Anti-Mouse CD172a [P84] – Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse CD172a [P84] – Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Product No.: P380
Clone P84 Target CD172a Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names SIRPα, SHPS-1, BIT, P84, PTPNS1, CD172 antigen-like family member A Isotype Rat IgG1 κ Applications B , CyTOF® , FC , IHC FF , in vivo , IP |
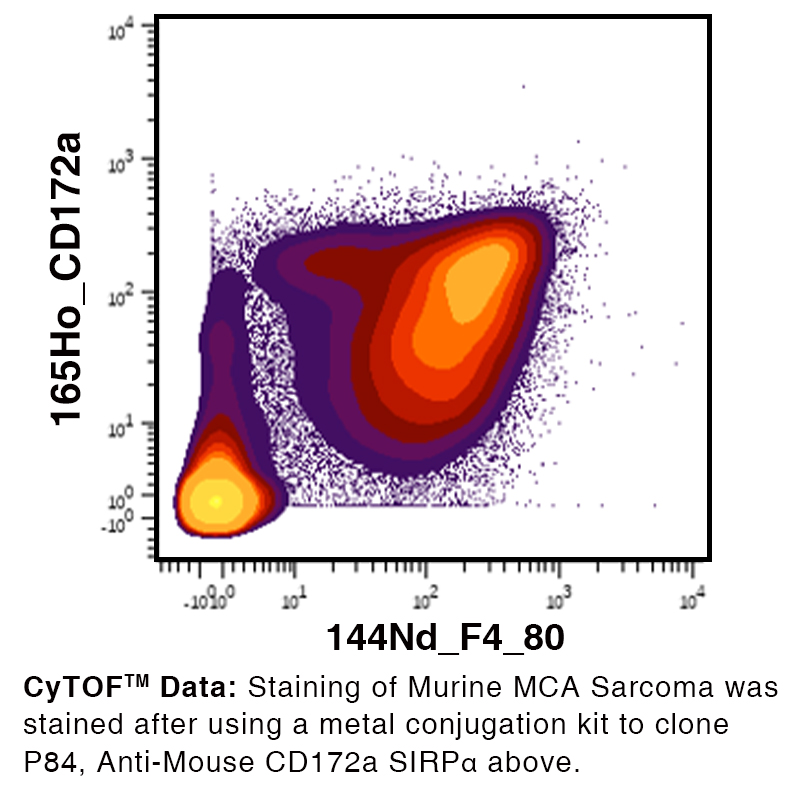
Data
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Rat Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Dilution Buffer Immunogen Mouse brain membrane protein Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level < 1.0 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥95% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2831653 Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco FC The suggested concentration for this P84 antibody for staining cells in flow cytometry is ≤ 1.0 μg per 106 cells in a volume of 100 μl. Titration of the reagent is recommended for optimal performance for each application. CyTOF® Additional Applications Reported In Literature ? IHC FF IP B Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Clone P84 recognizes an epitope on mouse CD172a.
Background CD172a antibody, clone P84, recognizes CD172a, also known as single regulatory protein α (SIRPα) (signal regulatory protein alpha) or Src homology 2 domain-containing phosphatase substrate-1 (SHP-1), a type I transmembrane glycoprotein with three Ig-like extracellular domains and two cytoplasmic immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibition motifs (ITIMs)1. SIRPα is expressed predominantly in myeloid cells2 - including monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells (DCs) - and neuronal cells3. The extracellular ligand for SIRPα, CD47 (or integrin-associated protein [IAP])4, is expressed in most cell types5. In macrophages, ligation of SIRPα by CD47 inhibits macrophage phagocytosis of self cells6,7. SIRPα also negatively regulates DC-mediated T cell activation and DC maturation8-10. CD47 is also upregulated on tumor cells, inhibiting the phagocytosis of tumor cells by macrophages11. Therapeutics targeting the CD47-SIRPα interaction, including antibodies and fusion proteins, are currently under preclinical and clinical study for various malignancies as a monotherapy or in combination with other therapeutics12.
Antigen Distribution CD172a is expressed on monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and neuronal cells.
Ligand/Receptor CD47, SP-A, SP-D Function Negative regulation of several biological processes NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Cell Adhesion . Innate Immunity . Neuroscience Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Clone P84 is most commonly used in vivo in mice to block or neutralize CD172a (SIRPα), a receptor expressed primarily on myeloid cells, in order to modulate immune responses—particularly to study phagocytosis and tumor immunotherapy, as well as to investigate dendritic cell migration and function. Typical in vivo applications include:
Additional reported experimental uses:
In summary, clone P84’s most established in vivo use is as a function-blocking antibody for SIRPα, primarily in contexts that investigate innate anti-tumor immunity, phagocytosis, or myeloid cell regulation in mouse models. Commonly used antibodies or proteins that are used in conjunction with p84 antibodies in the literature include a range of both secondary detection reagents and cell/component specific markers for multiplex or co-localization studies. The most frequent companions for p84 antibodies are:
Below is a summary table for clarity:
Context and application: If your question concerns the p84 subunit in the PI3Kγ signaling complex (not the nuclear matrix protein), frequently co-studied proteins are p110γ and p101, and their analysis often includes co-immunoprecipitation, interaction studies, and signaling pathway readouts. If this alternative meaning is relevant, please specify. Key Scientific Findings from Clone P84 CitationsMolecular Identity and Structure Functional Mechanisms Applications in Research Comparative Functional Studies with Other Antibodies Summary Table
ConclusionClone P84 is a foundational reagent for studying SIRPα biology, particularly in mouse models. Its scientific value lies in its specificity for SIRPα, enabling detailed characterization of this immune checkpoint molecule’s expression, structure, and signaling functions, but it does not disrupt the CD47-SIRPα interaction, which is of therapeutic interest in cancer immunology. Overview of Clone P84 Dosing RegimensClone P84 is a monoclonal antibody targeting mouse CD172a (SIRPα), commonly used in preclinical research—especially in immunology and cancer immunotherapy studies. While there is no single standardized dose for all applications, dosing regimens for P84 can vary based on experimental design, route of administration, target cell population, and the specific mouse model being employed. Dosing for In Vitro and Flow Cytometry ApplicationsFor flow cytometry and in vitro studies, the recommended concentration is typically ≤ 1.0 µg per 10⁶ cells in a volume of 100 µl. Some sources specify even lower amounts for staining, such as ≤ 0.25 µg per test, where a "test" is defined by the manufacturer as the amount of antibody staining a cell sample in a final volume. These guidelines are specific to cell staining and not in vivo administration. Dosing for In Vivo Mouse StudiesThere is limited published data detailing exact in vivo dosing regimens for clone P84 across diverse mouse models. However, some studies and suppliers provide general guidance:
Key Considerations and Variability
Summary Table: Reported Dosing Examples
ConclusionThere is no universal dosing regimen for clone P84 across all mouse models. For in vitro applications, precise, low-dose guidelines exist (≤1.0 µg/10⁶ cells). For in vivo studies, dosing is less standardized and must be empirically determined by the researcher, with published examples showing variability (e.g., 100 µg in an infection model). Suppliers strongly advise titration and optimization for each experimental setup. Researchers should consult recent literature, antibody datasheets, and pilot experiments to establish the most effective dose, route, and schedule for their specific mouse model and research question. References & Citations1. Fujioka, Y., et al. (1996) Mol. Cell. Biol. 16:6887 2. Adams, S., et al. (1998) J. Immunol. 161:1853 3. Chuang W, et al. (1990) Dev Biol. 137:219–232 4. Seiffert, M., et al. (1999) Blood 94:3633 5. Oldenborg P. A. (2013) ISRN Hematol. 2013:614619 6. Oldenborg, P. A., et al. (2000) Science 288:2051 7. Oldenborg, P. A., et al. (2001) J. Exp. Med. 193:855 8. Brooke, G. P., et al. (1998) Eur. J. Immunol. 28:1 9. Seiffert, M., et al. (2001) Blood 97:2741 10. Latour, S., et al. (2001) J. Immunol. 167:2547 11. Jaiswal S, et al. (2009) Cell. 138(2):271-85 12. Jalil AR, et al. (2020) Antib Ther. 3(2):80-94 Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
S211 | |
R1364 | |
I-1195 | |
C247 | |
F1175 | |
R1214 | |
S571 |
Formats Available
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
P386 | |
P387 | |
P380 | |
P390 | |
P391 | |
P392 | |
P385 | |
P389 | |
P388 | |
P680 | |
S200 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.