Anti-Mouse IFNγ [Clone H22] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse IFNγ [Clone H22] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Product No.: I-438
Clone H22 Target IFNγ Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names Immune Interferon, Type II Interferon, T Cell Interferon, MAF, IFNG, IFG, IFI Isotype IgG Applications ELISA , IF , in vivo , IP , N , WB |
Data
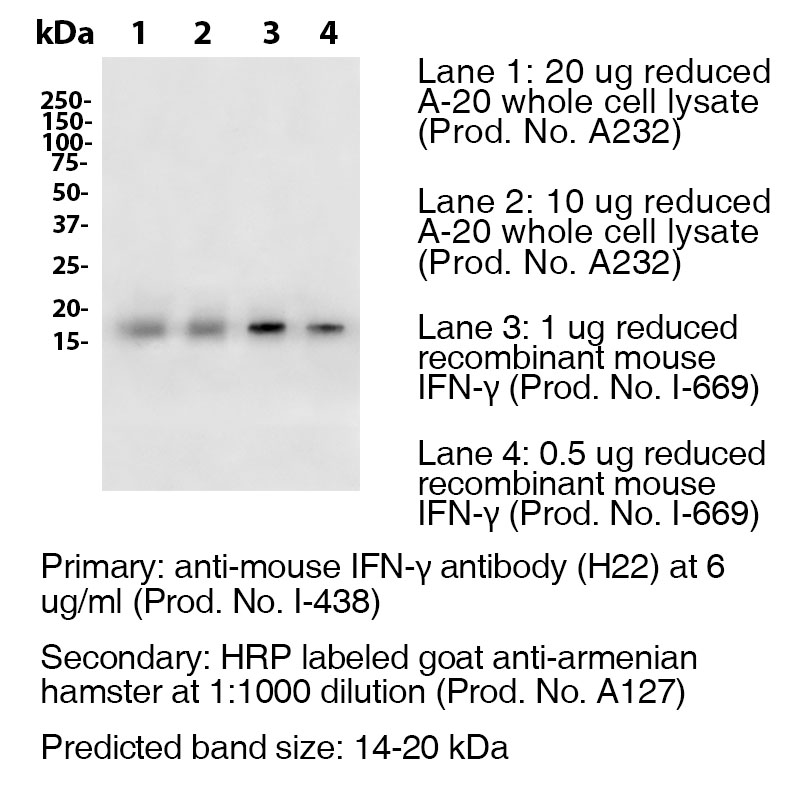
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Armenian Hamster Recommended Dilution Buffer Immunogen Purified Recombinant Mouse IFN-γ (>98%) Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level < 1.0 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥95% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2737542 Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco Western Blotting: For Western blotting, the suggested use of this Anti-Interferon Gamma antibody (clone H22) is 0.6 µg/ml., (See Image Above). Additional Reported Applications For Relevant Conjugates ? N For specific conjugates of this clone, review literature for suggested application details. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Anti-Interferon Gamma antibody (IFN-γ) (Clone H22) recognizes an epitope on Mouse IFN-γ. This monoclonal Anti-Interferon Gamma antibody was purified using multi-step affinity chromatography methods such as Protein A or G depending on the species and isotype. Background Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) or type II interferon is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons.4 It is a cytokine critical for innate and adaptive immunity against viral and intracellular bacterial infections and for tumor control. IFNG is produced predominantly by natural killer (NK) and natural killer T (NKT) cells as part of the innate immune response, and by CD4 and CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) effector T cells once antigen-specific immunity develops.5 IFN-γ has antiviral, immunoregulatory, and anti-tumour properties.6 Ligand/Receptor IFN-γRα (CDw119) dimerized with IFN-γRβ (AF-1) PubMed NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Immunology Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Clone H22 in mice has two distinct and common in vivo applications:
Essential details and context: 1. H22 Murine Hepatoma Cell Line:
2. Clone H22 Monoclonal Antibody (Anti-IFN-γ):
Summary Table:
Notes:
If you need detail on a specific application (e.g., dosing, protocol, or disease model), please specify the context (cell line or antibody). Commonly Used Antibodies and Proteins Used with H22 in the LiteratureThe term "H22" appears in several distinct scientific contexts, so it is crucial to clarify whether the user is referring to the H22 clone as a monoclonal antibody (e.g., anti-IFNγ, anti-CD64), the H22 hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, or another context. Here, we focus on the H22 antibody context, especially as related to CD64 (FcγRI) and IFNγ. H22 as an Anti-CD64 (FcγRI) AntibodyWhen H22 is used as an antibody (either the original murine mAb22, its humanized version H22, or the single-chain fragment H22(scFv)), it specifically targets CD64 (FcγRI), the high-affinity IgG receptor. In research and applications involving H22, several other antibodies and proteins are commonly referenced:
H22 as an Anti-IFNγ AntibodyWhen H22 refers to the anti-mouse IFNγ monoclonal antibody, its typical uses are in immunoassays (e.g., ELISA), immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation to detect or neutralize mouse interferon-gamma. In these contexts, it is used alongside:
Summary Table
Key Point: If you have a specific experimental or therapeutic context, please specify, and a more targeted summary can be provided. Key findings from clone H22 in scientific literature span multiple distinct biological contexts, each with important applications in research and potential therapeutic development. H22 Hepatoma Cell LineThe murine H22 hepatocellular carcinoma cell line serves as a widely-used experimental model in cancer research. This ascites hepatoma model has been instrumental in studying tumor biology, particularly regarding metastatic potential. Research has demonstrated that nm23 mRNA expression levels correlate with the metastatic capacity of H22 clones, suggesting this molecular marker may be associated with tumor spread. The H22 cell line has proven valuable for evaluating anti-cancer therapeutics and immunotherapy approaches. Studies have utilized H22 tumors to test DNA vaccines targeting VEGFR-2 (flk-1 domains 1–3), which successfully induced immune responses capable of blocking tumor growth by inhibiting angiogenesis. This demonstrates the utility of the H22 model for immunotherapy research and preclinical validation of novel treatment strategies. H22 Anti-IFNγ Monoclonal AntibodyIn immunology research, clone H22 refers to a monoclonal antibody that specifically targets mouse interferon-gamma (IFNγ). This antibody has become an essential tool for studying immune responses and inflammatory processes. IFNγ plays critical roles in antiviral activity, tumor antiproliferative effects, induction of class I and II MHC molecules, and macrophage activation. The H22 antibody clone is frequently employed in functional studies to neutralize IFNγ activity in vivo and in vitro, enabling researchers to dissect the specific contributions of this cytokine to various immunological phenomena. Its purified format makes it suitable for demanding experimental applications requiring high specificity and minimal cross-reactivity. H22(scFv) CD64-Blocking FragmentA distinct application involves H22(scFv), a recombinant single-chain variable fragment derived from the original murine mAb22, later humanized to full-length mAb H22. This engineered antibody fragment selectively binds and blocks CD64 (FcγRI), preventing the receptor from capturing therapeutic antibodies like anti-TNF monoclonal antibodies. Research has revealed several advantageous properties of H22(scFv). It binds an epitope on CD64 outside the Fcγ domain binding site, allowing it to function independently of other IgG molecules in human serum. The fragment effectively blocks CD64-mediated phagocytosis and downregulates receptor surface expression under physiological conditions. Critically, H22(scFv) binding does not trigger receptor activation or induce pro-inflammatory cytokine expression, unlike some therapeutic antibodies that can paradoxically stimulate TNF production when binding CD64. These characteristics position H22(scFv) as a promising therapeutic candidate for chronic inflammatory diseases. HT22 Differentiated Hippocampal Cell LineThough labeled "HT22" rather than "H22," this immortalized mouse hippocampal neuronal cell line warrants mention due to naming similarity. When differentiated, HT22 cells exhibit significant upregulation of NMDA receptors, choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), with morphological changes resembling mature neurons. This makes differentiated HT22 cells valuable for screening neuroprotective compounds and studying hippocampal neuron physiology. The diverse applications of H22-designated clones across cancer biology, immunology, and antibody engineering underscore the importance of specifying context when referencing this nomenclature in scientific literature. Dosing regimens involving clone H22 (including both the H22 murine tumor cell line and anti-mouse IFNγ [Clone H22] antibody) differ across mouse models depending on experimental goals, administration route, and the agent (e.g., cell line, antibody, or drug being tested). There is no universal dosing standard for clone H22 regimens. Key variations across studies include:
Summary Table of Common H22 Experimental Regimens
In conclusion, dosing regimens are highly tailored to the specific mouse model, cell line, intervention strategy, and research question involved, with adjustments in cell number, timing, frequency, and drug or antibody dose. References & Citations1. Schreiber, RD. et al. (2017) Cancer Immunol Res. 5(2):106-117. PubMed 2. Diamond, MS. et al. (2017) J Virol. 91(22): e01419-17. PubMed 3. Schreiber, RD. et al. (2015) PLoS One.10(5):e0128636. PubMed 4. Goeddel, DV. et al. (1982) Nature 298: 859 5. Wilson, CB. et al. (2007) Adv. Immunol. 96: 41 6. Hume, DA. et al. (2004) J Leukoc Biol. 75: 163 7.) Winkler, E. et al. (2020) Cell 182(4):901-918.e18 Journal Link Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
S211 | |
R1364 | |
I-140 | |
F1175 | |
A132 |
Formats Available
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.