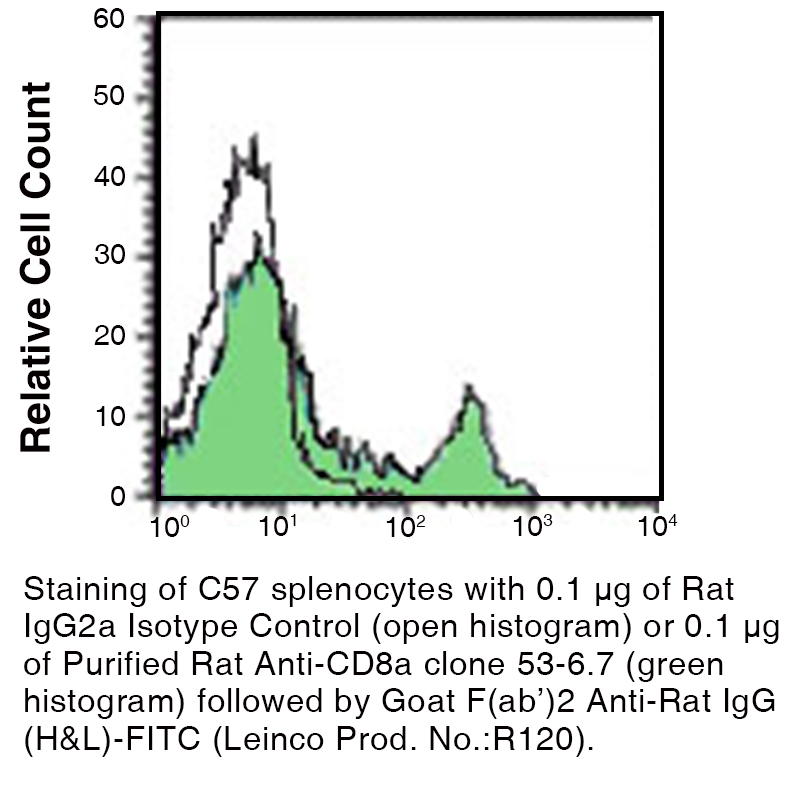
Anti-Mouse CD8a (Ly 2) [Clone 53-6.7] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse CD8a (Ly 2) [Clone 53-6.7] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Product No.: C375
Clone 53-6.7 Target CD8a Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names T8, Lyt2, Ly-2 Isotype Rat IgG2a κ Applications B , CyTOF® , Depletion , FC , IHC FF , in vivo , IP , PhenoCycler® , WB |
Data
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Rat Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Dilution Buffer Immunogen Mouse thymus or spleen Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level < 1.0 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥95% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2-8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2737478 Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco FC The suggested concentration for this 53-6.7 antibody for staining cells in flow cytometry is ≤ 0.25 μg per 106 cells in a volume of 100 μl. Titration of the reagent is recommended for optimal performance for each application. WB The suggested concentration for this 53-6.7 antibody for use in western blotting is 1-10 μg/ml. Additional Applications Reported In Literature ? CyTOF® CODEX® IHC (Frozen) IHC (Paraffin) Clone 53-6.7 has been reported for use in zinc-fixed paraffin-embedded sections and is NOT recommended for immunohistochemistry of formalin-fixed paraffin sections. IP B Depletion Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Clone 53-6.7 recognizes Lyt 2. Clone 53-6.7 competes with clone 5H10-1 for binding to thymocytes. Background CD8 is made up of disulfide-linked α and β chains that form the α(CD8a)/β(CD8b) heterodimer and α/α homodimer. CD8 is part of the Ig superfamily that expresses primarily as CD8a homodimers. CD8a is a 32-34 kD type I glycoprotein that can also form heterodimers with CD8b. CD8 is an antigen co-receptor on T cells that mediates efficient cell to cell interactions within the immune system. CD8 coupled with the T cell receptor on the T lymphocyte recognizes an antigen displayed by an antigen presenting cell (APC) in the context of class I MHC molecules. The CD8 co-receptor also plays a role in T cell signaling by interacting with Lck (lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase) which leads to the activation of transcription factors that affect the expression of certain genes. Antigen Distribution Lyt 2 is present on the surface of most thymocytes and a subpopulation of mature T-lymphocytes which include most T suppressor/cytotoxic cells. Ligand/Receptor MHC class I molecule Function Co-receptor for TCR PubMed NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Clone 53-6.7 is most commonly used in vivo in mice for depletion of CD8α+ cells (cytotoxic T cells), functional blocking of CD8+ T cell activity, and blocking antigen presentation via MHC class I. Essential applications and supporting details:
Additional relevant information:
In summary, in vivo applications of clone 53-6.7 in mice center on CD8+ T cell depletion, functional blocking, and studies of T cell–dependent immunity. Commonly Co-Used Antibodies/Proteins with 53-6.7The 53-6.7 antibody recognizes mouse CD8α, a coreceptor expressed on cytotoxic T cells and a subset of thymocytes. In experimental immunology, it is often used in combination with other antibodies and proteins to characterize immune cell populations or to facilitate functional studies. Here are the most commonly co-used reagents in the literature: Frequently Co-Used Antibodies
Additional Markers and Controls
Co-Used Proteins and Functional Ligands
Summary Table
These combinations are standard in mouse immunology to characterize, isolate, and functionally manipulate CD8⁺ T cells in both in vitro and in vivo contexts. The exact panel will vary depending on the experimental question, but CD4, CD3, and CD45 are nearly universal partners for 53-6.7 in multiparameter flow cytometry and related techniques. Clone 53-6.7 is a widely used monoclonal antibody specific for mouse CD8α, and key findings in the literature center on its diverse experimental uses and mechanistic properties.
Summary Table: Main Uses and Effects
Overall, clone 53-6.7 is considered a key reagent for mouse immunology research, essential for studying CD8 T cell biology, immune responses, and experimental immunodepletion or blockade protocols. The dosing regimens for clone 53-6.7, a rat anti-mouse CD8α monoclonal antibody, can vary significantly across different mouse models. This variation is influenced by several factors, including the specific experimental objective, mouse strain, route of administration, and whether the goal is acute depletion or chronic suppression of CD8+ T cells. Factors Influencing Dosing Regimens
Typical Dosing RangesWhile specific dosing ranges for clone 53-6.7 are not universally standardized, typical applications often involve administering doses in the range of 100 μg to several hundred micrograms per mouse. However, precise dosages can depend on the specific requirements of the study and are often determined experimentally. Applications and Considerations
In summary, the dosing regimen for clone 53-6.7 in mouse models is highly dependent on the specific experimental context, and dosages should be optimized based on preliminary studies or established protocols for similar applications. References & Citations1.) Sarmiento, M. et al. (1980) Journal of Immunology 125(6):2665 2.) Gubin, M. et al. (2018) Cell. 175(4):1014–1030 Journal Link 3.) Sharma S. et al. (2020) Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics 16(9):2196-2203 Journal Link Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
S211 | |
R1364 | |
I-1177 | |
C247 | |
F1175 | |
R1214 | |
S571 |
Formats Available
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
C1744 | |
C1746 | |
C215 | |
C216 | |
C218 | |
C1738 | |
C1739 | |
C1740 | |
C1742 | |
C217 | |
C339 | |
C2269 | |
C514 | |
C375 | |
C2848 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.