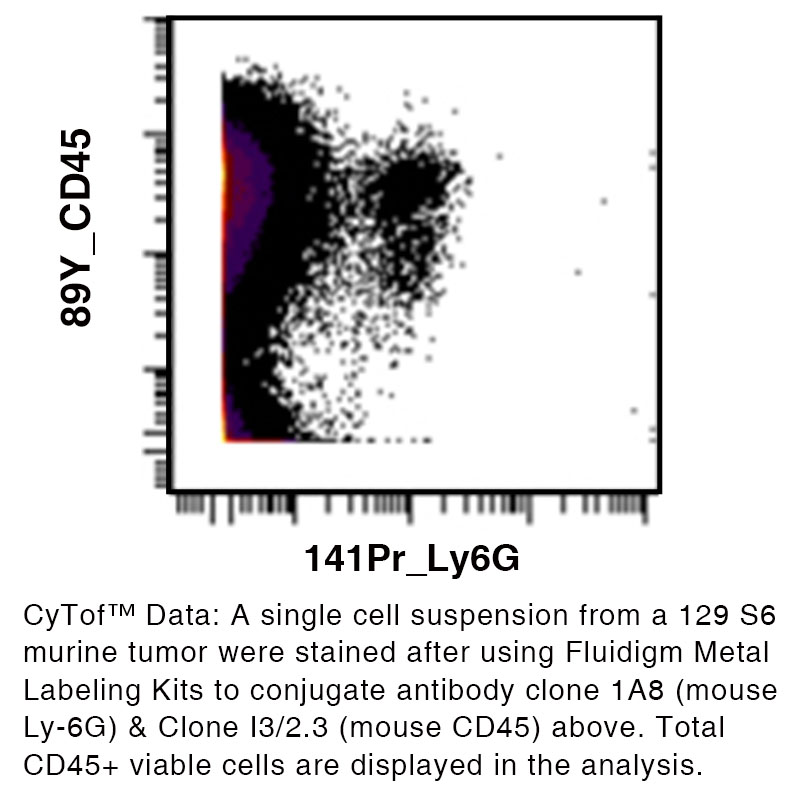
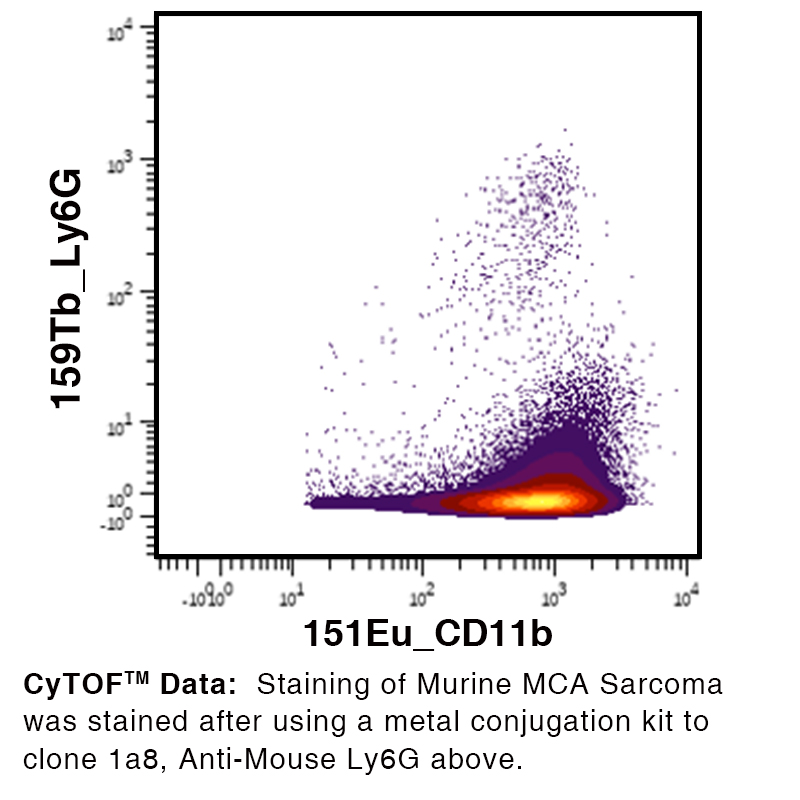
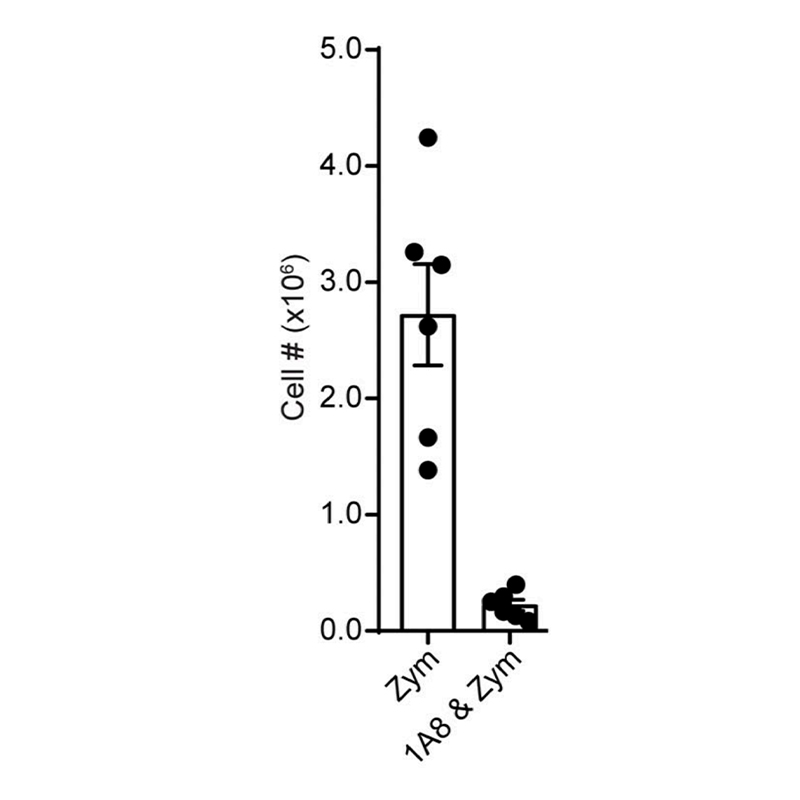
Anti-Mouse Ly-6G [Clone 1A8] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse Ly-6G [Clone 1A8] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Product No.: L280
Clone 1A8 Target Ly-6G Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names Lymphocyte antigen 6 complex, locus G Isotype Rat IgG2a κ Applications CyTOF® , Depletion , FC , IHC FF , in vivo , PhenoCycler® , WB |
Data
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Rat Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Dilution Buffer Immunogen Mouse Ly-6G transfected EL-4J cell line Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level < 1.0 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥95% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2737551 Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco FC The suggested concentration for this Ly6G antibody (clone 1a8) for staining cells in flow cytometry is ≤ 0.25 μg per 106 cells in a volume of 100 μl. Titration of the reagent is recommended for optimal performance for each application. Additional Applications Reported In Literature ? CyTOF® Depletion IHC (Frozen) IHC (Paraffin) WB Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Ly6G antibody (clone 1A8) recognizes an epitope on mouse Ly6G. Clone 1A8 does not cross react with Ly6C. Background Ly6G antibody (clone 1A8) recognizes lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus G6D (Ly6G; also called Gr-1), a 21-25 kDa glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored protein1. Ly6G belongs to the lymphocyte antigen-6 (Ly6)/urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) superfamily, characterized by a Ly6/uPAR (LU) domain-containing a three-fingered structural motif stabilized by disulfide bonds2. Ly6G is expressed by murine neutrophils regardless of location and activation1,4,5. Eosinophils may also express low levels of Ly6G5. There is no human ortholog for Ly6G; however, a structurally related L76/uPAR protein, CD177 (also known as HNA-2a, NB1, or PRV-1) is expressed in human neutrophils and is implicated in neutropenia6. Although the exact function and ligand of Ly6G remain unknown, Ly6G ligation may impair neutrophil migration to sites of inflammation via a β2-integrin-dependent mechanism7. Antigen Distribution Ly6G is expressed by neutrophils.
PubMed NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Immunology . Innate Immunity Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. The clone 1A8, specifically targeting the mouse Ly-6G marker, is widely used in several in vivo applications in mice. Here are some of the common applications:
In addition to in vivo applications, clone 1A8 is also used in various in vitro techniques such as flow cytometry, immunohistochemistry, and immunofluorescence for analyzing neutrophil populations. Commonly used antibodies or proteins alongside 1A8 (anti-Ly6G, a neutrophil marker) in the literature include those targeting cell lineage and immune subset markers, particularly in flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry studies. Key antibodies frequently used with 1A8:
In summary, CD45, CD11b, F4/80, and Ly6C are the most commonly used antibodies with 1A8, especially in flow cytometric analysis to precisely identify and separate neutrophils from other myeloid and immune cell subsets. This panel allows researchers to:
RB6-8C5 is used primarily as a reference or for cross-validation of depletion efficacy because it also targets Ly6C, affecting additional cell types. Additional markers such as CD101, CXCR2, and CXCR4 are chosen for more specialized functional or maturity studies. These combinations provide comprehensive immune profiling alongside 1A8, ensuring high specificity and accuracy in both depletion and identification studies. Clone 1A8 is widely cited in scientific literature as a monoclonal antibody that specifically targets mouse Ly6G, enabling depletion of neutrophils for functional studies in vivo. Key findings from 1A8 citations highlight its critical role in uncovering neutrophil functions in immunity, disease models, and optimizing depletion protocols. Essential context and key insights:
Additional supporting details:
Summary Table: Clone 1A8 Key Findings
These findings have made clone 1A8 a standard tool in immunology for dissecting the roles of neutrophils in host defense, inflammation, and disease mechanisms. Variability in 1A8 (Anti-Ly6G) Dosing Regimens Across Mouse ModelsSummary Key Variables Affecting 1A8 DosingStrain and Age Experimental Context Dose Range and Administration Route
Specific Examples from the Literature
Recommendations for Protocol Optimization
Table: Typical 1A8 Dosing Regimens in Mouse Models
ConclusionWhile the standard 1A8 dosing regimen is 100–250 µg per mouse i.p. three times per week, significant variability exists based on mouse strain, age, experimental model, and desired depth of depletion. Researchers must tailor the regimen to their specific context and rigorously validate depletion efficiency, especially when working with non-standard strains, older mice, or complex disease models. Always consult recent literature and product guidelines to optimize the protocol for your study. References & Citations1. Fleming TJ, et al. (1993) J Immunol. 151(5):2399-408 2. Tsetlin VI. et al. (2015) Trends Pharmacol Sci. 36(2):109-23 3. Daley JM, et al. (2008) J Leukoc Biol. 83(1):64-70 4. Lee PY, et al. (2013) J Leukoc Biol. 94(4):585-594 5. Percopo CM, et al. (2017) J Leukoc Biol. 101(1):321-328. 6. Stroncek DF. et al. (2007) Curr Opin Hematol. 14(6):688-93 7. Wang JX, et al. (2012) Blood. 120(7):1489-1498 8. Gubin, M. et al. (2018) Cell. 175(4):1014–1030.e19 Journal Link 9. Lebratti, T.et al. (2021) eLife 10: e65762 Journal Link 10. 1. Tzetzo, S. L., Kramer, E. D., Mohammadpour, H., Kim, M., Rosario, S. R., Yu, H., Dolan, M., Oturkar, C. C., Morreale, B., Bogner, P. N., Stablewski, A., Benavides, F., Brackett, C. M., Ebos, J. M., Das, G. M., Opyrchal, M., Nemeth, M. J., Evans, S. S., & Abrams, S. I. (2024). Downregulation of IRF8 in alveolar macrophages by G-CSF promotes metastatic tumor progression. iScience, 109187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.109187 Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
S211 | |
R1364 | |
I-1177 | |
C247 | |
F1175 | |
R1214 | |
S571 |
Formats Available
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
L286 | |
L279 | |
L283 | |
L282 | |
L285 | |
L281 | |
L287 | |
L288 | |
L289 | |
L500 | |
L280 | |
L284 | |
L305 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.