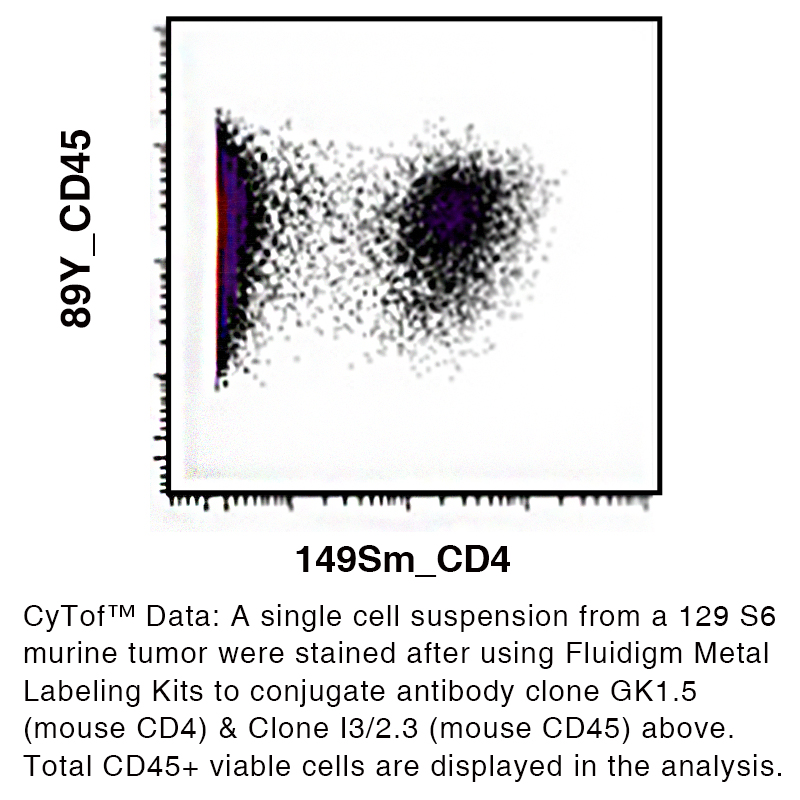
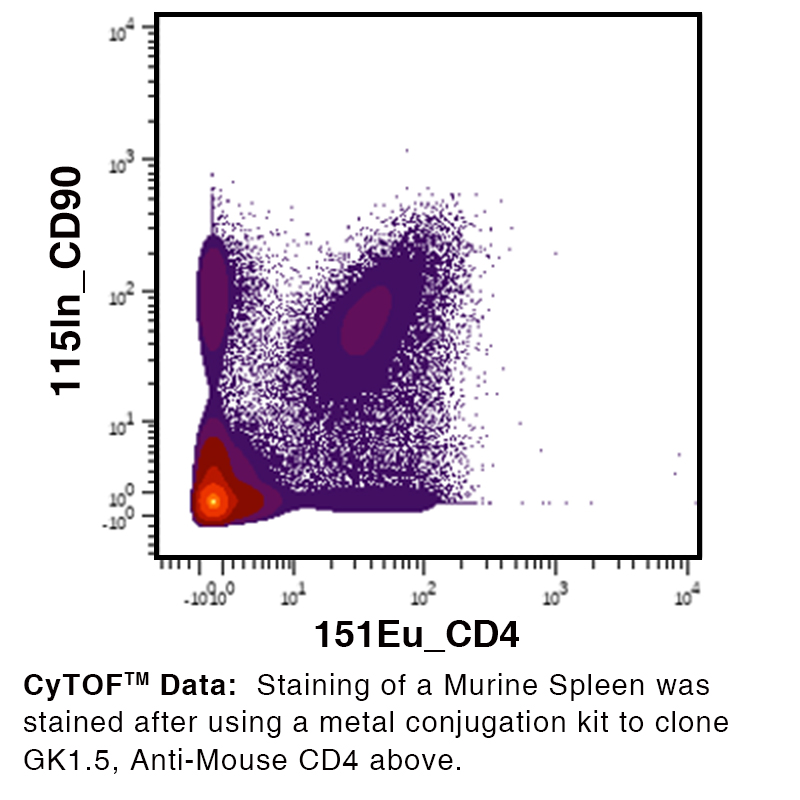
Anti-Mouse CD4 [Clone GK1.5] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse CD4 [Clone GK1.5] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Product No.: C1333
Clone GK1.5 Target CD4 Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names CD4mut, L3T4, Ly-4, Cd4, CD4 Antigen Isotype Rat IgG2b κ Applications B , Costim , CyTOF® , Depletion , FA , FC , IHC , in vivo , IP |
Data
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Rat Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Dilution Buffer Immunogen Mouse CTL clone V4 Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level < 1.0 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥95% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal CD4 antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2737452 Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco CyTOF® FC The suggested concentration for this GK1.5 antibody for staining cells in flow cytometry is ≤ 1.0 μg per 106 cells in a volume of 100 μl. Titration of the reagent is recommended for optimal performance for each application. Additional Applications Reported In Literature ? B Costim Depletion IHC IP Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Rat Anti-Mouse CD4 antibody (Clone GK1.5) recognizes an epitope on Mouse CD4. This monoclonal CD4 antibody was purified using multi-step affinity chromatography methods such as Protein A or G depending on the species and isotype. Background CD4 (cluster of differentiation 4) is a glycoprotein expressed on the surface of T helper cells, regulatory T cells, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. CD4 interacts with class II molecules of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) enhancing the signal for T-cell activation.6 Antigen Distribution Majority of thymocytes, T cell subset Ligand/Receptor MHC class II molecule Function T cell activation PubMed NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Immunology Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Clone GK1.5 is most commonly used in vivo in mice for depletion of CD4+ T cells, enabling researchers to study the roles of these cells in immune responses, disease models, and therapeutic interventions. Additional in vivo applications include blocking CD4-mediated cell functions to disrupt helper T cell interactions with MHC class II molecules and impair T cell activation. Key in vivo applications of GK1.5 in mice:
Experimental contexts where GK1.5 is extensively used in vivo:
GK1.5 is primarily chosen for its high specificity, efficiency in vivo, and well-documented depletion kinetics in the mouse model. The antibody is available in forms and buffers designed specifically for in vivo work, ensuring low endotoxin and the absence of toxic preservatives. In summary, in vivo depletion and functional blockade of CD4+ T cells represent the principal applications of GK1.5 in mice. These experimental strategies underpin research in immunology, infectious disease, oncology, and transplantation biology. Other antibodies and proteins commonly used with GK1.5 (anti-mouse CD4) in the literature include anti-CD8 (for cytotoxic T cells), anti-CD3 (pan-T cell marker), anti-CD25 (Treg marker), and various isotype controls. Below is a summary of typical pairings and markers observed in experimental setups:
Supporting context:
Typical panel configuration example:| Marker | Clone Example | Cell Subset/Function ||-----------------------|--------------|----------------------------------------------|| CD4 | GK1.5 | Helper T cells || CD8 | 53-6.7 | Cytotoxic T cells || CD3 | 145-2C11 | Pan-T cells || CD25 | PC61 | Regulatory T cells || Foxp3 | FJK-16s | Regulatory T cells (intracellular) || Isotype control | LTF-2 | Non-specific staining control || CD44, CD62L, CD45, etc. | Various | Memory/activation state || CD11b, CD11c | M1/70, N418 | Myeloid (monocytes, DCs) | References to recommended controls and typical applications are given by multiple manufacturers and validated protocols. Most peer-reviewed publications investigating mouse T-cell subsets or immune depletion strategies in vivo will use at least one of these in tandem with GK1.5. Clone GK1.5, a monoclonal antibody targeting mouse CD4, is extensively used in scientific research for in vivo T cell depletion, particularly focusing on CD4+ T cells. Here are key findings and applications from scientific literature: Key Uses and Findings
ConclusionClone GK1.5 is a valuable tool in immunological research, enabling precise depletion of CD4+ T cells to understand their roles in health and disease. Its applications span various disease models, providing insights into immune function and therapeutic potential. However, careful consideration of dosage and potential off-target effects is necessary for effective use. Dosing regimens for the anti-mouse CD4 antibody clone GK1.5 vary significantly across different mouse models and experimental objectives. Here are some key factors that influence dosing regimens: Dose Range
Route of Administration
Dosing Schedule
Experimental Objectives and Conditions
Overall, while there is a general range of dosing for GK1.5, researchers must conduct dose-response experiments to determine the most effective regimen for their specific mouse model and experimental objectives. References & Citations1.) Ardolino, M. et al. (2018) J Clin Invest. 128(10):4654-4668. PubMed 2.) Schreiber, RD. et al. (2017) Cancer Immunol Res. 5(2):106-117. PubMed 3.) Nicolas, JF. et al. (2002) J Immunol.168(6):3079-87. Article Link 4.) Shin, H. et al. (2018) J Virol. 92(7): e00038-18. PubMed 5.) Chiang, BL. et al. (2001) Immunology. 2001 103(3): 301–309. PubMed 6.) Hendrickson, WA. et al. (1994) Structure 2: 59 7.) Skyberg, J. A. et al. (2020) Infection and Immunity. 88: 5 Journal Link 8.) Raju et al. (2019) Cell Reports. 29:2556–2564 Journal Link 9.) Gubin, M. et al. (2018) Cell. 175(4):1014–1030 Journal Link 10.) Sharma S. et al. (2020) Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics 16(9):2196-2203 Journal Link 11.) Hawman DW, et al. (2021) Microorganisms 9(2):279 Journal Link Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
S211 | |
R1364 | |
I-1034 | |
C247 | |
F1175 | |
R1214 | |
S571 |
Formats Available
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
C1840 | |
C211 | |
C214 | |
C212 | |
C213 | |
C338 | |
C1640 | |
C1636 | |
C1333 | |
C1638 | |
C1637 | |
C2838 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.