Anti-Mouse CD32/CD16 [Clone 2.4G2] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse CD32/CD16 [Clone 2.4G2] — Purified in vivo PLATINUM™ Functional Grade
Product No.: C681
Clone 2.4G2 Target CD32/CD16 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names Fcγ R III/II, Ly-17 Isotype Rat IgG2b Applications B , FA , FC , IHC FF , in vivo , IP , PhenoCycler® , WB |
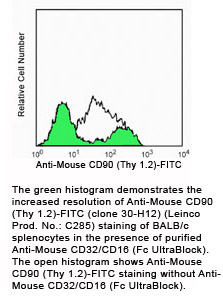
Data
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Rat Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Dilution Buffer Immunogen Sorted pre-B cells Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level <0.5 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥98% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Pathogen Testing To protect mouse colonies from infection by pathogens and to assure that experimental preclinical data is not affected by such pathogens, all of Leinco’s Purified Functional PLATINUM™ antibodies are tested and guaranteed to be negative for all pathogens in the IDEXX IMPACT I Mouse Profile. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2829820 Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco FC The suggested concentration for this 2.4G2 antibody for staining cells in flow cytometry is ≤ 1.0 μg per 106 cells in a volume of 100 μl. Titration of the reagent is recommended for optimal performance for each application.
WB The suggested concentration for this 2.4G2 antibody for use in western blotting is 1-10 μg/ml. Additional Applications Reported In Literature ? PhenoCycler-Fusion (CODEX)® FC Receptor Blocking IP Additional Reported Applications For Relevant Conjugates ? B For specific conjugates of this clone, review literature for suggested application details. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Clone 2.4G2 recognizes the FcγIII and FcγII receptors. Background CD16 is expressed in two forms: CD16a and CD16b. CD16a (FcγRIIIA) is a 50-65 kD polypeptide-anchored transmembrane protein. CD16b (FcγRIIIB) is a 48 kD GPI-anchored protein whose extracellular domain is over 95% homologous to that of CD16a. CD16 regulates both phagocytosis and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. It has been reported that CD16 is involved in Natural Killer Cell activation and plays a role in signal transduction. The receptors, CD32 (FcγRIII) and CD16 (FcγRII), are 40-60 kD and bind antibody-antigen immune complexes and mediate adaptive immune responses. Antigen Distribution These receptors are present on B cells, monocyte/macrophages, NK cells, neutrophils, mast cells and dendritic cells. Ligand/Receptor IgG Function Low affinity receptors for IgG PubMed NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Immunology . Innate Immunity Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Clone 2.4G2 is widely used in immunology research, particularly in mouse models, for its ability to block Fc gamma receptors II (CD32) and III (CD16). Common in vivo applications of this antibody include:
The dosing regimen typically involves a single intraperitoneal injection of 500 µg per mouse, administered 24 hours before experimental challenge. The 2.4G2 antibody is most frequently used as an Fc receptor blocking reagent in combination with various cell surface marker antibodies for multiparameter flow cytometry and immunofluorescence applications in mouse samples. Understanding which antibodies and proteins are commonly paired with 2.4G2 helps researchers design effective immunology experiments. Cell Surface Marker AntibodiesWhen using 2.4G2 for Fc receptor blockade, researchers routinely combine it with antibodies targeting specific immune cell markers. The most commonly used cell surface marker antibodies include B220, CD3, CD19, CD11b, Gr1, and NK1.1. These antibodies enable precise identification and phenotyping of different immune cell subsets while the 2.4G2 blockade minimizes non-specific staining through Fc receptor binding. These marker antibodies target various immune cell populations. For example, B220 and CD19 identify B cells, CD3 marks T cells, CD11b labels myeloid cells, Gr1 identifies granulocytes, and NK1.1 recognizes natural killer cells. By blocking Fc receptors with 2.4G2 before staining with these markers, researchers achieve more specific and accurate immune cell characterization. Isotype ControlsAppropriate isotype controls are standard practice when using 2.4G2. Common isotype controls include mouse IgG2a and irrelevant IgG antibodies. These controls help establish specificity baselines and distinguish true antibody binding from background or non-specific interactions in flow cytometry and immunofluorescence experiments. Secondary AntibodiesWhen 2.4G2 is used in indirect detection methods, careful selection of secondary antibodies is critical. Researchers must use anti-IgG secondary antibodies while specifically avoiding anti-rat IgG2b reagents. This precaution is necessary because 2.4G2 itself is a rat IgG2b antibody, and using anti-rat IgG2b secondary antibodies would create unwanted cross-reactivity and non-specific detection. Functional Assay ComponentsIn functional studies examining Fc receptor biology, 2.4G2 is frequently combined with Fc fragments and complement proteins. These combinations allow researchers to validate Fc receptor blockade effectiveness and study mechanisms such as phagocytosis and antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Additional Blocking AntibodiesFor comprehensive Fc receptor blockade, researchers sometimes use 2.4G2 alongside other blocking antibodies. Notably, clone 9E9 is used to block FcγRIV, which is not effectively blocked by 2.4G2 alone. This combination ensures more complete Fc receptor blocking when studying multiple receptor types simultaneously. The key findings from citations of clone 2.4G2 in scientific literature highlight its primary role as a monoclonal antibody used to block FcγRII (CD32) and FcγRIII (CD16) receptors on mouse immune cells. Here are the main points:
Dosing regimens of clone 2.4G2 (anti-mouse CD32/CD16 monoclonal antibody) are generally standardized across mouse models, with the most common protocol being a single 500 µg intraperitoneal injection administered 24 hours prior to experimental intervention. Context and Supporting Details:
Protocol Summary Table:
Conclusion: References & Citations1.) Titas, J. A. et al. (1982) J. Immunol. 133:556 2.) Rodewald, H. et al. (1992) Cell 69:139 3.) Skyberg, J. A. et al. (2020) Infection and Immunity. 88: 5 Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
S211 | |
R1364 | |
I-1034 | |
C247 | |
F1175 | |
R1214 | |
S571 |
Formats Available
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
C2078 | |
C2080 | |
C2082 | |
C2084 | |
C524 | |
C381 | |
C247 | |
C250 | |
C348 | |
C681 | |
C248 | |
C249 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.