD18 (LFA-1) or CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1) and CD11c/CD18, CD43, hyaluronan, fibrinogen Function Immune reaction, inflammation, adhesion PubMed NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Cell Adhesion . Cell Biology . Costimulatory Molecules . Immunology . Innate Immunity . Neuroscience . Neuroscience Cell Markers . Stem Cell Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Clone YN1/1.7.4 is a monoclonal antibody targeting mouse CD54 (ICAM-1), most commonly used in vivo in mice to block CD54 function and study cell adhesion, leukocyte migration, and inflammatory processes. Common in vivo applications of clone YN1/1.7.4 in mice include:
Additionally, YN1/1.7.4 is suitable for immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry analysis of mouse tissues, but its functional blocking application is most relevant for in vivo studies of immune processes. In summary, the principal in vivo applications of clone YN1/1.7.4 in mice are as a functional blocking tool for CD54 to study leukocyte adhesion, migration, and immune regulation in models of inflammation and immune-mediated disease. Frequently, YN1/1.7.4, a monoclonal antibody targeting mouse CD54 (ICAM-1), is used in conjunction with antibodies against common immune cell surface markers, such as CD3, CD4, CD8, CD19, CD11b, CD11c. In typical research applications like flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry, investigators combine YN1/1.7.4 with the following antibodies or proteins to delineate immune cell types and states:
These combinations enable identification of CD54 expression across various immune cell subsets, measurement of activation/adhesion status, and investigation of cell-cell interactions during immune responses. Additionally, in functional studies examining adhesion, YN1/1.7.4 is often used with antibodies or proteins targeting LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18) and Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18), which are key ligands for ICAM-1. These interactions are essential for T cell and leukocyte trafficking, so researchers may employ YN1/1.7.4 alongside:
Some publications also mention combining YN1/1.7.4 with other endothelial antibodies such as clone 390, especially in imaging perfused tissue segments to analyze vascular boundaries and antibody capture efficacy. Isotype controls and secondary antibodies are standard for specificity and detection, with rat IgG2b often matched for controls in studies employing YN1/1.7.4. In summary, the most commonly paired antibodies/proteins with YN1/1.7.4 in the literature are:
Pairing YN1/1.7.4 with these antibodies allows researchers to investigate immune cell phenotypes, cell adhesion, and tissue localization in complex immunological settings. Clone YN1/1.7.4 is a rat monoclonal antibody extensively used in scientific research for specific targeting and functional blockade of mouse CD54 (ICAM-1), and its main citations reveal several consistent key findings:
These findings make YN1/1.7.4 a key tool for studying immune cell trafficking, inflammation, and barrier function across various mouse models used in immunology, oncology, and vascular biology. Dosing regimens of clone YN1/1.7.4 (anti-mouse CD54/ICAM-1) vary depending on the mouse model, disease context, and experimental aim. There is no universal protocol, but published studies and supplier data provide typical regimens and methodologies. Key variations in dosing regimens:
Example regimens from the literature:
Conclusions and best practice:
If you need a protocol for a specific disease model or mouse strain, please clarify for more tailored dosing recommendations. References & Citations1. Li, S. et al. (2009) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 381: 459
2. Wolf, S. et al. (2009) Pharmacol. Rep. 61: 22
3. Ozcan, U. et al. (2009) Arch Gynecol. Obstet. Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
S211 | |
R1364 | |
I-1034 | |
C247 | |
F1175 | |
R1214 | |
S571 |
Formats Available
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
C2401 | |
C2396 | |
C2151 | |
C2392 | |
C2394 | |
C2393 | |
C2397 | |
C2398 | |
C2399 | |
C2400 | |
C2395 | |
C527 | |
C2391 | |
C6391 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.