Anti-Mouse CD11c [Clone N418] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Anti-Mouse CD11c [Clone N418] — Purified in vivo GOLD™ Functional Grade
Product No.: C2119
Clone N418 Target CD11c Formats AvailableView All Product Type Monoclonal Antibody Alternate Names αX integrin, integrin αX chain, CR4, p150, ITGAX Isotype IgG Applications CyTOF® , FC , IHC FF , IP , PhenoCycler® , WB |
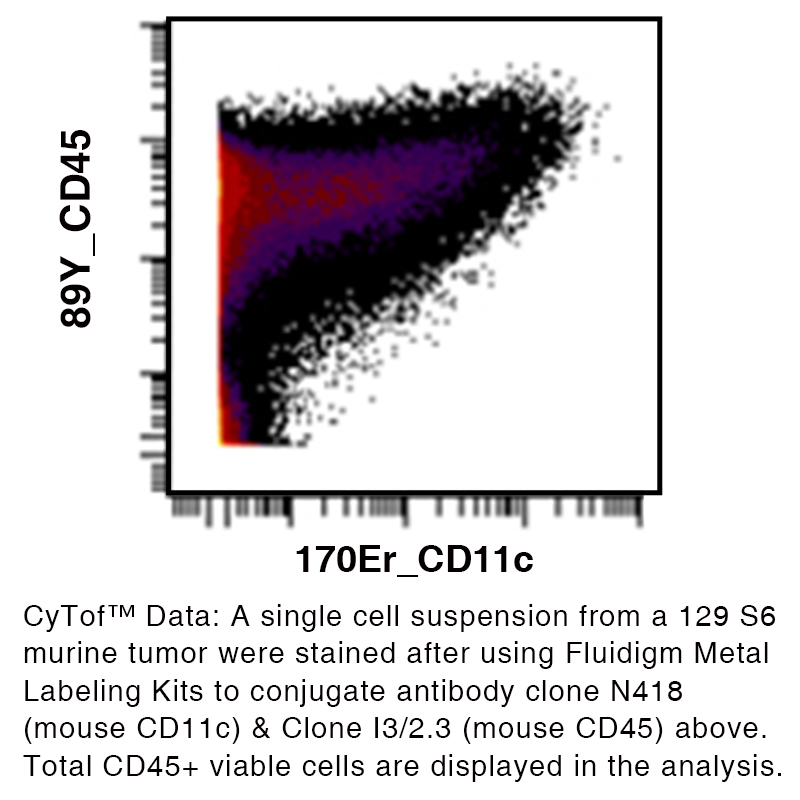
Data
Antibody DetailsProduct DetailsReactive Species Mouse Host Species Armenian Hamster Recommended Isotype Controls Recommended Dilution Buffer Immunogen Mouse spleen dendritic cells Product Concentration ≥ 5.0 mg/ml Endotoxin Level < 1.0 EU/mg as determined by the LAL method Purity ≥95% monomer by analytical SEC ⋅ >95% by SDS Page Formulation This monoclonal antibody is aseptically packaged and formulated in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline (150 mM NaCl) PBS pH 7.2 - 7.4 with no carrier protein, potassium, calcium or preservatives added. Due to inherent biochemical properties of antibodies, certain products may be prone to precipitation over time. Precipitation may be removed by aseptic centrifugation and/or filtration. Product Preparation Functional grade preclinical antibodies are manufactured in an animal free facility using in vitro cell culture techniques and are purified by a multi-step process including the use of protein A or G to assure extremely low levels of endotoxins, leachable protein A or aggregates. Storage and Handling Functional grade preclinical antibodies may be stored sterile as received at 2° to 8°C for up to one month. For longer term storage, aseptically aliquot in working volumes without diluting and store at ≤ -70°C. Avoid Repeated Freeze Thaw Cycles. Country of Origin USA Shipping Next Day 2-8°C RRIDAB_2737458 Applications and Recommended Usage? Quality Tested by Leinco FC The suggested concentration for this N418 antibody for staining cells in flow cytometry is ≤ 1.0 μg per 106 cells in a volume of 100 μl. Titration of the reagent is recommended for optimal performance for each application. WB The suggested concentration for this N418 antibody for use in western blotting is 1-10 μg/ml. Additional Applications Reported In Literature ? CyTOF® B Additional Reported Applications For Relevant Conjugates ? IF Microscopy For specific conjugates of this clone, review literature for suggested application details. Each investigator should determine their own optimal working dilution for specific applications. See directions on lot specific datasheets, as information may periodically change. DescriptionDescriptionSpecificity Clone N418 recognizes an epitope on mouse CD11C. Background LFA-1α (CD11a) and CD18 are the Integrin alpha-L and beta-2 chains respectively that combine to form LFA-1, a glycoprotein and a member of the Integrin family. Integrin alpha-L/beta-2 is a receptor for ICAM1, ICAM2, ICAM3, ICAM4 and for F11R. LFA-1 participates in the immunological synapses between CD8+ T lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells. The absence of LFA-1α or ß may induce LAD. The antigen contributes to natural killer cell cytotoxicity, and is involved in various immune phenomena such as leukocyte-endothelial cell interaction, cytotoxic T-cell mediated killing, and antibody dependent killing by granulocytes and monocytes. The CD11b/CD18 antigen is a heterodimeric surface glycoprotein on leukocytes and belongs to the ß2 integrin family. CD11b functions as a receptor for C3bi complement, clotting factor X, fibrinogen and ICAM-1. CD11c forms an α/ß heterodimeric glycoprotein (CD11c/CD18 complex) which belongs to the ß2 integrin family. The complex binds fibrinogen and reportedly serves as a receptor for iC3b and ICAM-1. During inflammatory responses, it mediates cell to cell interaction and is important in both monocyte adhesion and chemotaxis. Antigen Distribution CD11c is primarily expressed on dendritic cells, NK cells, a subset of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes (IEL), and some activated T cells. Ligand/Receptor iC3b, fibrinogen Function Cellular adhesion PubMed NCBI Gene Bank ID UniProt.org Research Area Cell Adhesion . Cell Biology . Costimulatory Molecules . Immunology . Neuroscience . Neuroscience Cell Markers Leinco Antibody AdvisorPowered by AI: AI is experimental and still learning how to provide the best assistance. It may occasionally generate incorrect or incomplete responses. Please do not rely solely on its recommendations when making purchasing decisions or designing experiments. Clone N418 is most commonly used in vivo in mice to label, target, or deplete CD11c-positive dendritic cells, providing a powerful tool for immunology research focused on the function and roles of these cells. The most typical in vivo applications are:
Dosage and Considerations:
Examples from Research:
In summary, clone N418 is a standard tool for in vivo manipulation of mouse dendritic cells, most often for depletion, targeted antigen delivery, or immune function studies. N418, an anti-CD11c antibody commonly used for dendritic cell labeling, is frequently employed alongside various other antibodies and proteins in immunological research. The specific combinations depend on the experimental context and research objectives. Dendritic Cell Subset MarkersWhen studying dendritic cells with N418, researchers commonly use markers that help identify and characterize different dendritic cell subsets. These markers allow for more precise identification and functional analysis of specific dendritic cell populations. T Cell and Myeloid Lineage MarkersN418 is regularly combined with T cell markers and other myeloid lineage markers to comprehensively profile immune cell populations. For example, in flow cytometry experiments, N418 has been used simultaneously with CD3 PE-conjugated antibodies to distinguish between dendritic cells and T lymphocytes. Additionally, studies have employed N418 alongside CD45 and CD11b markers, with gating strategies targeting CD45+ CD11b+ populations to identify specific myeloid cell subsets. Polyclonal and Targeting AntibodiesIn immunization studies, N418 has been used in combination with several polyclonal antibodies, including polyclonal goat anti-hamster IgG antibody, goat anti-Armenian hamster IgG, and mouse anti-goat IgG. These combinations were utilized to study targeted delivery to dendritic cells. The research demonstrated that specific interaction between the antigen and N418 was required for enhanced antibody responses, as control experiments using hamster anti-TNP (trinitrophenol) IgG and goat anti-biotin IgG showed different immune response patterns. Functional Context ProteinsThe antibodies and proteins used alongside N418 also include those relevant to immune function, though the specific combinations vary based on whether researchers are conducting Western blot analyses, examining cell-specific markers, or performing functional assays in different experimental systems. Clone N418 is a monoclonal antibody widely cited in scientific literature for its utility in immunology, particularly for identifying and studying mouse CD11c, a key marker of dendritic cells. The key findings and applications from N418 citations are:
In summary, clone N418 is foundational for mouse immunology research, especially for studies of dendritic cell biology, immune response modulation, and preclinical models of disease. Its specificity for CD11c, versatility in diverse assays, and broad adoption are confirmed by hundreds of citations in the literature. Dosing regimens of clone N418 (anti-mouse CD11c antibody) vary substantially depending on the mouse model and experimental objective, typically ranging from 1–10 µg per mouse for ex vivo labeling to 50–200 µg per mouse for in vivo depletion or targeting. Key details include:
Further considerations:
In summary, clone N418 dosing is highly context-dependent, and must be empirically optimized for each specific mouse model and experimental aim. References & Citations1.) Gubin, M. et al. (2018) Cell. 175(4):1014–1030.e19 Journal Link Technical ProtocolsCertificate of Analysis |
Related Products
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
S211 | |
R1364 | |
I-140 | |
C247 | |
F1175 | |
S225 | |
A132 | |
S571 |
Formats Available
Prod No. | Description |
|---|---|
C2130 | |
C2131 | |
C2439 | |
C2124 | |
C2122 | |
C2120 | |
C2121 | |
C2087 | |
C2123 | |
C2125 | |
C2126 | |
C2127 | |
C2129 | |
C516 | |
C2119 | |
C6119 |
 Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.
Products are for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.